30 ESL Troublespots: Common Sentence Problems
ESL TROUBLESPOTS
30
Common Sentence Problems
As you edit and proofread your writing, watch out for the following problems involving word order, relative pronouns, and negatives.
30a Place sentence elements in the correct order
Place words and phrases that indicate time or place at the beginning or at the end of a clause. Do not place them between the verb and its direct object (DO).
INCORRECT |
 |
CORRECT |
 |
Place the indirect object (IO) after the verb and before the direct object (DO).

Exception: When a prepositional phrase takes the place of an indirect object, the phrase should follow the direct object.

Some verbs (such as describe, explain, illustrate, mention, open, and say) cannot be followed by an indirect object.
INCORRECT |
Lu described us the figurine. |
CORRECT |
Lu described the figurine to us. |
30b Do not omit a relative pronoun when it is the subject of a relative clause or the object of a verb or preposition within a relative clause
A relative clause is a dependent clause that begins with a relative pronoun (such as that, which, who, whom, or whose) and modifies a noun or pronoun. Sometimes a relative clause begins with a preposition followed by a relative pronoun (the reason for which I am writing).
INCORRECT |
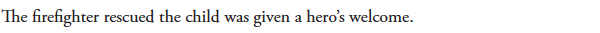 |
REVISED |
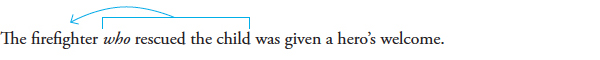 |
INCORRECT |
 |
REVISED |
 |
Exception: The relative pronoun and the verb be are often omitted in relative clauses when the clause is restrictive (essential to the meaning of the word or phrase it modifies); they should usually be included in a nonrestrictive clause (not essential to the meaning of the word or phrase it modifies). For more on nonrestrictive word groups, see 12e.
RESTRICTIVE |
Michael grabbed the newspapers [that were] on the table. |
That were is optional because the clause is restrictive; it tells which newspapers are meant. |
|
NONRESTRICTIVE |
Michael tripped over the stack of day-old newspapers, which were ready to be recycled. |
The clause supplies additional but nonessential information about the newspapers. It is nonrestrictive, so which were should be included. |
Use the relative pronoun whose to show possession with a relative clause.
INCORRECT |
The committee sat at a table that its surface was scratched. |
REVISED |
The committee sat at a table whose surface was scratched. |
Use relative pronouns, not personal pronouns, to introduce relative clauses.
INCORRECT |
Computer terminals, they are scarce at certain times of the day, are an obsession for many students. |
REVISED |
Computer terminals, which are scarce at certain times of the day, are an obsession for many students. |
30c Make a sentence negative by adding not or a negative adverb such as never or seldom
Place not after the first helping verb.

In questions, the helping verb should be followed by not or the contraction for not (-n’t). Place the helping verb and not before the subject and the main verb.
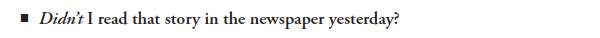
Place negative adverbs before the main verb. In a sentence with a helping verb, place the negative adverb after the first helping verb.

If a negative adverb is used at the beginning of a clause, the helping verb do is needed.
