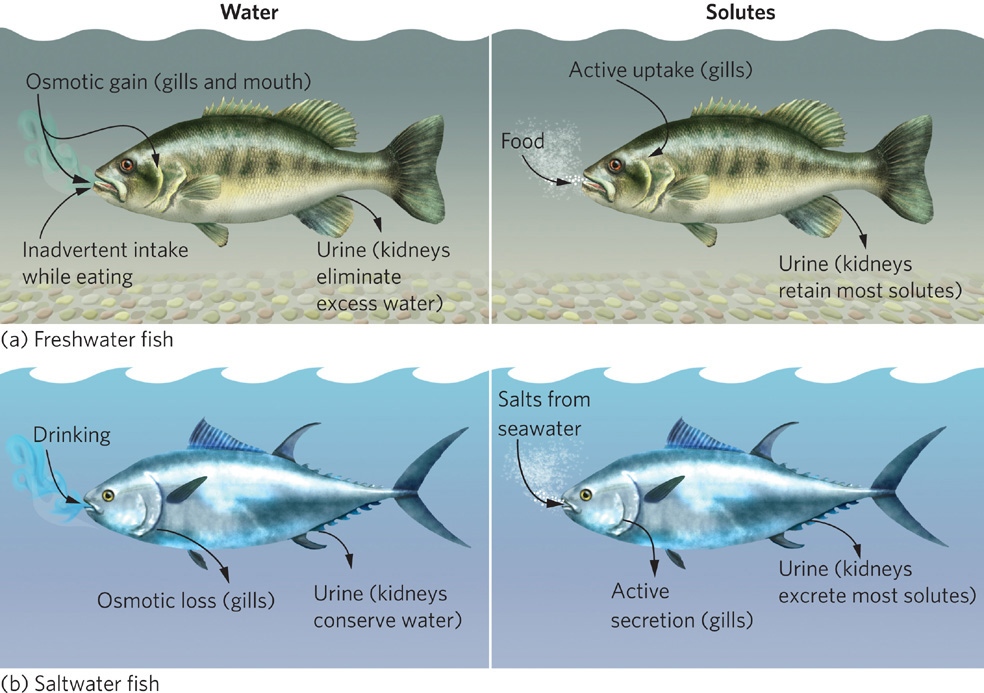
Figure 2.10 Osmoregulation in fish. Exchanges of water and solutes differ between freshwater and marine fish. (a) Freshwater fish are hyperosmotic: they have a higher salt concentration in their body than exists in the surrounding water. To maintain salt balance they must excrete large amounts of water and use their gills and kidneys to actively retain solutes. (b) Saltwater fish are hyposmotic: they have a lower salt concentration in their body than exists in the surrounding water. To maintain salt balance, they must excrete large amounts of solutes, so their gills and kidneys actively exclude solutes.