StatTutor Lesson - Significance Tests for Comparing Proportions
Question 1
Question 1.
If Ho: p1 = p2, what is the hypothesized value of p1 - p2?
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
Question 2
Question 2.
Why do we use as our estimates of both p1 and p2?
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
Question 3
Question 3.
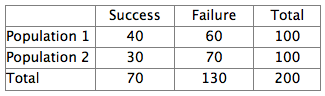
For the data in this two way table, what is the value of , the marginal proportion of success?
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
Question 4
Question 4.
In addition to appropriately collected data, what condition is necessary for using the following formula to find P-value using the standard Normal table?
z =
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
Question 5
Question 5.
What is the appropriate alternative hypothesis for testing whether aspirin reduces the risk of a heart attack? Use p1 = the heart attack rate for doctors taking aspirin and p2 = the heart attack rate for doctors taking a placebo.
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
Question 6
Question 6.
For these data, what is the value of ?
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
Question 7
Question 7.
Why is data collection appropriate for this two-sample proportion procedure?
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
Question 8
Question 8.
For these data, what is the heart attack rate for all doctors in the study?
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
Question 9
Question 9.
Knowing that 99.7% of all z-scores are between -3 and +3, what is the P-value for z = -5.14?
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
Question 10
Question 10.
With P-value = 0.000 and = 0.05, should we reject H0?
| A. |
| B. |
Question 11
Question 11.
Can we conclude that taking aspiring causes a reduction in the heart attack rate?
| A. |
| B. |