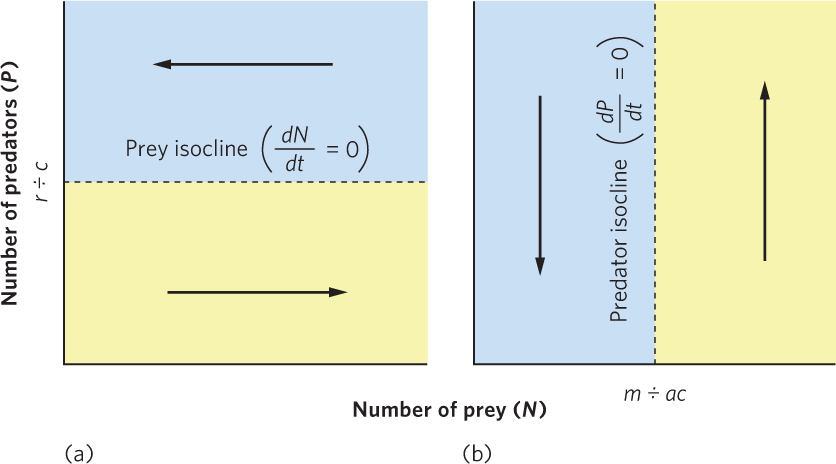
Figure 14.10 Equilibrium isoclines for prey and predator populations. (a) The prey population is stable when the number of predators is equal to r ÷ c. A higher number of predators causes the prey population to decrease, whereas a lower number of predators causes the prey population to increase. (b) The predator population is stable when the number of prey is equal to m ÷ ac. A higher number of prey causes the predator population to increase, whereas a lower number of prey causes the predator population to decrease.