CHAPTER 28 Test Your Knowledge
DRIVING QUESTION 1
What structures make up the respiratory system?
By answering the questions below and studying Infographics 28.1 and 28.6, you should be able to generate an answer for the broader Driving Question above.
KNOW IT
 Add the names of the structures indicated by the labels A-F in the diagram below.
Add the names of the structures indicated by the labels A-F in the diagram below.
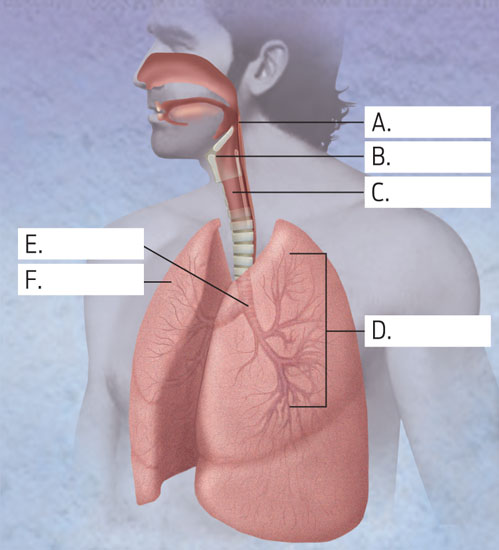
(A) pharynx; (B) larynx; (C) lung; (D) bronchioles
 Which part of the respiratory system is the site of exchange of gases between blood and air?
Which part of the respiratory system is the site of exchange of gases between blood and air?
a. alveoli
b. bronchioles
c. trachea
d. pharynx
e. bronchi
a
 Inhalation is accompanied by
Inhalation is accompanied by
a. muscular relaxation and a decrease in lung volume.
b. muscular relaxation and an increase in lung volume.
c. muscular contraction and a decrease in lung volume.
d. muscular contraction and an increase in lung volume.
e. muscular contraction and no change in lung volume.
d
USE IT
 Emphysema is a form of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). In this disease, the alveoli have been damaged, most often by cigarette smoking. The alveolar damage results in overinflation of the alveoli that can’t exchange their “spent air,” and causes an affected person to exhale through pursed lips.
Emphysema is a form of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). In this disease, the alveoli have been damaged, most often by cigarette smoking. The alveolar damage results in overinflation of the alveoli that can’t exchange their “spent air,” and causes an affected person to exhale through pursed lips.
a. From this description, explain the following symptoms of emphysema: breathlessness; inability to exercise.
b. Explain why supplemental oxygen is often a treatment for emphysema.
a: If the alveoli can’t exchange their “spent air,” the air in the alveoli will have a higher CO2 concentration and a lower O2 concentration than “fresh air.” This means that blood carrying gases in the body will also have a higher CO2 concentration and a lower O2 concentration than normal. Inadequate oxygen delivery will result in feelings of breathlessness and an inability to exercise (exercise creates a higher demand for oxygen). b: People with emphysema have insufficient oxygen in the alveoli. Having these people breathe additional oxygen (at a higher than normal level) will help increase the oxygen concentration in the air spaces in the alveoli.
 Asthma is a disease that causes swelling and constriction of the airways. Compare the predicted symptoms of asthma with the predicted symptoms of emphysema. Can you think of any treatments for asthma that might be different from treatments for emphysema?
Asthma is a disease that causes swelling and constriction of the airways. Compare the predicted symptoms of asthma with the predicted symptoms of emphysema. Can you think of any treatments for asthma that might be different from treatments for emphysema?
In the case of swollen and constricted airways, air may not be able to move readily between the outside of the body and the alveoli in exchanging alveolar air with fresh air. This would lead to shortness of breath. Because the air is moving through constricted passages, asthma often causes wheezing. Both asthma and emphysema can impair the exchange of air in the alveoli, leading to shortness of breath. Asthma symptoms can be treated by drugs that open the airways, but these drugs wouldn’t be expected to alleviate emphysema.
DRIVING QUESTION 2
How do the respiratory and cardiovascular systems cooperate to deliver oxygen to body cells and remove carbon dioxide from tissues?
By answering the questions below and studying Infographics 28.2 and 28.3, you should be able to generate an answer for the broader Driving Question above.
KNOW IT
 How is O2 transported throughout the body?
How is O2 transported throughout the body?
a. dissolved in the plasma of blood
b. bound to hemoglobin in plasma
c. bound to hemoglobin in white blood cells
d. bound to hemoglobin in red blood cells
e. dissolved in the cytoplasm of red blood cells
d
 What can cause a drop in blood pH?
What can cause a drop in blood pH?
a. a decrease in O2
b. an increase in O2
c. a decrease in CO2
d. an increase in CO2
e. b or d
d
USE IT
 If blood pH drops, what happens to the breathing rate? Explain your answer.
If blood pH drops, what happens to the breathing rate? Explain your answer.
If blood pH drops and the blood becomes more acidic, breathing rate will increase, increasing the rate of removal of CO2 from the lungs. This is important to restore blood pH, as elevated CO2 contributes to acidification of the blood.
 Oxygen diffuses from the air in alveoli to the blood in lung capillaries. Diffusion occurs rapidly over short distances, but decreases dramatically with increases in distance. Pneumonia is an accumulation of fluid in the alveolar air spaces. Why does pneumonia cause shortness of breath and give a bluish tint to the skin and nails?
Oxygen diffuses from the air in alveoli to the blood in lung capillaries. Diffusion occurs rapidly over short distances, but decreases dramatically with increases in distance. Pneumonia is an accumulation of fluid in the alveolar air spaces. Why does pneumonia cause shortness of breath and give a bluish tint to the skin and nails?
The accumulation of fluid in the alveoli increases the distance between the oxygen in the air in the alveoli and the capillaries underlying the alveoli. Because of this increased distance, diffusion of oxygen is not as efficient, and less oxygen enters the blood as it passes through the lungs. This causes shortness of breath, and less-oxygenated blood appears bluish under the skin.
 Breathing in and out of a paper bag will ________ pH and therefore ________ ventilation.
Breathing in and out of a paper bag will ________ pH and therefore ________ ventilation.
a. not change; not change
b. increase; increase
c. increase; decrease
d. decrease; decrease
e. decrease; increase
e
DRIVING QUESTION 3
What factors influence the oxygen-carrying capacity of blood and breathing rate?
By answering the questions below and studying Infographics 28.3, 28.4, 28.8, and 28.9, you should be able to generate an answer for the broader Driving Question above.
KNOW IT
 Relative to a tissue at rest, actively exercising tissues have
Relative to a tissue at rest, actively exercising tissues have
a. higher temperature, higher ![]() , and higher pH.
, and higher pH.
b. higher temperature, lower ![]() and lower pH.
and lower pH.
c. higher temperature, higher ![]() and lower pH.
and lower pH.
d. lower temperature, higher ![]() and higher pH.
and higher pH.
e. lower temperature, lower ![]() and lower pH.
and lower pH.
b
 What is the particular feature of altitude that increases the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood?
What is the particular feature of altitude that increases the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood?
a. the actual height (elevation)
b. the reduced atmospheric (barometric) pressure
c. the reduced partial pressure of oxygen
d. the increased atmospheric (barometric) pressure
e. the decreased relative humidity
c
USE IT
 Hemoglobin releases O2 at low pH. Give two reasons why a tissue would have a low pH.
Hemoglobin releases O2 at low pH. Give two reasons why a tissue would have a low pH.
A tissue could have a low pH because of high rates of aerobic respiration (e.g., with exercise). This will cause a local increase of CO2, which reduces the local pH. A tissue could also have a low pH if it is carrying out fermentation, which produces lactic acid, which will reduce the local pH. In both these cases, the tissue is needs more oxygen, so the enhanced release of oxygen by hemoglobin under these conditions is beneficial.
 Carbon monoxide (CO) binds to hemoglobin more tightly than oxygen does. In fact, CO can displace oxygen from hemoglobin. Predict the symptoms of CO poisoning, and provide an explanation.
Carbon monoxide (CO) binds to hemoglobin more tightly than oxygen does. In fact, CO can displace oxygen from hemoglobin. Predict the symptoms of CO poisoning, and provide an explanation.
CO poisoning reduces the ability of hemoglobin to carry oxygen. This will result in symptoms of oxygen deficits, of which shortness of breath is a symptom.
 Why do people “suck wind” (that is, breathe very heavily) with vigorous exercise?
Why do people “suck wind” (that is, breathe very heavily) with vigorous exercise?
With heavy exercise, the demand for oxygen to sustain high rates of aerobic respiration is elevated. Tissues, particularly muscle tissues, use more oxygen, dropping the local oxygen levels. Similarly, with high rates of aerobic respiration, more CO2 is being produced during glycolysis and the citric acid cycle. The combination of lowered oxygen and elevated carbon dioxide increases the rate and depth of breathing, removing excess carbon dioxide and bringing in oxygen.
DRIVING QUESTION 4
How can scientific knowledge of the respiratory system be used to design training regimens for elite athletes?
By answering the questions below and studying Infographics 28.5, 28.7, and 28.9, you should be able to generate an answer for the broader Driving Question above.
KNOW IT
 Which of the following mimics high altitude?
Which of the following mimics high altitude?
a. sleeping in a high-O2 chamber
b. sleeping in a low-O2 chamber
c. transfusing RBC into the circulation
d. a and c
e. b and c
b
 What does EPO do?
What does EPO do?
a. stimulates RBCs to release stored O2
b. stimulates RBC production
c. increases the number of heme groups per molecule of hemoglobin
d. increases ventilation rate.
e. b and c
b
 Design an experiment to determine whether hypoxic chambers confer an advantage relative to altitude training. Consider how you will set up your experiment, including appropriate controls, and the variables that you will consider and measure.
Design an experiment to determine whether hypoxic chambers confer an advantage relative to altitude training. Consider how you will set up your experiment, including appropriate controls, and the variables that you will consider and measure.
There are many possibilities. The independent variable will be the treatment- altitude training, hypoxic chambers or no oxygen manipulation. The dependent variable could be a variety of factors relative to athletic performance- speed, endurance, strength- and there are a variety of ways to measure these. You would also have to consider whether any advantage was to be measured at sea level or at altitude. You could also consider the relative timing of the treatmentand the duration of the treatment before assessing athletic advantage.
USE IT
 WADA must be able to test for a variety of banned substances. How could WADA test for each of the following? Rank them in order of easiest to detect (1) to hardest to detect (4).
WADA must be able to test for a variety of banned substances. How could WADA test for each of the following? Rank them in order of easiest to detect (1) to hardest to detect (4).
______ EPO doping
______ Transfusion of whole blood
______ Transfusion of RBC
______ Use of a hypoxic chamber
These are hard to rank, given the range of possibilities. The key point is to consider the each possibility and the challenges associated with each. EPO doping could be directly measured by trying to measure EPO levels (this would be easier if genetically engineered EPO, which differs slightly from natural EPO, had been used in the doping), or less directly by observing an increase in RBCs. Transfusion of whole blood would increase the cell counts of all blood cell types (not just RBCs). If it was the patient’s own blood, there would be no way to detect a genetic difference. If the whole blood came from someone else, then it may be possible to detect DNA from the donor. Transfusion of RBCs would increase the concentration of RBCs, but EPO and use of a hypoxic chamber would also have this effect. Use of a hypoxic chamber would increase the concentration of RBCs. Transfusion of whole blood might be easiest to detect, as this would increase the number of all blood cell types, not just RBCs. It may be possible to detect EPO doping by measuring EPO levels, although EPO levels would also be elevated by use of a hypoxic chamber. Because RBCs do not have nuclei (and therefore have no nuclear DNA), it is hard to detect transfusion of donor RBCs. WADA clearly faces challenges in detecting serious attempts to enhance athletic performance.
INTERPRETING DATA
 Look at Infographic 28.7.
Look at Infographic 28.7.
a. Start with the 3000-m performance data for the elite athletes. How many seconds did the men improve by? How many seconds did the women improve by? Now determine that improvement as a % of the pre-altitude race time. What % improvement did altitude training confer? In your opinion, is this method of training worth it for that % improvement?
b. Now look at the graph with both the collegiate and the elite athletes. Even if the graph were not labeled, how could you know which group was which? (Hint: Look at their pre-altitude race times.) Did every athlete experience an improvement in race time? Was the change in race time identical for every athlete? Given the variability in results in this small sample size of conditioned athletes, what do you think you can extrapolate about altitude training in a larger population of active people?
a: The men improved by (8:18.4 – 8:12.6) = 5.8 seconds. The pre-altitude race time was 8:18.4 = 498.4 seconds. A 5.8/498.4-second improvement = 1.16%. Women improved by (9:32.4 – 9:26.9) = 5.5 seconds. The pre-altitude race time was 9:32.4 = 572.4 seconds. A 5.5/572.4-second improvement = 0.96%. Opinions will vary about the value of these % improvements. b: Elite runners’ times are generally faster than collegiate runners’, giving a hint about which group is which. There was variability in improvement in race time. While many athletes (both collegiate and elite) improved their race time (positive values on the y axis), a few were at close to 0 (no change in race time) or negative (a slower race time after altitude training). More collegiate athletes than elite athletes had negative improvements. From these data, it seems that the elite athletes may have experienced a larger benefit from altitude training than the collegiate athletes. As collegiate athletes are still very fit and well trained, it seems less likely that a general population of active people will experience the same benefits from altitude training as elite athletes.
BRING IT HOME
 Your friend wants to join a new gym. The gym has many amenities, including personal trainers (for an additional fee) and a hypoxic chamber for “performance training.” There is a steep sign-up fee and high monthly dues at this gym. Another gym is offering a no-fee sign-up and lower monthly dues. This gym has the same cardiovascular equipment and access to personal trainers (at an additional fee comparable to that at the new gym). Your friend is fit. She runs local 10K races, and often places in the top 10 in her age group in your small town. Given the costs of the two gyms and your friend’s fitness level and goals, would you advise her to join the new gym or the old one? Explain your reasoning.
Your friend wants to join a new gym. The gym has many amenities, including personal trainers (for an additional fee) and a hypoxic chamber for “performance training.” There is a steep sign-up fee and high monthly dues at this gym. Another gym is offering a no-fee sign-up and lower monthly dues. This gym has the same cardiovascular equipment and access to personal trainers (at an additional fee comparable to that at the new gym). Your friend is fit. She runs local 10K races, and often places in the top 10 in her age group in your small town. Given the costs of the two gyms and your friend’s fitness level and goals, would you advise her to join the new gym or the old one? Explain your reasoning.
There are a variety of possible answers here; many would be based on the friend’s ability to pay for the more expensive gym and hypoxic training. If the new gym would pose a financial burden, joining the new gym might not be worth the added expense. As shown in Question 21 and Infographic 28.7, even very fit collegiate athletes do not derive benefit from altitude training, which hypoxic training mimics—performance benefits seem to be associated with elite athletes. As the friend’s career and sponsorships do not rely on improved athletic performance, the access to hypoxic chambers may not be worth the cost, especially for very small improvements in performance.