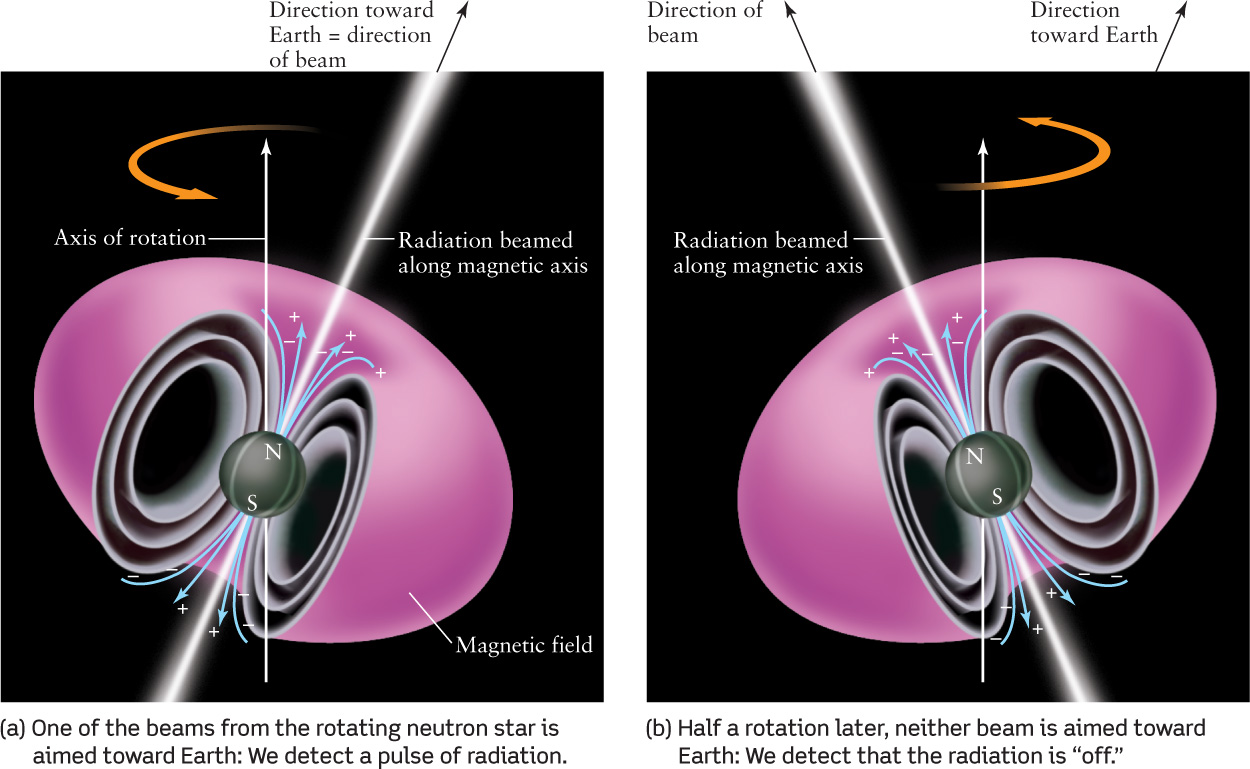
Figure 12-10 A Rotating, Magnetized Neutron Star Charged particles are accelerated near a magnetized neutron star’s magnetic poles (labeled N and S), producing two oppositely directed beams of radiation. If the star’s magnetic axis (a line that connects the north and south magnetic poles) is tilted at an angle from the axis of rotation, as shown here, the beams sweep around the sky as the star rotates. If Earth happens to lie in the path of one of the beams, we detect radiation that appears to pulse (a) on and (b) off.