Introduction
_activity_type_title: Question Suites
_sequenced_sections: true
_restore_last_viewed_section: true
_section_sequence_message: You must read each slide, and complete any questions on the slide, in sequence.
Author: Mark Hens & Melissa Michael
Core Concepts:
4.1 Proteins are linear polymers of amino acids that form three-dimensional structures with specific functions.
4.2 Translation is the process in which the sequence of bases in messenger RNA is used to specify the order of successive amino acids in a newly synthesized protein.
4.3 Proteins evolve by combining functional units and through mutation and selection.
Learning Objectives:
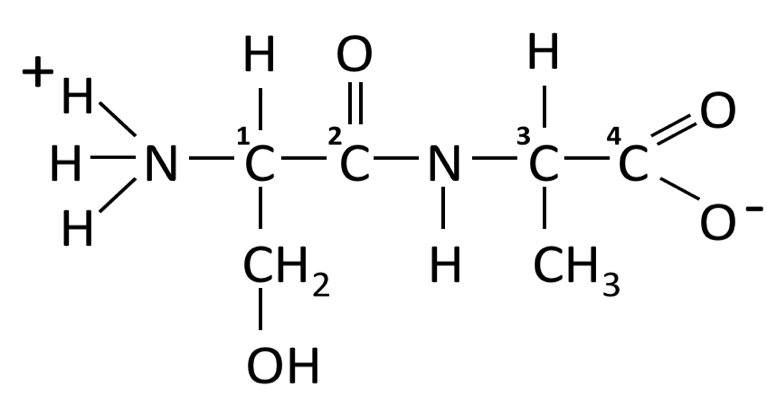
- Draw one of the twenty amino acids and label the amino group, the carboxyl group, the side chain (R group), and the asymmetric carbon.
- Name the four major groups of amino acids based on the properties of their side chains.
- Describe the importance of peptide bonds, hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, disulfide bridges, and noncovalent interactions to proteins.
- Explain why the order of amino acids determines how a protein folds.
- Explain the relationship between protein folding and protein function.
- Describe the relationship between codons of mRNA, anticodons of tRNA, and amino acids, which, in turn, determines its function.
- Describe the process by which ribosomes synthesize polypeptides.
- (CHECK ON THIS ONE. NOW IN CHAPTER 5?) Explain why protein sorting is important to the cell, and three ways in which it is accomplished.
- Name and describe two ways that proteins can acquire new functions in the course of evolution.
Click the Next button to start this activity
1.4 Activity Completed!
Activity results are being submitted...
REFERENCES:
[Center for Disease Control] CDC Grand Rounds: Childhood Obesity in the United States. URL: http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/mm6002a2.htm?s_cid=mm6002a2_w Retrieved 3/31/11
Collins, A. & Peebles, R. (2011). Pediatric obesity: A pediatrician’s viewpoint. In Debasis Bagchi (Editor) Global Perspectives on Childhood Obesity: Current Status, Consequences and Prevention. Pages 257-264.