So Fast
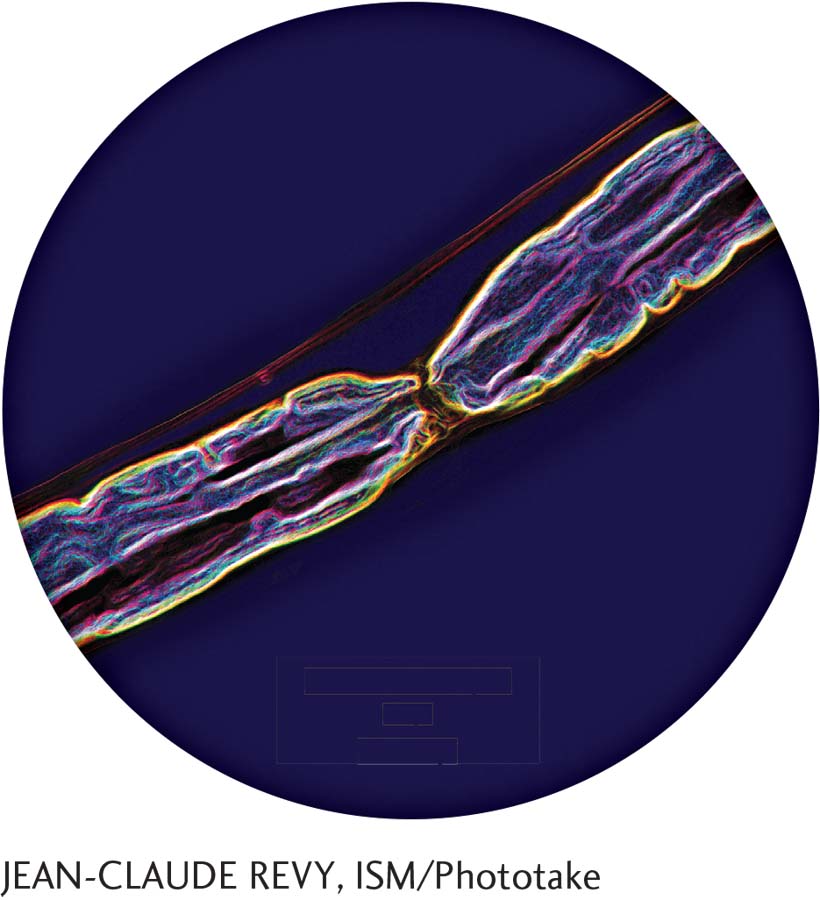
Action potentials may travel as fast as 268 miles per hour through a myelinated axon (Susuki, 2010). Myelin is a protein that envelops and insulates the axon, facilitating faster transmission of the impulse. The action potential “skips” over the segments of myelin, hopping from one node of Ranvier to the next (see small space in the center), instead of traversing the entire length of the axon.
Action potentials may travel as fast as 268 miles per hour through a myelinated axon (Susuki, 2010). Myelin is a protein that envelops and insulates the axon, facilitating faster transmission of the impulse. The action potential “skips” over the segments of myelin, hopping from one node of Ranvier to the next (see small space in the center), instead of traversing the entire length of the axon.
JEAN-