CHAPTER 17 Test Your Knowledge
Driving Question 1
What do we know about the history of life on Earth, and how do we know it?
By answering the questions below and studying Infographics 17.1, 17.2, and 17.3, you should be able to generate an answer for the broader Driving Question above.
KNOW IT
 What do uranium-238, carbon-14, and potassium-40 have in common?
What do uranium-238, carbon-14, and potassium-40 have in common?
They are all radioactive isotopes that decay into other elements at constant rates.
 To date what you suspect to be the very earliest life on Earth, which isotope would you use: uranium-238, carbon-14, or potassium-40? Explain your answer.
To date what you suspect to be the very earliest life on Earth, which isotope would you use: uranium-238, carbon-14, or potassium-40? Explain your answer.
You would use uranium-238, which has the longest half-life of the three (4.5 billion years). Isotopes with shorter half-lives may no longer be present in very ancient sample, having completely decayed.
 Place the following evolutionary milestones in order from earliest (1) to most recent (7), providing approximate dates to support your answer.
Place the following evolutionary milestones in order from earliest (1) to most recent (7), providing approximate dates to support your answer.
_________ The first multicellular eukaryotes
_________ The first prokaryotes
_________ The Permian extinction
_________ The Cambrian explosion
_________ The first animals
_________ The extinction of dinosaurs
_________ An increase in oxygen in the atmosphere
(1) the first prokaryotes (~3 billion years ago); (2) an increase of oxygen in the atmosphere (~2.5 billion years ago); (3) the first multicellular eukaryotes (~1.2 billion years ago); (4) the Cambrian explosion (~545 million years ago); (5) the first animals (~540 million years ago); (6) the Permian extinction (~248 million years ago); (7) the extinction of dinosaurs (~65 million years ago)
USE IT
 Consider a rock formed at about the same time as Earth was formed.
Consider a rock formed at about the same time as Earth was formed.
a. How old is this rock?
b. How much of the original uranium-238 is likely to be left today in that rock?
a: The rock is approximately 4.5 billion years old. b: Approximately half of the original uranium-238 is left (after one half-life)
 Diverse animal fossils are found dating from the Cambrian Period, not earlier. Why might these organisms have made their first appearance in the fossil record only then, even though their ancestors may have been living, and evolving, for a long time before the Cambrian? (Think about what kinds of new structures might have evolved during the Cambrian Period that would have allowed these organisms to leave fossils.)
Diverse animal fossils are found dating from the Cambrian Period, not earlier. Why might these organisms have made their first appearance in the fossil record only then, even though their ancestors may have been living, and evolving, for a long time before the Cambrian? (Think about what kinds of new structures might have evolved during the Cambrian Period that would have allowed these organisms to leave fossils.)
The ancestors of these organisms may have been primarily soft-bodied organisms that did not leave fossils. The development of shells and other hard body parts would allow fossilized remains of these organisms to be left in the fossil record at this time.
MINI CASE
 Along the banks of a river, some sedimentary rock strata have been revealed by erosion. By radiometric dating, the layer above these strata is determined to be ~290 million years old, and the layer beneath has been dated to ~354 million years ago. A paleontologist starts to uncover fossils in the sedimentary rock strata. The fossils are clearly land-dwelling vertebrates. Are they more likely to be reptiles or amphibians? Explain your answer.
Along the banks of a river, some sedimentary rock strata have been revealed by erosion. By radiometric dating, the layer above these strata is determined to be ~290 million years old, and the layer beneath has been dated to ~354 million years ago. A paleontologist starts to uncover fossils in the sedimentary rock strata. The fossils are clearly land-dwelling vertebrates. Are they more likely to be reptiles or amphibians? Explain your answer.
These land-dwelling vertebrates lived between 354 and 290 million years ago. There were clearly amphibians present during this time (the earliest amphibians date from ~368 million years ago), but the earliest reptiles were also likely present.
INTERPRETING DATA
 You have carried out radiometric analysis on four igneous rocks uncovered at several sites you are exploring. From the % lead you determine in each case, what is the approximate age of the rock?
You have carried out radiometric analysis on four igneous rocks uncovered at several sites you are exploring. From the % lead you determine in each case, what is the approximate age of the rock?
Rock A: 75% lead ___________
Rock B: 50% lead ___________
Rock C: 30% lead ___________
Rock D: 10% lead ___________
From Infographic 17.2:
Rock A: 75% lead, 9 billion years old
Rock B: 50% lead, 4.5 billion years old
Rock C: 30% lead, 2.25 billion years old
Rock D: 10% lead, ~1 billion years old
Driving Question 2
What factors help to explain the distribution of species on Earth?
By answering the questions below and studying Infographic 17.4, you should be able to generate an answer for the broader Driving Question above.
KNOW IT
 If two organisms strongly resemble each other in their physical traits, can you necessarily conclude that they are closely related? Explain your answer.
If two organisms strongly resemble each other in their physical traits, can you necessarily conclude that they are closely related? Explain your answer.
No. While they may be closely related, they may also represent convergent evolution, in which unrelated groups of organisms share common characteristics because of independent natural selection in similar environments.
 What did the arrangement of landmasses on Earth look like between 135 and 65 million years ago? What happened to these landmasses, and how does this change help explain the distribution of organisms found on the planet?
What did the arrangement of landmasses on Earth look like between 135 and 65 million years ago? What happened to these landmasses, and how does this change help explain the distribution of organisms found on the planet?
See Infographic 17.5. Several of the continental landmasses were much closer together (e.g., North America and Eurasia). Over time, through plate tectonics, the landmasses have moved to their present locations. As the landmasses moved, organisms moved with them and were subjected to changing environments, which influenced the evolution of organisms.
USE IT
 A cactus called ocotillo (Fouquieria splendens), which grows in New Mexico, looks very much like Alluaudia procera, a species of plant that grows in the deserts of Madagascar. These two plant species are not closely related—they are in different orders in the kingdom Plantae. Why then do they look so alike?
A cactus called ocotillo (Fouquieria splendens), which grows in New Mexico, looks very much like Alluaudia procera, a species of plant that grows in the deserts of Madagascar. These two plant species are not closely related—they are in different orders in the kingdom Plantae. Why then do they look so alike?
These two plant species may look alike because of convergent evolution; both have adapted to a desert climate.
 If penguins and polar bears had evolved before Pangaea split into northern and southern continents, what might you predict about their geographic distribution today?
If penguins and polar bears had evolved before Pangaea split into northern and southern continents, what might you predict about their geographic distribution today?
If they had evolved while Pangaea was still intact, then both polar bears and penguins would have been found across Pangaea, and when Pangaea split both would have migrated to the northern and southern polar regions, and both polar bears and penguins would be found at both poles.
 Both bats and insects fly, but bat wings have bones and insect wings do not. Would you consider bat and insect wings to be a result of convergent evolution, or of homology—evolution based on inheritance of similar structures from a common ancestor? Explain your answer.
Both bats and insects fly, but bat wings have bones and insect wings do not. Would you consider bat and insect wings to be a result of convergent evolution, or of homology—evolution based on inheritance of similar structures from a common ancestor? Explain your answer.
This is an example of convergent evolution. The wings of insects and of bats are not based on homologous structures inherited from a common ancestor.
Driving Question 3
What are the major groups of organisms, and how are organisms placed in groups?
By answering the questions below and studying Infographics 17.5, 17.6, 17.7, and 17.8, you should be able to generate an answer for the broader Driving Question above.
KNOW IT
 Which of the following is not a domain of life?
Which of the following is not a domain of life?
a. Animalia
b. Eukarya
c. Bacteria
d. Archaea
e. Plantae
f. Neither a nor e is a domain of life.
f
 Put the following terms in order from most inclusive (1) to least inclusive (5).
Put the following terms in order from most inclusive (1) to least inclusive (5).
_________ Domain
_________ Species
_________ Kingdom
_________ Genus
_________ Phylum
(1) domain; (2) kingdom; (3) phylum; (4) genus; (5) species
 A phylogenetic tree represents
A phylogenetic tree represents
a. a grouping of organisms on the basis of their shared structural features.
b. a grouping of organisms on the basis of their cell type.
c. a grouping of organisms on the basis of their complexity.
d. a grouping of organisms on the basis of their evolutionary history.
e. a grouping of organisms on the basis of where they are found.
d
USE IT
 Why was the classification of the kingdom Monera split into two domains? What are these two domains?
Why was the classification of the kingdom Monera split into two domains? What are these two domains?
The kingdom Monera originally included all prokaryotic organisms. However, genetic evidence indicated that not all prokaryotes are closely related, and that there are two distinct groups of prokaryotic organisms. Today, these two groups are the domains Bacteria and Archaea.
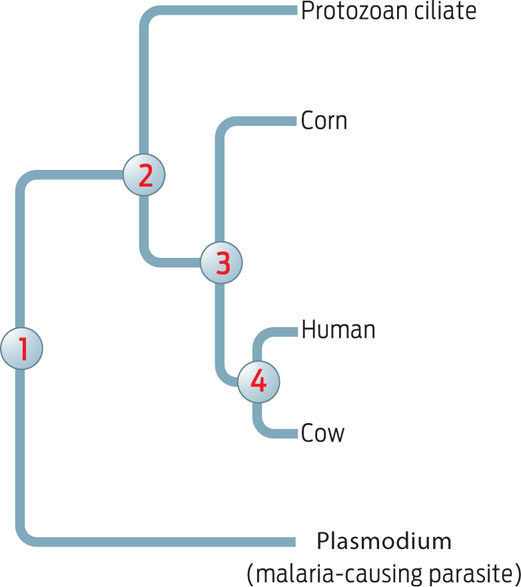
 On the tree below, which number represents the most recent common ancestor of humans and corn?
On the tree below, which number represents the most recent common ancestor of humans and corn?
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
e. Humans and corn do not share any ancestors.
c
BRING IT HOME
 Carry out some online research on the fossils found in your home state. What groups of organisms are represented in the statewide fossil record? What is the oldest fossil found in your state? What do the fossils in your state suggest about the pattern(s) of evolution in your state?
Carry out some online research on the fossils found in your home state. What groups of organisms are represented in the statewide fossil record? What is the oldest fossil found in your state? What do the fossils in your state suggest about the pattern(s) of evolution in your state?
Answers will vary.