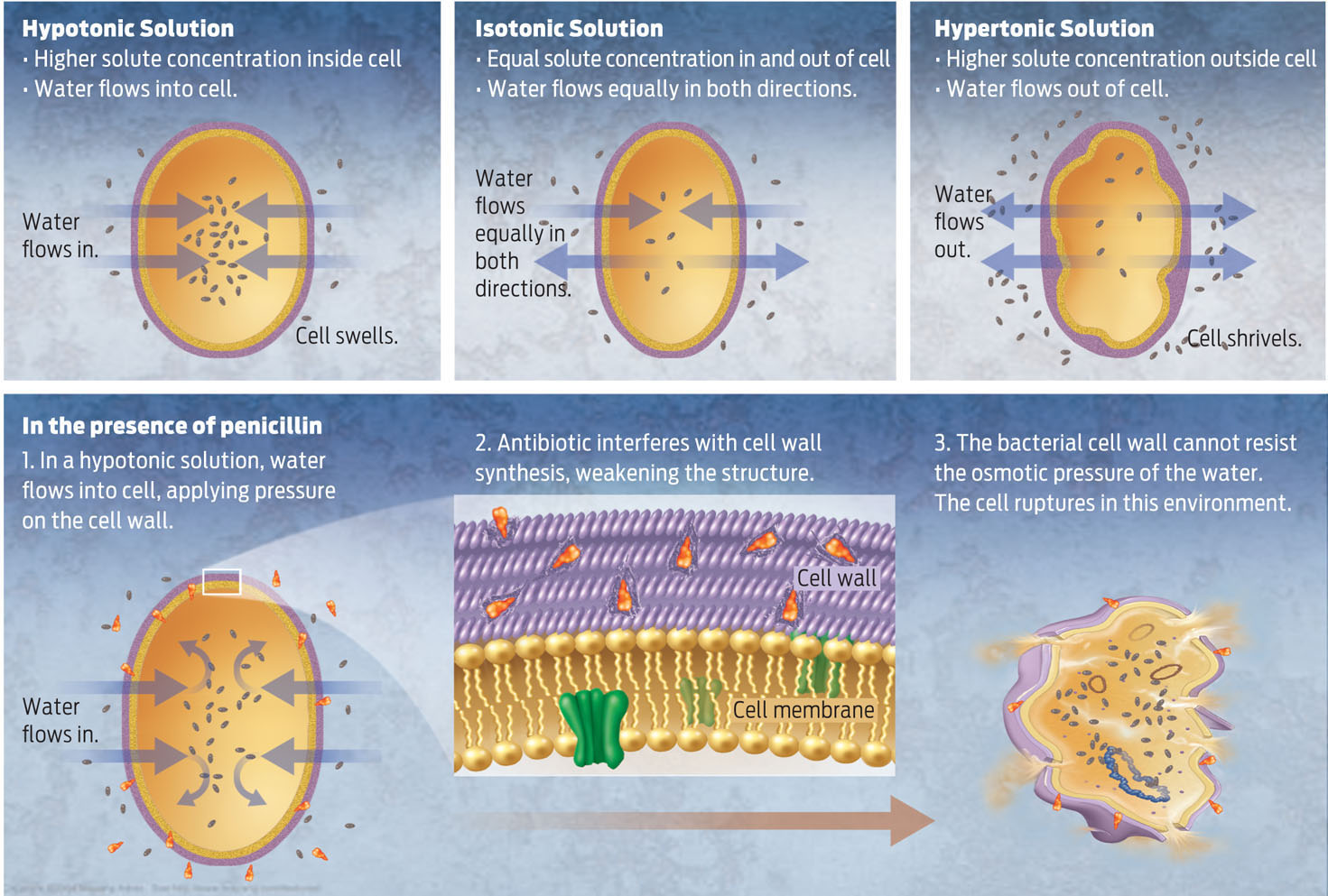
The direction of water movement across the cell membrane is determined by the solute concentration on either side. Water always moves toward the side with the higher solute concentration. In a hypotonic solution, water will flow into the cell, and in a hypertonic solution, water will flow out of a cell. The bacterial cell wall helps protect the cell from lysing in a hypotonic environment. In the presence of some antibiotics the cell wall is disrupted, leaving the cell susceptible to lysis.