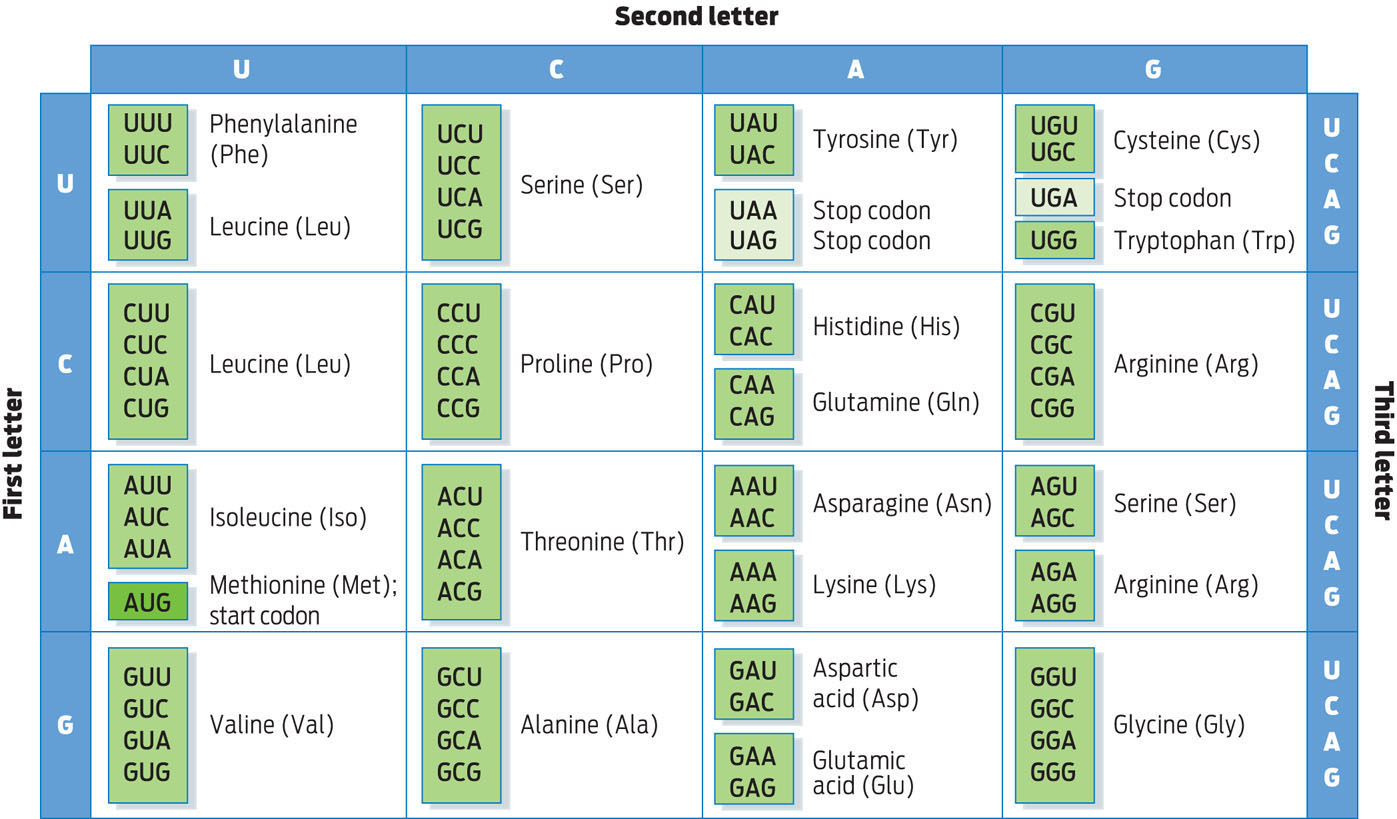
Codons are groups of three-nucleotide sequences within chains of mRNA. Most codons specify a particular amino acid. Some codons specify where to start translation (start codons) and where to end (stop codons). There is redundancy in the genetic code, as 64 possible codons code for only 20 different amino acids. Since the genetic code is universal, the same gene will be transcribed and translated into the same protein in virtually all cells and organisms.