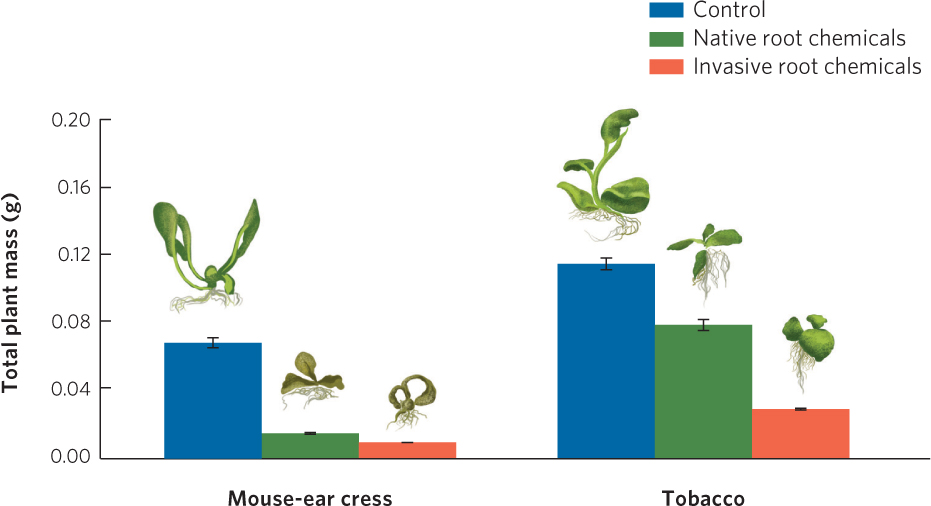
Figure 16.16 Allelopathy in the common reed. Root chemicals from native or invasive strains of the common reed were extracted and then added to pots of mouse-ear cress or tobacco plants. The addition of the root chemicals caused both plant species to grow poorly compared to the control. In the case of the tobacco plant, chemicals from the invasive strain of the reed inhibited growth more than the native strain. Error bars are standard deviations.
Data from T. Rudrappa et al., Root-secreted allelochemical in the noxious weed Phragmites australis deploys a reactive oxygen species response and microtubule assembly disruption to execute rhizotoxicity, Journal of Chemical Ecology 33 (2007): 1898–1918.