The American Promise: Printed Page 852
The American Promise, Value Edition: Printed Page 770
The American Promise: A Concise History: Printed Page 882
Vietnam Becomes Nixon’s War
“I’m going to stop that war. Fast,” Nixon asserted. He gradually withdrew ground troops, but he was no more willing than his predecessors to be the president who let South Vietnam fall to the Communists. (See “Analyzing Historical Evidence: Ending the War in Vietnam.”) That goal was tied to the larger objective of maintaining American credibility. Regardless of the wisdom of the initial intervention, Kissinger asserted, “the commitment of 500,000 Americans has settled the importance of Vietnam. For what is involved now is confidence in American promises.”
From 1969 to 1972, Nixon and Kissinger pursued a three-
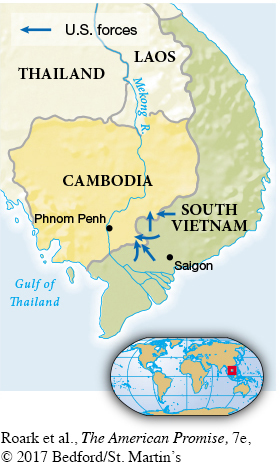
Second, Nixon gradually reduced the U.S. presence in Vietnam, a move that somewhat disarmed the antiwar movement at home. American forces decreased from 543,000 in 1968 to 140,000 by the end of 1971, although casualties remained high. Third, the United States replaced U.S. forces with intensive bombing. In the spring of 1969, Nixon began a ferocious air war in Cambodia, hiding it from Congress and the public for more than a year. Seeking to knock out North Vietnamese sanctuaries in Cambodia, Americans dropped more than 100,000 tons of bombs but succeeded only in sending the enemy to other hiding places. Echoing Johnson, Kissinger believed that a “fourth-
To support a new, pro-
In response to this escalation of the war, more than 100,000 people protested in Washington, D.C., and students boycotted classes on hundreds of campuses. At a rally on May 4 at Kent State University in Ohio, National Guard troops opened fire, killing four and wounding ten others. “They’re starting to treat their own children like they treat us,” commented a black woman in Harlem. In a confrontation at Jackson State College in Mississippi on May 14, police shot into a dormitory, killing two black students.

The American Promise: Printed Page 852
The American Promise, Value Edition: Printed Page 770
The American Promise: A Concise History: Printed Page 882
Page 853Congressional reaction to the invasion of Cambodia revealed increasing concern about abuses of presidential power. In the name of national security, presidents since Franklin Roosevelt had conducted foreign policy without the consent or sometimes even the knowledge of Congress—
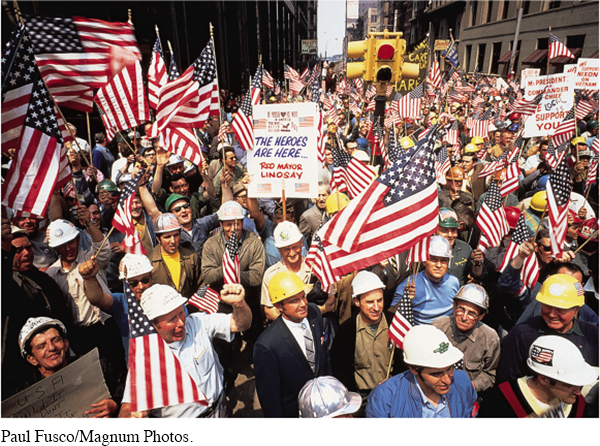
In 1971, Vietnam veterans became a visible part of the peace movement, the first men in U.S. history to protest a war in which they had fought. They held a public investigation of “war crimes” in Vietnam, rallied in front of the Capitol, and cast away their war medals. In May 1971, veterans numbered among the 40,000 protesters who engaged in civil disobedience in an effort to shut down Washington. Officials made more than 12,000 arrests, which courts later ruled violations of protesters’ rights.
After the spring of 1971, there were fewer massive antiwar demonstrations, but opposition to the war continued. Public attention focused on the court-
Administration policy suffered another blow in June 1971 when the New York Times published portions of the Pentagon Papers, a secret internal study of the war begun in 1967. Nixon sent government lawyers to court to stop further publication, in part out of fear that other information would be leaked. The Supreme Court, however, ruled that suppression of the publication violated the First Amendment. Subsequent circulation of the Pentagon Papers, which revealed pessimism among officials even as they made rosy promises, heightened disillusionment with the war by casting doubts on the government’s credibility. More than 60 percent of Americans polled in 1971 considered it a mistake to have sent American troops to Vietnam; 58 percent believed the war to be immoral.
Military morale sank in the last years of the war. Having been exposed to the antiwar movement at home, many soldiers had less faith in the war than their predecessors had had. Racial tensions among the troops mounted, many soldiers sought escape in illegal drugs, and enlisted men committed hundreds of “fraggings,” attacks on officers. In a 1971 report, The Collapse of the Armed Forces, a retired Marine colonel described the lack of discipline: “Our army that now remains in Vietnam [is] near mutinous.”