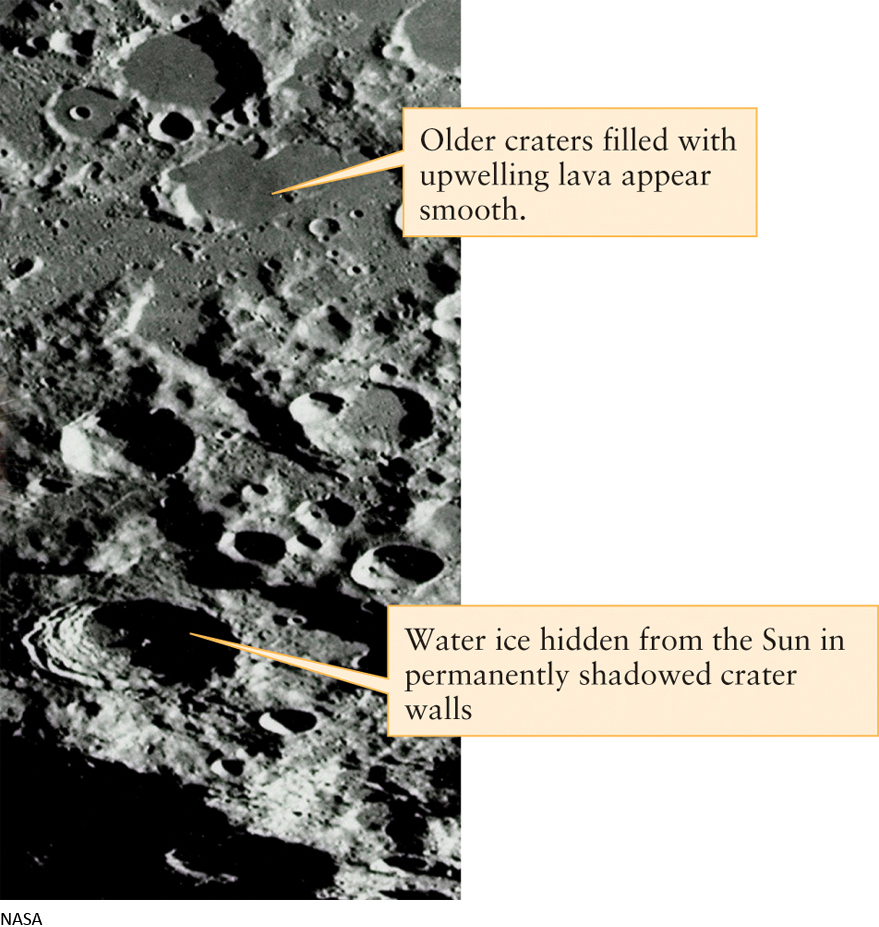
Figure 6-5 RIVUXG Craters and Shadows The complexity of the Moon’s surface near its south pole shows light-colored, rugged highlands with ancient craters and smooth younger surfaces covered with maria. The maria formed after the surrounding light-colored terrain, so they have not been exposed to meteoritic bombardment for as long and hence have fewer craters. Some of these shadowed crater walls rarely receive any sunlight and can serve as protected storage places for frozen water ice.