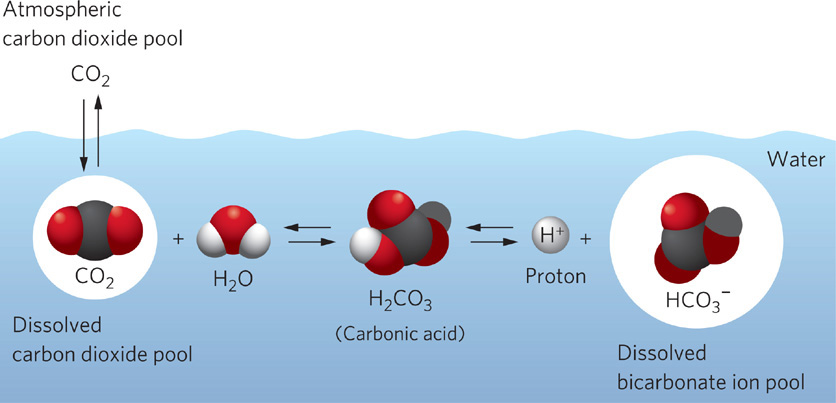
Figure 2.14 An equilibrium reaction for carbon in water. The reaction converting CO2 into bicarbonate ions (HCO₃-) is an equilibrium reaction. When photosynthetic organisms preferentially use CO2, because it is used more efficiently, the amount of dissolved CO2 in the water declines. As the amount of CO2 declines, some of the bicarbonate ions are converted to CO2 to replenish the supply. The size of each circle represents the relative size of the carbon pool.