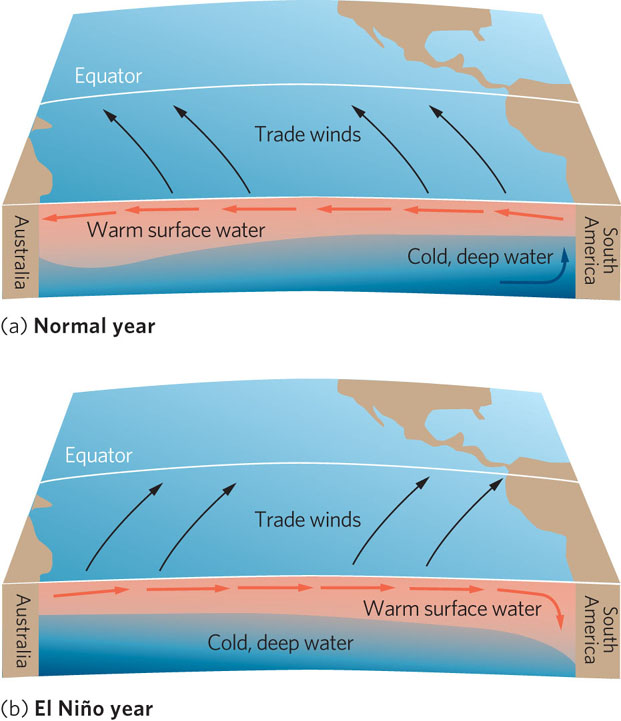
Figure 5.12 The El-Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO). Changes in the strength of trade winds near the equator can have major impacts on the climates of the world. (a) In most years, strong trade winds push warm surface waters away from the west coast of South America. This causes cold, deep waters to upwell along the coast. (b) During an ENSO year, the trade winds weaken or reverse and the warm surface water moves from west to east. As a result, warm water builds up along the west coast of South America and prevents the upwelling of the cold, deep water. This change in ocean circulation alters climates around the world.