1.1 Presenting Psychology
AND IT ALL CAME FALLING DOWN Thursday, August 5, 2010: It was a crisp morning in Chile’s sand-
Darío Segovia started his workday reinforcing the mine’s narrow passageways, a process that entailed covering the roof with metal nets. The nets were intended to catch falling rocks, like the one that had sheared off a fellow miner’s leg just a month before, but Segovia knew the nets were nothing more than a stopgap solution. For over a century, miners had been chipping away at the mountain’s rocky foundation, boring through its belly with drills and dynamite, and taking very few steps to ensure it remained stable (Franklin, 2011).
At about 11:30 A.M., the mountain issued its warning call. A loud splintering sound reverberated through the mine’s dim caverns. Then about 2 hours later, the mountain hit its breaking point. A section of tunnel collapsed some 1,300 feet underground (a depth of 4 football fields), sending a thick whoosh of stones and dirt howling through the shaft (Associated Press, 2010, August 25; Franklin, 2011). The blast of air was so strong it knocked loose Victor Zamora’s false teeth (Franklin, 2011). As miners scrambled up the dark passageways slipping on loose rocks and gravel, the mountain shook again, delivering a fresh downpour of debris. The final rumble ended with an enormous thunk—
Meanwhile above ground, workers stood by as a plume of dust collected at the entrance. They knew something was terribly wrong. Those thunderous noises from inside the mountain did not sound like routine dynamite detonations. Below the cave-
LEARNING OBJECTIVES After reading and studying this chapter, you should be able to:
LEARNING OBJECTIVES After reading and studying this chapter, you should be able to:
LO 1 Define psychology and describe its scope.
LO 2 Summarize the goals of the discipline of psychology.
LO 3 Identify influential people in the formation of psychology as a discipline.
LO 4 List and summarize the major perspectives in psychology.
LO 5 Evaluate pseudopsychology and its relationship to critical thinking.
LO 6 Describe how psychologists use the scientific method.
LO 7 Summarize the importance of a random sample.
LO 8 Recognize the forms of descriptive research.
LO 9 Explain how the experimental method relates to cause and effect.
LO 10 Demonstrate an understanding of research ethics.
Take a minute and put yourself in the place of the Chilean miners. Squeezed into a small, dark hole half a mile beneath the earth’s surface, a place where it’s approximately 90°F with 90% humidity (Cohen, 2011), you are crowded among 32 other sweaty men. The main supply of drinking water is tainted with oil and dirt, and your daily food ration amounts to one spoonful of canned tuna fish and a few sips of milk (Franklin, 2011). Sleep is dangerous because you never know when a slab of rock might break off the ceiling and crush you. Besides, there is no dry spot to lie on; water trickles through every vein and crevice of this miserable dungeon. Crouched on the wet rock floor, you wonder what your family is doing. Have they heard about the accident? Surely, they will worry when you don’t show up for dinner tonight. Maybe a rescue team is on its way. Maybe there is no rescue team.
The story of the Chilean miners is largely based on Jonathan Franklin’s 33 Men: Inside the Miraculous Survival and Dramatic Rescue of the Chilean Miners. Publisher: G.P. Putnam’s Sons.
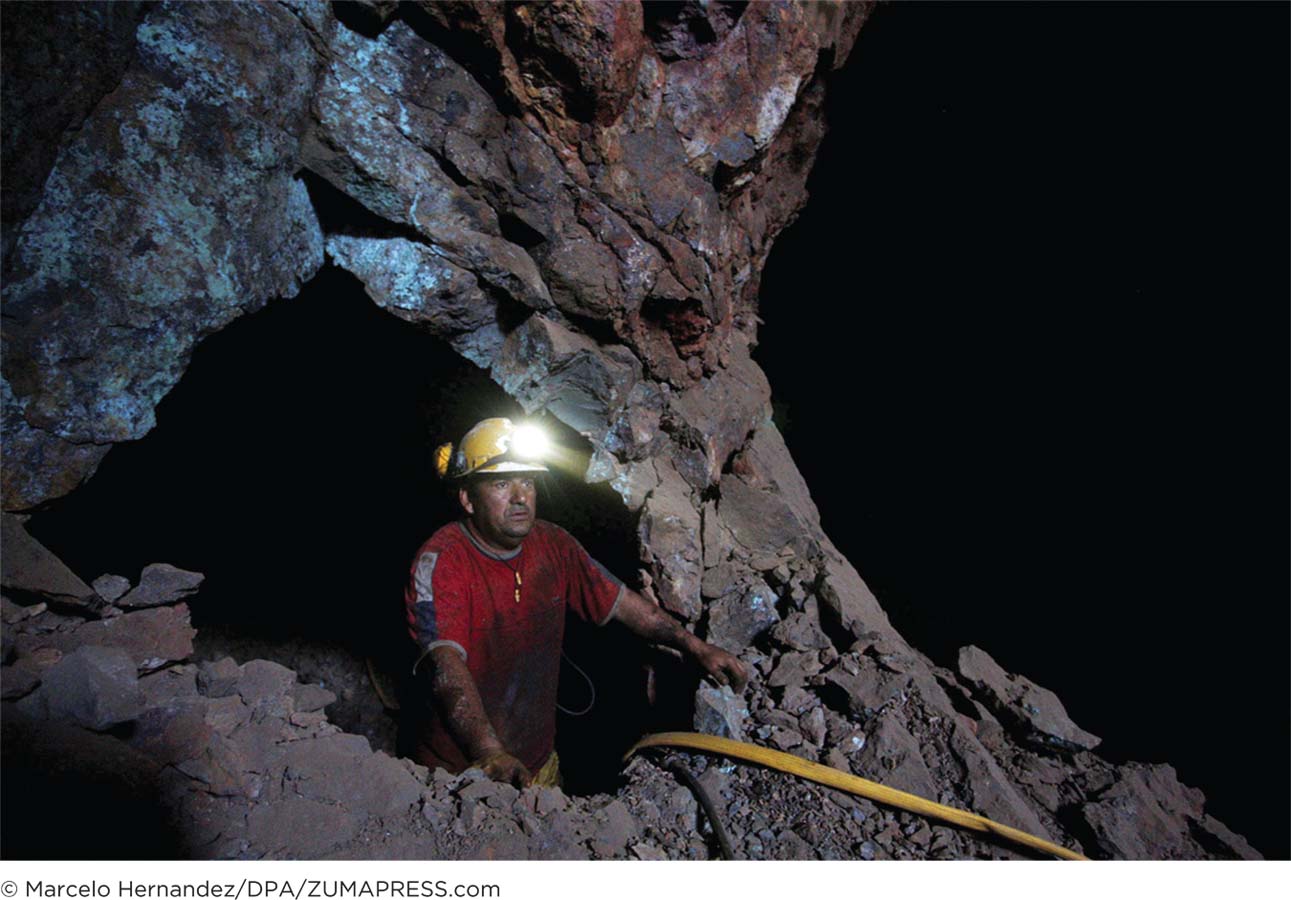

A miner navigates through the dark caverns of a Chilean mineral mine. On August 5, 2010, a large section of the San José copper mine in Copiapo collapsed, sealing 33 miners deep inside the earth with barely any food or drinking water.
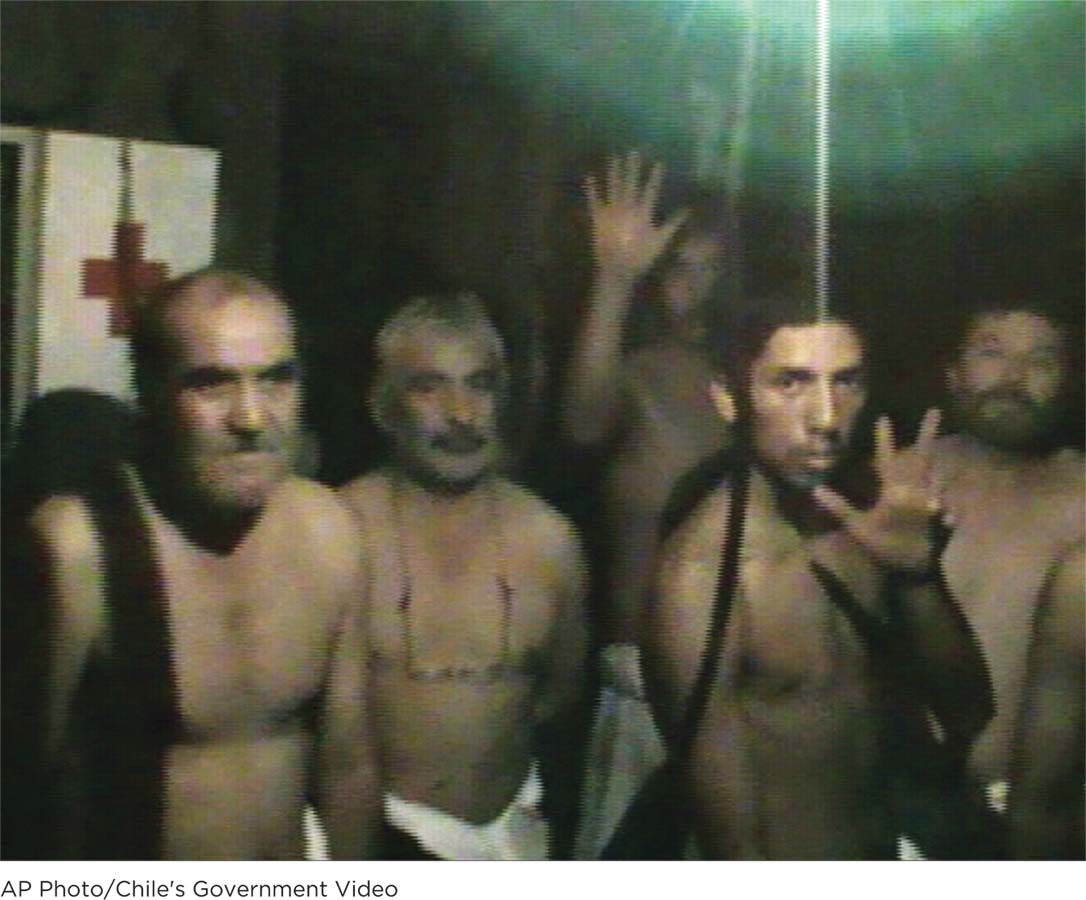

A government video shows a handful of the trapped miners standing in el refugio, a safety shelter half a mile beneath the earth’s surface. At the time this footage was captured, the men had been trapped for 23 days. They appear worn and weary, but if you look closely, you might notice a glimmer of hope in their eyes, for they know that rescue teams are working 24-
In this type of situation, our first concern tends to be physical safety. The average healthy adult can only survive about 3 to 5 weeks without food (Lieberson, 2004, November 8); the humid, filthy mine shaft is an ideal breeding ground for dangerous skin infections; and the dust and noxious air particles are a perfect recipe for lung disease (Associated Press, 2010, September 7; Franklin, 2011). But was physical harm the only type of danger the miners faced? Think about what might happen to a man’s mind when he is crowded into a sweltering rock pit for a prolonged period. How might it affect the way he thinks, feels, and acts? The miners’ story can illustrate a great deal of what psychologists know about human thoughts, emotions, and behavior, and a variety of other topics covered in this textbook. For example, you can read about changes to sleep-
What Is Psychology?
LO 1 Define psychology and describe its scope.
psychology The scientific study of behavior and mental processes.
Psychology is the scientific study of behavior and mental processes. Running, praying, and gasping were observable activities of the miners when the mountain collapsed above them, all potentially a focus of study in psychology. And although their thoughts and emotions were not observable, they are valid topics of study in psychology as well.
psychologists Scientists who study behavior and mental processes.

The pie charts on the left show the primary place of work for full-
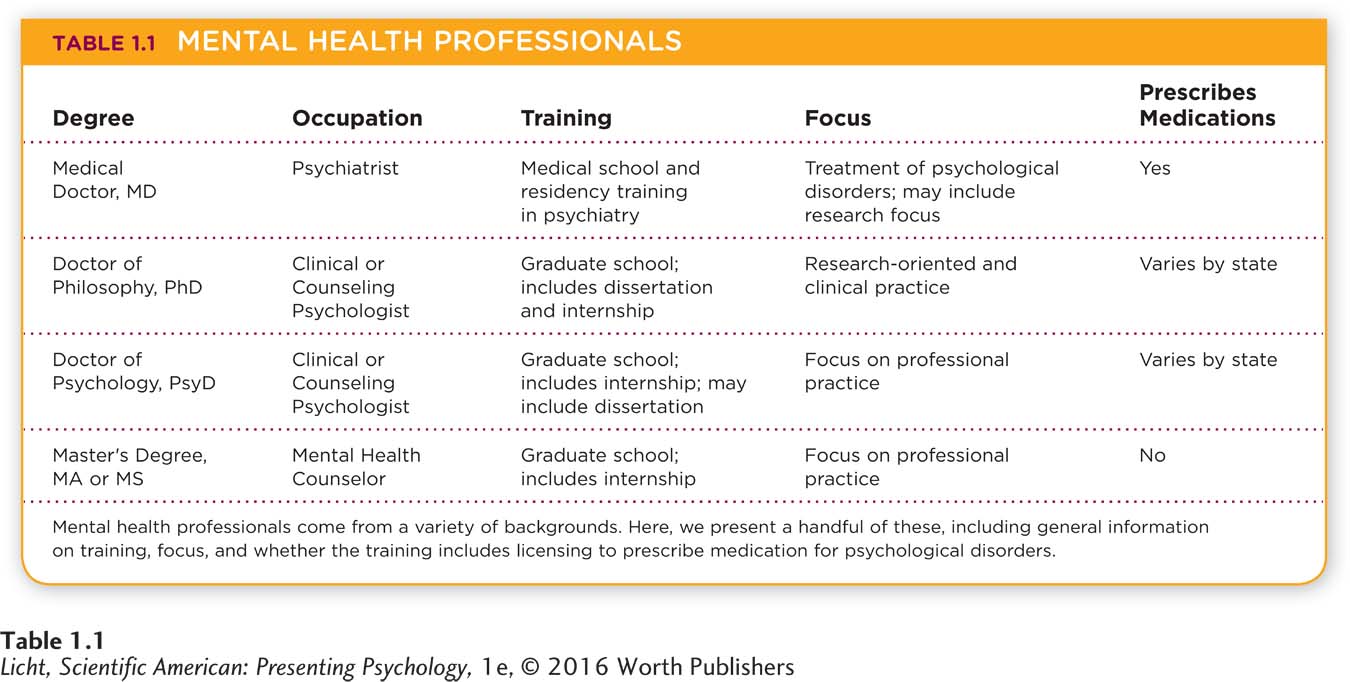
Psychologists are scientists who work in a variety of fields, all of which include the study of behavior and underlying mental processes. People often associate psychology with therapy, and many psychologists do provide therapy. These counseling psychologists and clinical psychologists might also conduct research on the causes and treatments of psychological disorders (Table 1.1, below; Chapters 12 and 13). Clinical practice is just one slice of the gigantic psychology pie. There are psychologists who spend their days observing rats in laboratories or assessing the capabilities of children in schools. Psychologists may also be found poring over brain scans in major medical centers, spying on monkeys in the Brazilian rainforest, and meeting with corporate executives in skyscrapers (Figure 1.1; see Appendix B for more on careers in psychology).
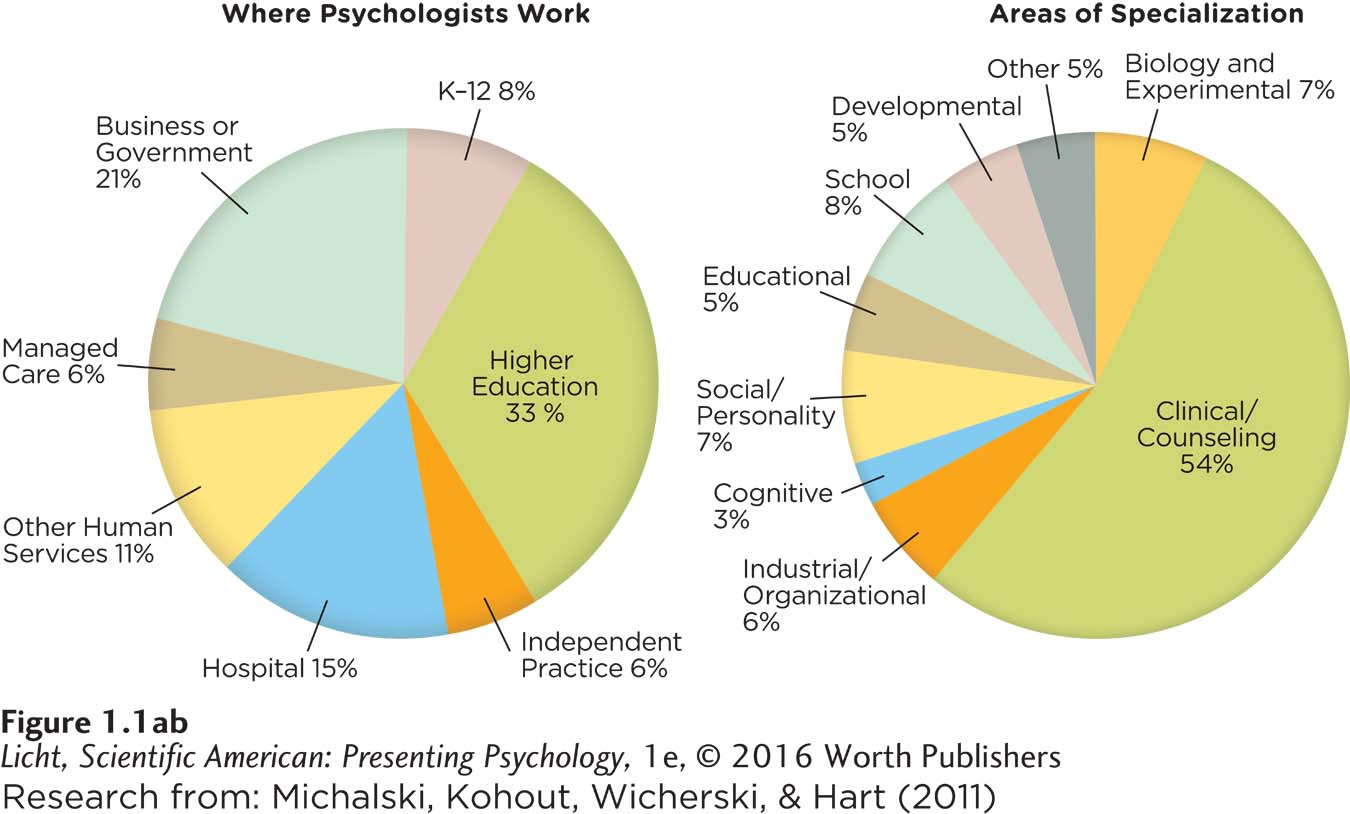
Psychology is a broad field that includes many perspectives and subfields. The American Psychological Association (APA), one of psychology’s major professional organizations, has over 50 divisions representing various subdisciplines and areas of interest (APA, 2012a). The Association for Psychological Science (APS), another major professional organization in the field, offers a list on its Web site of over 100 different societies, organizations, and agencies that are considered to have some affiliation with the field of psychology (APS, 2012). In fact, each of the chapters in this textbook covers a broad subtopic that represents a subfield of psychology.
BASIC AND APPLIED RESEARCH Psychologists conduct two major types of research. Basic research, which often occurs in university laboratories, focuses on collecting data to support (or refute) theories. The goal of basic research is not to find solutions to specific problems, but rather to gather knowledge for the sake of knowledge. General explorations of human sensory abilities, responses to trauma, and memory are examples of basic research. Applied research, on the other hand, focuses on changing behaviors and outcomes, and often leads to real-

Throughout this book, you will find parenthetical notes like this one. These citations tell you the source of research or findings being discussed, in this case a book published by Stanovich in 2013. If you want to know more about a topic, you can look up the source and read the original article or book. Information provided in this brief citation allows you to locate the full reference in the alphabetized reference list at the back of the textbook: Look for Stanovich, K. E. (2013) on page R-41. There are many systems and formats for citing sources, but this textbook uses the APA style established by the American Psychological Association (APA, 2010c).
MISCONCEPTIONS ABOUT PSYCHOLOGY Looking at Figure 1.1;, you may have been surprised to learn about the variety of subjects that psychologists study. If so, you are not alone. Researchers report that students often have misconceptions about psychology (Hughes, Lyddy, & Lambe, 2013). Most of what the average person knows about psychology comes from the popular media, which fails to present an accurate portrayal of the field, its practitioners, and its findings. Frequently, guests who are introduced as “psychologists” or “therapists” by television talk show hosts really aren’t psychologists as defined by the leading psychological organizations (Stanovich, 2013).
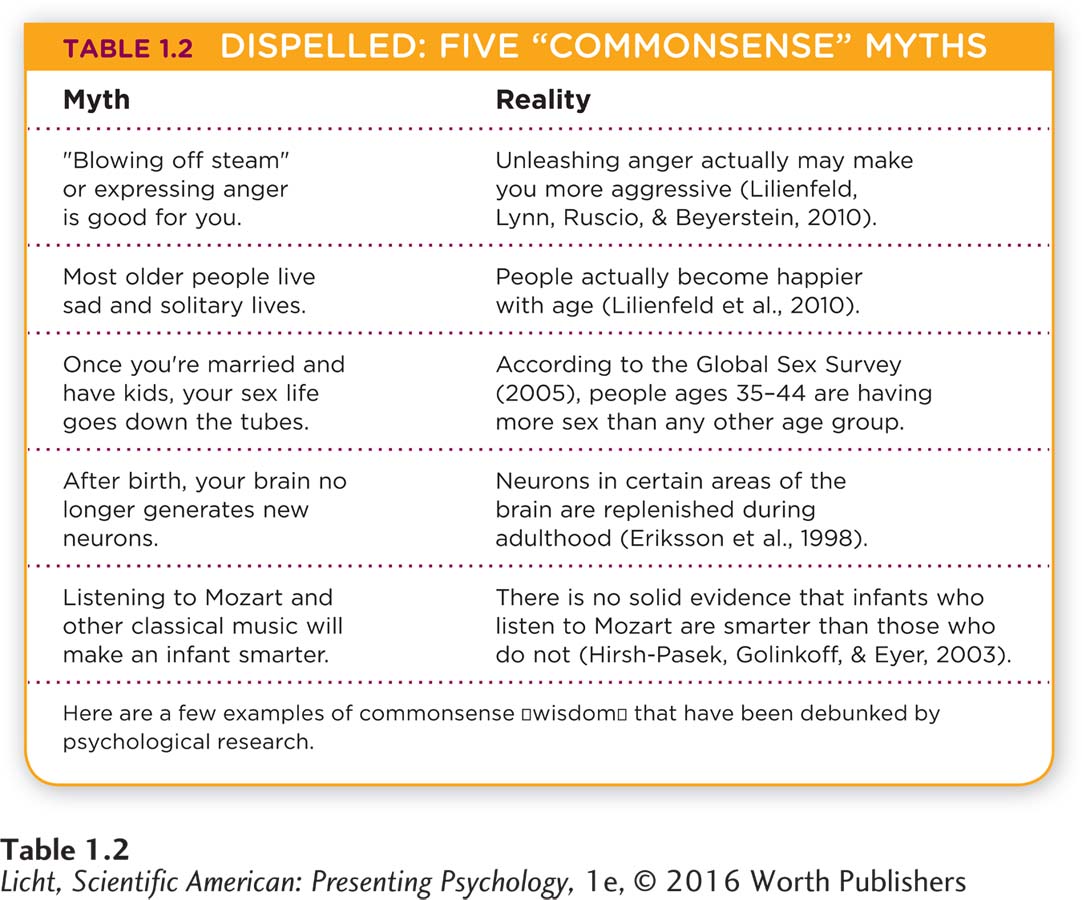
One common misconception is that psychology is simply common sense, meaning it is just a collection of knowledge that any reasonably smart person can pick up through everyday experiences. This sense of the obviousness of psychological findings might be related to the hindsight bias, or the feeling that “I knew it all along.” When a student learns of a finding from psychology, she may believe she knew it all along because the finding seems obvious to her in retrospect, even though she wouldn’t necessarily have predicted the outcome beforehand. We fall prey to the hindsight bias in part because we are constantly seeking to explain events; we come up with plausible explanations after we learn of a finding from psychological research (Lilienfeld, 2012). Or sometimes, students insist they know all there is to know about child development, for example, because they are parents. Just because a young man has experience as a father does not necessarily mean he can observe his family like a scientist. The problem is that common sense and “popular wisdom” are not always correct (Lilienfeld, 2012). Common sense is an important ability that helps us survive and adapt, but it should not take the place of scientific findings. As you learn more about the human mind, you will start to see that it is quite fallible and prone to errors (Chapter 6 and Chapter 7). Table 1.2 identifies some commonsense myths that have been dispelled through research. Have you fallen for any of them?
PSYCHOLOGY IS A SCIENCE Unlike common sense, which is based on casual observations, psychology is a rigorous science based on meticulous and methodical observation, as well as data analysis. Psychology is a science in the same sense that chemistry and biology are sciences.
Science is a systematic approach to gathering knowledge through careful observation and experimentation. It requires sharing results and doing so in a manner that permits others to duplicate and therefore verify work. Using this scientific approach, psychologists have determined that many popular beliefs, such as people only use 10% of their brains, are not true. There is a great deal of this type of “psychomythology,” which is “the collective body of misinformation about human nature” (Lilienfeld et al., 2010, p. 43). Reading this textbook, you might discover that some of your most cherished nuggets of commonsense “wisdom” do not stand up to scientific scrutiny.
The Goals of Psychology
LO 2 Summarize the goals of the discipline of psychology.
What exactly do those who study behavior and mental processes hope to accomplish? The answer to this question varies according to subfield, but there are four main goals: to describe, explain, predict, and control behavior. These goals lay the foundation for the scientific approach used in psychology. Let’s take a closer look at each goal.

A Chinese pilot in training boards a deep-
DESCRIBE Goal 1 is simply to describe or report what is observed. Imagine a psychologist who wants to describe the aftereffects of being trapped in a mine for a prolonged period. What kind of study would she conduct? To start, she would need access to a group of people who have survived this type of ordeal, such as the 33 Chilean miners. Following the men’s rescue, she might request permission to perform some assessments to evaluate their moods, social adjustment, and physical health. She might even monitor the miners over time, conducting more assessments at a later date. Eventually, she would present her observations in a scientific article published in a respected journal, and use her findings to help plan future research.
EXPLAIN Goal 2 is to organize and make sense of what researchers have observed. If the psychologist noticed an interesting pattern in her assessments of the miners, she might develop an explanation for this finding. Let’s say the miners’ health after confinement seemed to be poor compared to their prior status; then the psychologist might look for factors that could influence immunological health. Searching the scientific literature for clues, she might come across studies of people with experiences in similar situations, for example, sailors living and working for long periods in submarines. If she determined that health-
PREDICT Goal 3 is to predict behaviors or outcomes on the basis of observed patterns. If the researcher determined that the miners’ reduced immunological status resulted from sleep deprivation caused by confinement, then she could predict that prolonged confinement in another setting (such as a submarine) might lead to the same outcome: sleep deprivation, and therefore decreased immunity.
CONTROL Goal 4 is to use research findings to shape, modify, and control behavior. When we say “control behavior,” your mind might conjure up the image of an evil inventor who takes control of someone’s mind and makes him carry out a malicious plot. This is not the kind of control we are talking about. Instead, we are referring to how we can apply the findings of psychological research to change and direct (control) behaviors in a beneficial way. Perhaps the researcher could use her findings to help a mining company hire workers better suited to the confining characteristics of mining. Working in small spaces like mines and submarines is not for everyone.
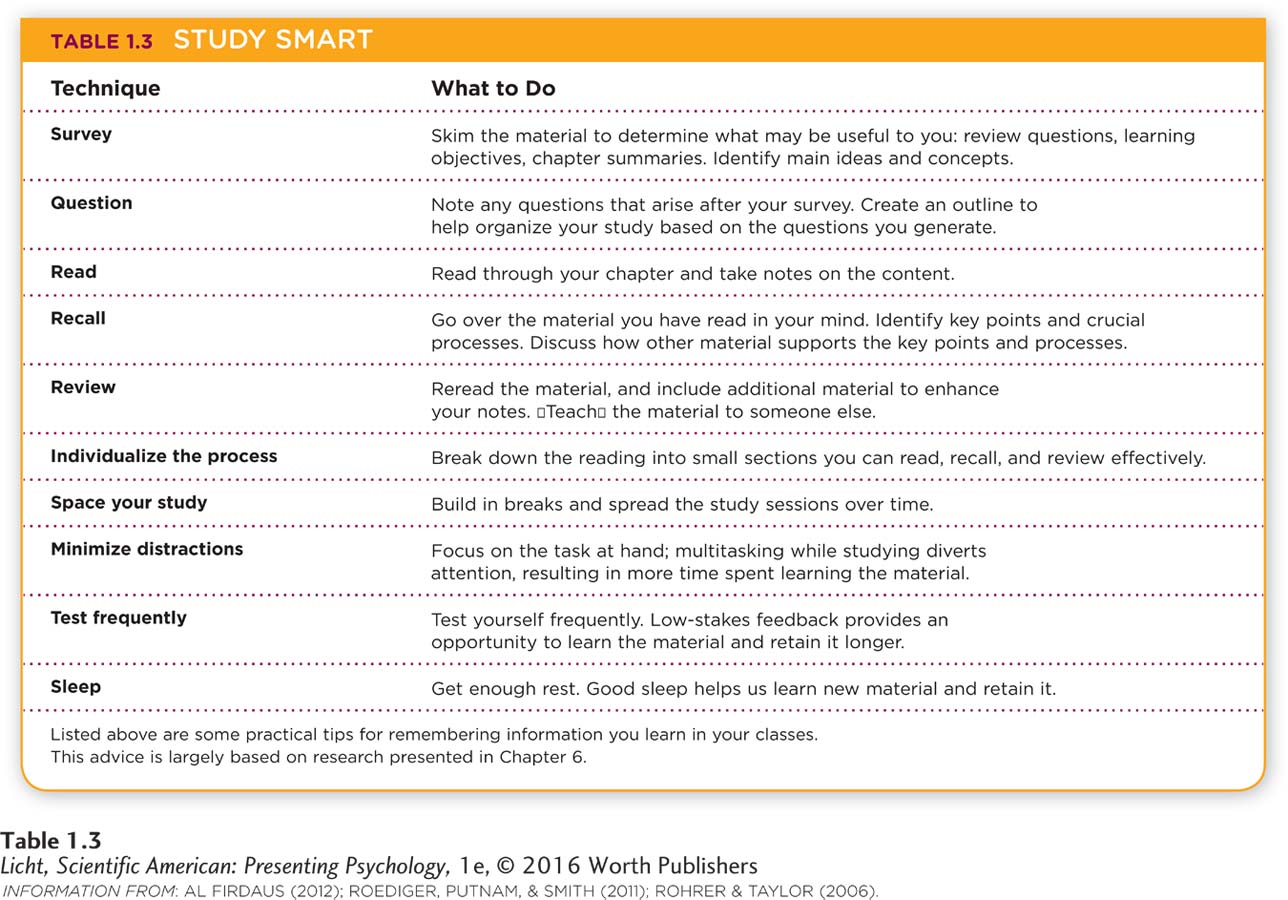
Psychological research has important applications in your life, too. See Table 1.3 for some useful tips on learning and remembering information for your classes. Much of this advice is based on studies presented in Chapter 6.
Apply This
You have now learned the definition, scope, and goals of psychology. You will soon explore the ins and outs of psychological research: how psychologists use a scientific approach, the many types of studies they conduct, and the ethical standards for acceptable conduct that guide them through the process. But we will start with some history, meeting the people whose philosophies, insights, and research findings molded psychology into the vibrant science it is today.
show what you know
Question 1
1. Psychology is the scientific study of ________ and ________.
behavior; mental processes
Question 2
2. A researcher is asked to devise a plan to help improve behavior in the confined space of subway trains. Based on his research findings, he creates some placards that he believes will modify the behavior of subway riders. This attempt to change behaviors falls under which of the main goals of psychology?
describe
explain
predict
control
d. control
Question 3
3. How is common sense different from the findings of psychology? If one of your friends says, “I could have told you that!” when you describe the findings of various studies on confinement, how would you respond?
Common sense is a collection of knowledge that any reasonably smart person can pick up through everyday experiences and casual observations. Findings from psychology, however, are based on meticulous and methodical observations of behaviors and mental processes, as well as data analysis. Many people respond to psychological findings with hindsight bias, or the feeling as if they knew it all along, when in reality they wouldn’t have predicted the outcome ahead of time.