SCIENCE LITERACY WORKING WITH DATA
In 2006, China began a short-lived decrease in the production and export of rare earth minerals. This precipitated a scramble to establish other sources of these necessary elements of modern technologies. There are now more than 25 new rare earth mining facilities in development outside China. (For help reading an area graph, see Appendix 2.)
Interpretation
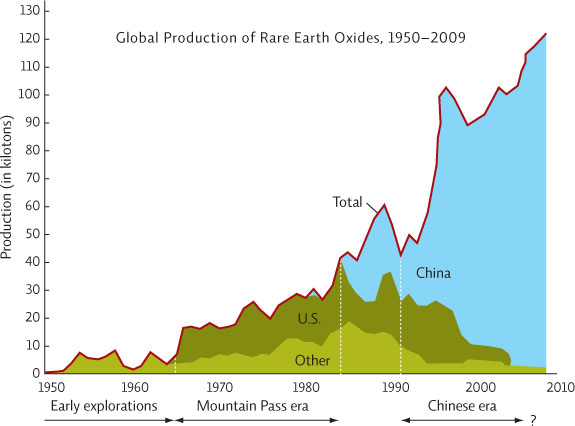
1. How did the quantity of rare earth minerals produced change between 1955 and 2009?
Rare earth mineral production has increased from less than 10 kilotons per year in 1955 to over about 120 kilotons in 2009; the annual amount has not increased steadily, some years show lower production than previous years
2. Compare the production of rare earth minerals in the United States and China since 1965.
The United States (Mountain Pass) contributed the majority of the world’s production until about 1985, when China took over as the world leader in production of rare earth minerals. After about 1998, U.S. production fell drastically and finally ended while China drastically increased its share of global production.
3. Based on your reading of the chapter, what caused the decrease in U.S. production of rare earth minerals after 1998?
Mountain Pass Mine essentially shut down at this time, due to numerous environmentally damaging spills and competition from Chinese mines.
Advance Your Thinking
4. Mountain Pass Mine began mining operations again in 2012 and anticipates an annual production of 19,050 metric tons per year by 2015. What impact will this have on the global market?
This will be only about 15% of the global production but is a substantial increase over the past 10 or 15 years so it may help increase competition and reduce prices. If the need for rare earth minerals increases, however, this production may simply meet the new demand for REEs.
5. Will increased recycling of e-waste cause a decrease in the production of rare earth minerals? Why or why not?
Possible answers would either be that, yes it would because recycling e-waste is more efficient than mining and processing rare earth minerals OR that, no it wouldn’t because global consumption of technology and thus rare earth minerals will rise more quickly than e-waste recycling can meet the demand.