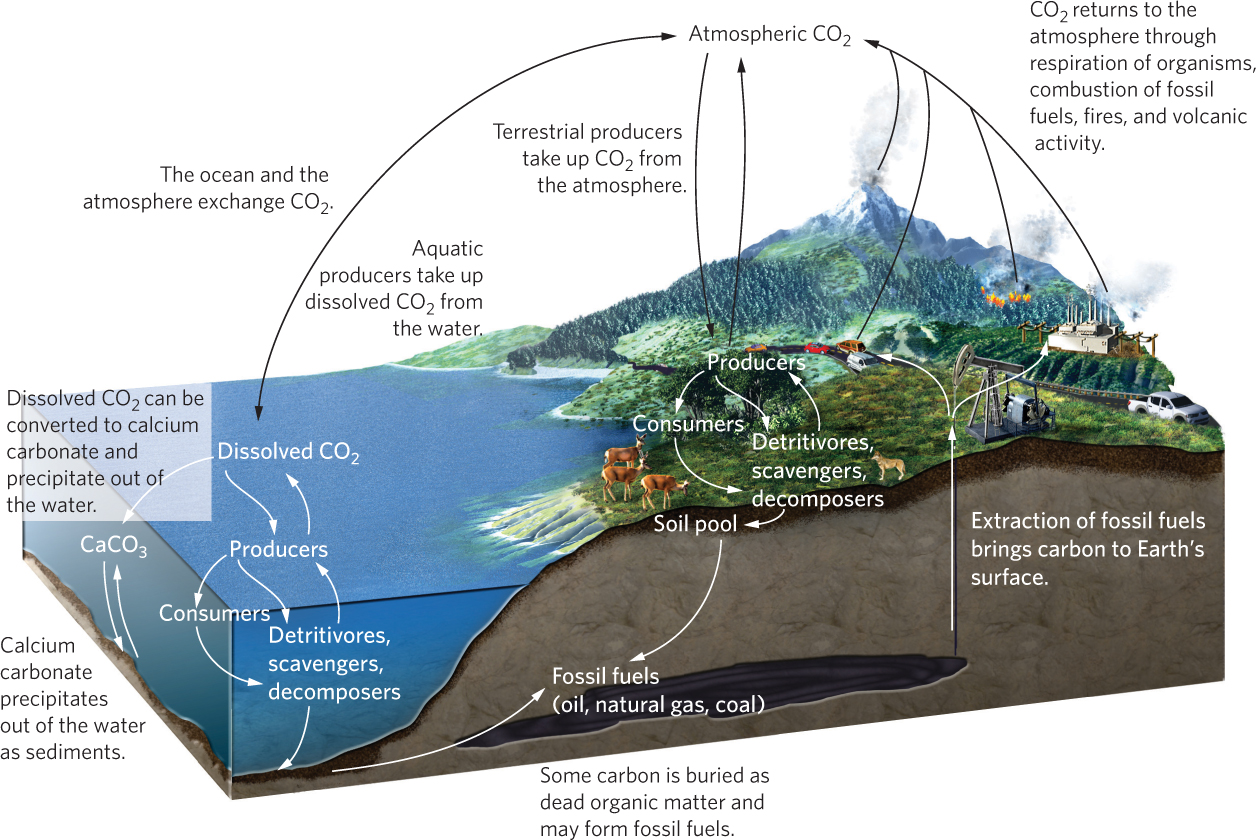
Figure 21.3 The carbon cycle. In the carbon cycle, producers take up CO2 from the atmosphere and the water. They transfer assimilated carbon to consumers, detritivores, scavengers, and decomposers. These organisms return CO2 to the atmosphere and oceans through respiration. Throughout an ecosystem, CO2 is exchanged between the atmosphere and the ocean and between the ocean and sediments. Carbon that has been stored underground for long periods turns into fossil fuels, which can be extracted. CO2 is returned to the atmosphere through combustion of fossil fuels, burning in terrestrial ecosystems, and volcanic activity.