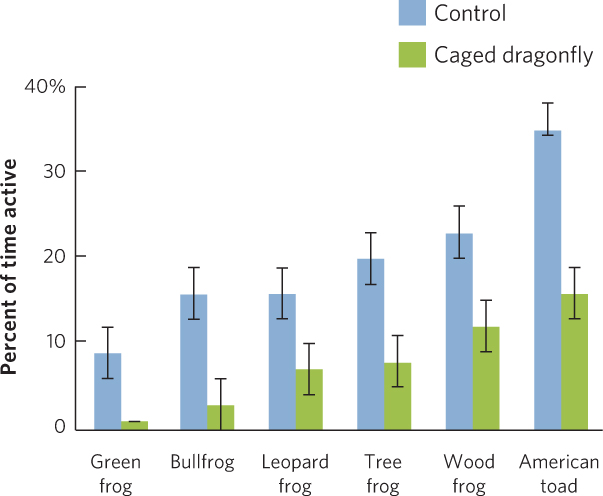
Figure 14.15 Behavioral defenses. Tadpoles commonly avoid predation by becoming less active, which is measured as the portion of the day that they spend moving. Being less active reduces the probability of being detected by a predator. Error bars are standard errors.
Data from R. A. Relyea, The relationship between predation risk and antipredator responses in larval anurans, Ecology 82 (2001): 541–544.