Chapter 1. Chapter
Infographic
Scientific American: Psychology
Infographic Activity 6.1: Sensory Memory
Sensory Memory
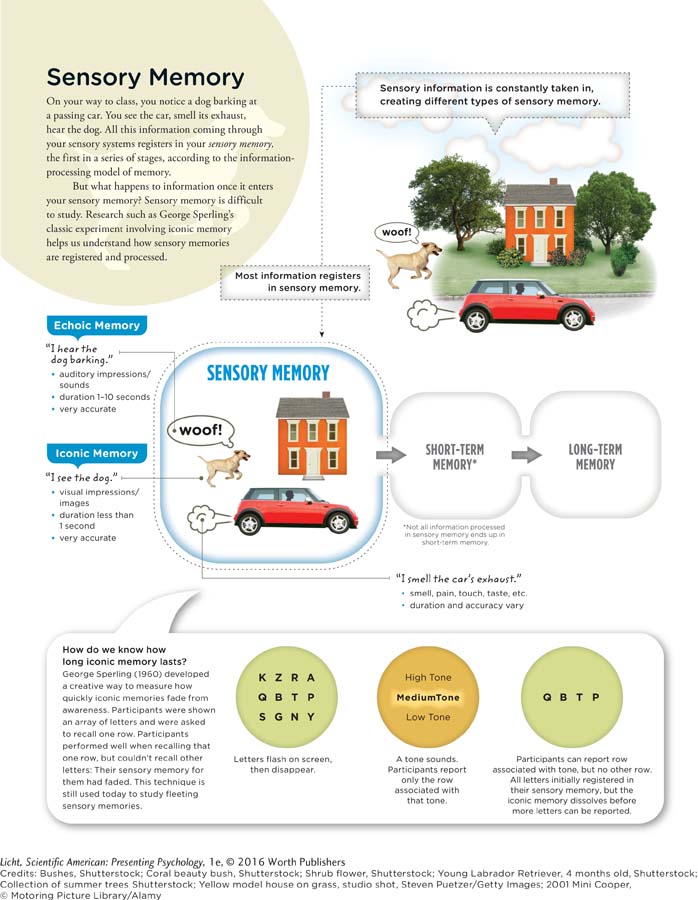
On your way to class, you notice a dog barking at a passing car. You see the car, smell its exhaust, hear the dog. All this information coming through your sensory systems registers in your sensory memory, the first in a series of stages in the information-processing model of memory.
But what happens to information once it enters your sensory memory? Sensory memory is difficult to study. Research such as George Sperling’s classic experiment involving iconic memory helps us understand how sensory memories are registered and processed.
Click the image to enlarge.
Click "Next" to continue.
1.1 Quiz
1. While you are watching television, your daughter asks you a question but you are really not paying attention to her. She then calls “Mom” (or “Dad”) sharply, and you look at her while she impatient asks if you heard what she just said. The fact that you are still aware of the question she asked even though you were not really listening to her is because of ________ memory.
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
2. Sensory memory for which of your sensory systems is believed to last for less than one second?
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
3. In George Sperling’s procedure to test sensory memory, a grid of letters was flashed on a screen for a very brief moment in time, and then the participant was cued to report the letters on the top, middle, or lowest line of that grid. What cue was used to give the participants information about which line to report?
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
4. Which of the following statements is true regarding the relationship between sensory memory and short-term memory?
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
5. You just heard a gunshot-like sound in the distance, and cannot decide whether it was in fact a gun that necessitates a call to the police, or whether it was a car backfiring. While you are trying to make this quick decision, you feel like you can still “hear” the sound, even though it is long gone. For how long will you be able to keep this type of sensation in your sensory memory?
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
6. Which of the following do you think makes it difficult to study sensory memories associated with experiences like smell, taste, touch, and pain?
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |