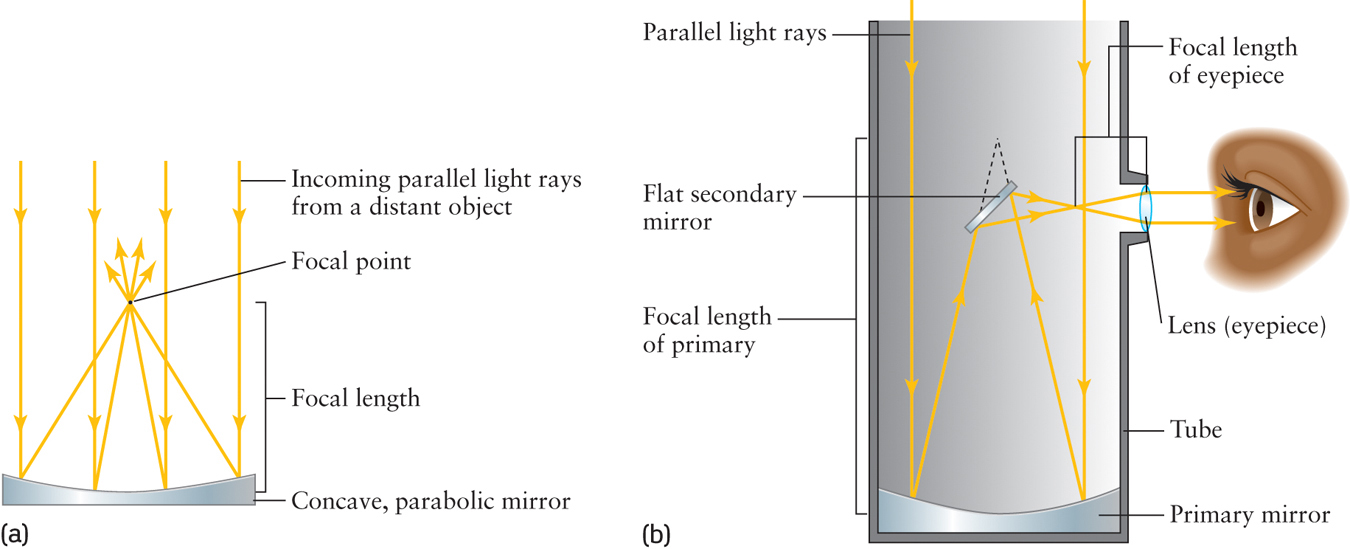
Figure 2-20 Reflecting Telescopes (a) A curved mirror causes parallel light rays from stars to converge and gather together at a focal point. The distance between the mirror and focal point is the focal length. (b) A Newtonian telescope uses a tiny flat mirror, called the secondary mirror, to send light outside the telescope. If small, this secondary mirror does not block too much of the incoming light. The light rays are made parallel again by passing through the magnifying eyepiece so the star can be observed. The dashed line shows where the focal point of this primary mirror would be if the secondary mirror were not in the way.