16.9 Analyzing The Science
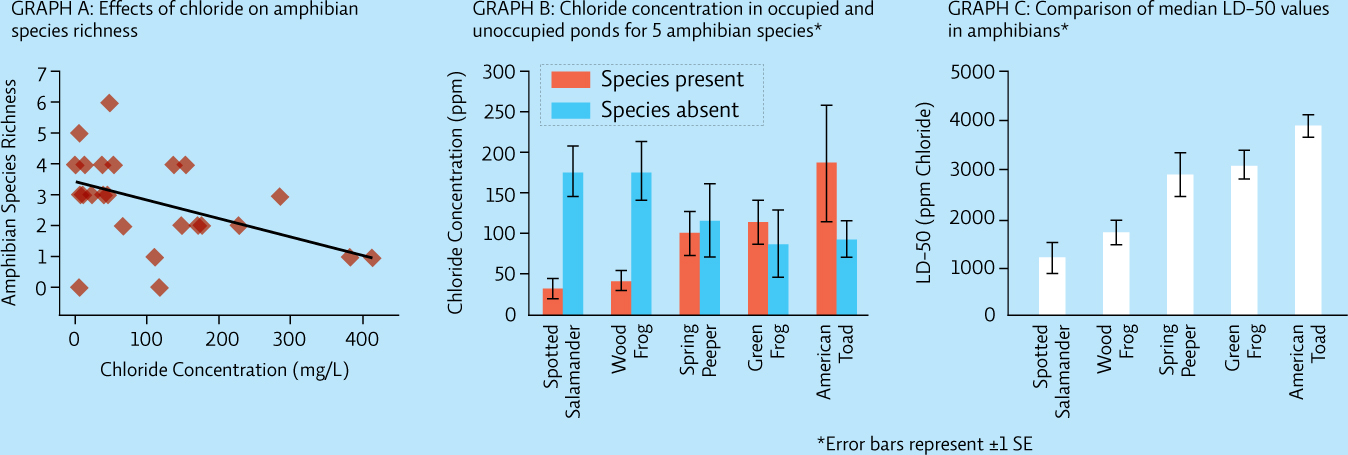
The application of road salt in cold climates can result in runoff pollution that can damage aquatic ecosystems. Researchers at Saint Mary’s University in Halifax surveyed local roadside ponds (some were occupied by amphibians and some were not) to determine chloride concentration and species richness of amphibian species. They also investigated the vulnerability of 5 amphibian species to sodium chloride (NaCl) by determining the LD-50, the dose or concentration of chloride that kills 50% of the population.
INTERPRETATION
Question 16.13
Look at Graph A. In a single sentence, explain the relationship between chloride concentration and species richness.
Question 16.14
Look at Graph B. Which species of amphibian is least affected by the presence of chloride in the water? Explain your reasoning.
Question 16.15
Look at Graph C. Which species is the most sensitive to chloride? Which is the least sensitive?
ADVANCE YOUR THINKING
Question 16.16
Look at Graph B and Graph C. Do the LD-50s for each species shown in Graph C correlate with the data (presence or absence of each species according to chloride concentration) shown in Graph B? Explain.
Question 16.17
Suggest two actions that could be taken to reduce the chance that road salt would enter ponds as runoff.
295