CHAPTER 5 Test Your Knowledge
Driving Question 1
What are the photosynthetic organisms on the planet, and why are they so important?
By answering the questions below and studying Infographics 5.3 and 5.6, you should be able to generate an answer for the broader Driving Question above.
KNOW IT
 What do algae, cyanobacteria, and plants have in common?
What do algae, cyanobacteria, and plants have in common?
They are all photosynthetic—that is, they carry out photosynthesis, using the energy from sunlight and carbon dioxide from air to synthesize sugars.
 Can animals directly use the energy of sunlight to make their own food (in their own bodies)?
Can animals directly use the energy of sunlight to make their own food (in their own bodies)?
No. Animals cannot carry out photosynthesis. However, they rely on photosynthesis, as they eat plant material that is the product of photosynthesis, and animal material that is sustained by eating plants.
 What organelle(s) would a nonphotosynthetic alga need to be able to carry out photosynthesis?
What organelle(s) would a nonphotosynthetic alga need to be able to carry out photosynthesis?
a. mitochondria
b. nucleus
c. chloroplast
d. solar transformer
e. cell membrane
c
 Why do many species of algae appear green?
Why do many species of algae appear green?
The main photosynthetic pigment is chlorophyll, which reflects green wavelengths.
 Compare and contrast the ways photosynthetic algae and animals obtain and use energy.
Compare and contrast the ways photosynthetic algae and animals obtain and use energy.
Photosynthetic algae rely on photosynthesis for the production of sugars that can be used for short-term energy needs or for longer-term energy storage. Animals cannot make their own sugars (or other energy-rich organic molecules) from scratch, so must obtain them from their diet.
USE IT
 What would happen to humans and other animals if algae, cyanobacteria, and plants were wiped out? Would we only lose a food source (e.g., plants), or would there be other repercussions?
What would happen to humans and other animals if algae, cyanobacteria, and plants were wiped out? Would we only lose a food source (e.g., plants), or would there be other repercussions?
There would be several repercussions for humans if photosynthetic organisms were wiped out. First, critical food and energy sources would be eliminated. Second, in the absence of photosynthesis by plants and algae, there would be a reduction in oxygen levels in the atmosphere, affecting our ability to carry out key energy-related reactions in our cells.
 Why would a dark dust cloud that prevented sunlight from reaching Earth’s surface be potentially devastating to animal life?
Why would a dark dust cloud that prevented sunlight from reaching Earth’s surface be potentially devastating to animal life?
A thick and dense dust cloud could prevent sunlight from reaching photosynthetic organisms at Earth’s surface. If these organisms are not able to “harvest” the energy in sunlight, they will not be able to grow and store valuable molecules. This will seriously (and negatively) affect the ability of animals (including humans) to meet their nutritional and energetic needs.
Driving Question 2
What are the different types of energy, and what transformations of energy do organisms carry out?
By answering the questions below and studying Infographics 5.4 and 5.5, you should be able to generate an answer for the broader Driving Question above.
KNOW IT
 The energy of sunlight exists in the form of
The energy of sunlight exists in the form of
a. glucose.
b. photons.
c. gamma rays.
d. ions.
e. particles.
b
 The energy in a cereal bar is_______energy. The energy of a cyclist pedaling is_______energy.
The energy in a cereal bar is_______energy. The energy of a cyclist pedaling is_______energy.
a. light; chemical
b. potential; chemical
c. chemical; kinetic
d. potential; potential
e. kinetic; potential
c
 Kinetic energy is best described as
Kinetic energy is best described as
a. stored energy.
b. light energy.
c. the energy of movement.
d. heat energy.
e. any of the above, depending on the situation.
c
USE IT
 If you wanted to get the most possible energy from photosynthetic algae, should you eat algae directly or feed algae to a cow and then eat a burger made from that cow? Explain your answer.
If you wanted to get the most possible energy from photosynthetic algae, should you eat algae directly or feed algae to a cow and then eat a burger made from that cow? Explain your answer.
You should eat the algae. If you eat the algae directly, you ingest 100% of their energy. If you feed the algae to a cow, only ~10% of the stored algal energy makes it into stored cow (burger) energy. A great deal of energy is lost between the algae and the cow.
Driving Question 3
How do plants and algae convert the energy in sunlight into energyrich organic molecules? (And why can’t humans do this?)
By answering the questions below and studying Infographics 5.7, 5.8, and 5.9, you should be able to generate an answer for the broader Driving Question above.
KNOW IT
 Which of the following photon wavelengths contains the greatest amount of energy?
Which of the following photon wavelengths contains the greatest amount of energy?
a. violet
b. red
c. green
d. yellow
e. blue
a
 Glucose is a product of photosynthesis. Where do the carbon atoms in glucose come from?
Glucose is a product of photosynthesis. Where do the carbon atoms in glucose come from?
a. starch
b. cow manure
c. molecules in air
d. water
e. soil
c
 Mark each of the following as an input (I) or an output (O) of photosynthesis.
Mark each of the following as an input (I) or an output (O) of photosynthesis.
Oxygen____
Carbon dioxide____
Photons____
Glucose____
Water____
oxygen (O); carbon dioxide (I); photons (I); glucose (O); water (I)
 Photosynthetic algae are
Photosynthetic algae are
a. eukaryotic autotrophs.
b. prokaryotic autotrophs.
c. eukaryotic heterotrophs.
d. prokaryotic heterotrophs
a
USE IT
 Global warming is linked to elevated atmospheric carbon dioxide levels. How might this affect photosynthesis? If global warming should cause ocean levels to rise, in turn causing forests to be immersed in water, how would photosynthesis be affected?
Global warming is linked to elevated atmospheric carbon dioxide levels. How might this affect photosynthesis? If global warming should cause ocean levels to rise, in turn causing forests to be immersed in water, how would photosynthesis be affected?
Increased levels of carbon dioxide should increase the amount of photosynthesis by plants, algae and photosynthetic bacteria. However, if land plants are submerged (because of rising ocean levels), they will not be able to survive to carry out photosynthesis.
 Why are energy-rich lipids from algae more useful as a fuel than energy-rich sugars and other carbohydrates produced by photosynthetic organisms like corn and wheat?
Why are energy-rich lipids from algae more useful as a fuel than energy-rich sugars and other carbohydrates produced by photosynthetic organisms like corn and wheat?
Lipids store more energy per gram than carbohydrates. This means that more energy is stored per gram of lipid than of carbohydrates.
 Draw a concept map for photosynthesis that includes the following forms of energy and molecules: sunlight; carbon dioxide; glucose (stored chemical energy); water; ATP; heat.
Draw a concept map for photosynthesis that includes the following forms of energy and molecules: sunlight; carbon dioxide; glucose (stored chemical energy); water; ATP; heat.
Answers (the maps) will vary; Infographics 5.6 and 5.8 provide relevant information.
Driving Question 4
How do algal biofuels compare to other fuels in terms of cost, benefits, and sustainability?
By answering the questions below and studying Infographic 5.2 and Table 5.1, you should be able to generate an answer for the broader Driving Question above.
KNOW IT
 Which of the following is/are necessary for biofuel production by algae?
Which of the following is/are necessary for biofuel production by algae?
a. sunlight
b. sugar
c. CO2
d. soil
e. all of the above
f. a and b
g. a and c
g
 Why are algae considered more valuable for biofuel than plants (such as corn)?
Why are algae considered more valuable for biofuel than plants (such as corn)?
a. because their photosynthetic products are an oil
b. because they are cheaper to grow
c. because they do not require as much CO2
d. because they do not require as much fertilizer
e. all of the above
e
USE IT
 Many types of algae can divert the sugars they make by photosynthesis into lipids that can be used to make biodiesel. Biodiesel is a promising replacement for fossil fuels. Describe the energy conversions required to make algal lipids for biodiesel and explain why biodiesel might be a more promising fuel than lipids extracted from animals.
Many types of algae can divert the sugars they make by photosynthesis into lipids that can be used to make biodiesel. Biodiesel is a promising replacement for fossil fuels. Describe the energy conversions required to make algal lipids for biodiesel and explain why biodiesel might be a more promising fuel than lipids extracted from animals.
In biofuel-producing algae, the energy of sunlight is converted to lipids. These store a large amount of energy per gram. Animals can produce lipids only after ingesting plant products. Animal lipids thus add a step (and additional energy transfer and loss) between the energy of sunlight and the energy stored in organic molecules.
 What do you think are some of the advantages and disadvantages of growing algae in enclosed tubes or bags compared to growing them in open vats? Make a table listing the advantages and disadvantages of each approach and explain your reasoning.
What do you think are some of the advantages and disadvantages of growing algae in enclosed tubes or bags compared to growing them in open vats? Make a table listing the advantages and disadvantages of each approach and explain your reasoning.
Advantages include the ability to control conditions (e.g., carbon dioxide concentration, temperature, nutrients, pH) to maximize lipid production from sunlight and carbon dioxide. The major disadvantage is the cost of maintaining such a sophisticated system. Growing algae in vats is far less expensive, but the process may be less efficient and is vulnerable to competing or harmful species entering and attacking the algae in the vats.
 Many biofuels require arable land for their production. Discuss competing needs for arable lands in the context of human needs for food and fuel, and how algae may alleviate this tension.
Many biofuels require arable land for their production. Discuss competing needs for arable lands in the context of human needs for food and fuel, and how algae may alleviate this tension.
Producing biofuels from traditional crops (e.g., corn) means that these crops are grown on land that could otherwise be used to for human food. By replacing food crops with fuel crops, the demand for (and price of) of crops to feed humans rises. In contrast, given water and nutrients, algae can be grown (in vats or closed systems) on land that is otherwise unsuitable for food crops. In this case, fuel crops are not competing with food crops for valuable arable land.
MINI CASE
 A CEO of a new algal biofuel company is trying to select the site for a production facility. There are three possible options:
A CEO of a new algal biofuel company is trying to select the site for a production facility. There are three possible options:
The desert of southern New Mexico (sunny, hot, mild winters, nonarable land, remote)
Denver, Colorado (sunny, cold winters, urban area with CO2 emissions from factories and cars)
Central Washington State (sunny, hot, a rich agricultural zone)
New Mexico has the advantage of abundant sunlight for photosynthesis, and biofuel production there would not compete with arable cropland. However, the site is remote and in a desert, so the cost of water and transporting nutrients could be high. Denver has the advantage of being centrally located, with abundant sources of carbon dioxide, but has a short growing season, given the short summers. Central Washington State has an ideal climate and likely has a ready supply of nutrients (fertilizers), given the other demands for fertilizers in the region. However, growing algae in this region will likely displace food crops for humans, taking over valuable cropland for fuel production.
Discuss the pros and cons of each site and make a recommendation to the CEO.
BRING IT HOME
 Richard Branson has committed his airline, Virgin Atlantic, to using a “green” fuel produced by microbes that use carbon monoxide (CO) from industrial emissions (such as from steel factories) as its carbon and energy source. Through a fermentation process that occurs in a reactor chamber, the microbes convert CO into usable ethanol, a viable green fuel. Consider how this fuel compares and contrasts with algal biofuel and corn ethanol. If this green fuel venture is successful, would Branson’s use of green fuel influence your decision to choose Virgin Atlantic over another air carrier? Why?
Richard Branson has committed his airline, Virgin Atlantic, to using a “green” fuel produced by microbes that use carbon monoxide (CO) from industrial emissions (such as from steel factories) as its carbon and energy source. Through a fermentation process that occurs in a reactor chamber, the microbes convert CO into usable ethanol, a viable green fuel. Consider how this fuel compares and contrasts with algal biofuel and corn ethanol. If this green fuel venture is successful, would Branson’s use of green fuel influence your decision to choose Virgin Atlantic over another air carrier? Why?
The process described here is similar to the production of algal biofuels in that it involves microbes (in this case, bacteria) growing in a chamber, and it doesn’t compete with food crops or arable land for food crops (this is in contrast to corn ethanol, which competes with food crops for its production). It also uses industrial waste gases (here CO instead of CO2). Because it uses CO instead of CO2, it doesn’t appear to take CO2 out of the atmosphere during its production (this is in contrast to algal biofuels and corn ethanol). The product is described as usable ethanol, so no further refining is required. And unlike corn ethanol, which first requires growing the crop and then transporting it to a fermenter to produce the ethanol, this ethanol is produced in a single step, so the transportation cost is less. Individual students will have their own opinions about whether this would influence their choice or air carrier.
INTERPRETING DATA
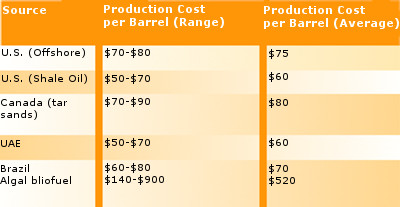
 The United States currently uses approximately 19 million barrels of oil per day. Of this, about half (9.67 million barrels per day) is imported, and the rest is from U.S. sources (offshore drilling or extraction from shale). The table shows production costs estimated for different oil sources. (The actual cost is driven by a variety of market and geopolitical factors, so we will use production costs as a substitute for actual cost.)
The United States currently uses approximately 19 million barrels of oil per day. Of this, about half (9.67 million barrels per day) is imported, and the rest is from U.S. sources (offshore drilling or extraction from shale). The table shows production costs estimated for different oil sources. (The actual cost is driven by a variety of market and geopolitical factors, so we will use production costs as a substitute for actual cost.)
a. Using the data for cost per barrel of various oils, calculate the cost to produce oil to meet current U.S. daily use. Assume that approximately half the imports are from the United Arab Emirates (UAE), and the remainder is split equally between imports from Canada and from Brazil.
b. Let’s say that the United States replaces half of its current oil imports from the UAE with domestically produced algal biofuel. What will this do to the cost of production to meet our daily needs?
c. From what you’ve read in this chapter, how are algal biofuel companies working to reduce the costs of algal biofuel?
a: If we assume that 9.67 million barrels are imported, then 9.33 million barrels are domestic. Of the 9.67 million barrels imported, half (~4.8 million) are from the UAE, a quarter (~2.4 million barrels) are from Canada, and the remaining ~ 2.5 million barrels are from Brazil. For domestic oil, assume half (4.67 million barrels) are from offshore and 4.66 million barrels are from shale.
Total: 4.8 million barrels from the UAE at $60 each: $288 million
2.4 million barrels from Canada at $80 each: $192 million
2.5 million barrels from Brazil at $70 each: $175 million
4.67 million barrels from U.S. offshore at $75 each: $350.25 million
4.66 million barrels from U.S. shale at $60 each: $279.6 million
Grand total: $1284.85 million or ~$1.3 billion
b: If we take the 4.8 million barrels from the UAE and split them between algal biofuel and the UAE, we get:
2.4 million barrels from algal biofuel at $520 each: $1,248 million
2.4 million barrels from the UAE at $60 each: $144 million
Add these totals to the figures above for Canadian, Brazilian, and U.S. sources:
New grand total: ~$2.4 billion (compared to $1.3 billion)
c: Some of the measures discussed that aim to decrease the cost of algal biofuel include genetically engineering the algae to maximize growth and oil production, using less expensive strategies to aerate the algal cultures, and using heterotrophic strains of algae.