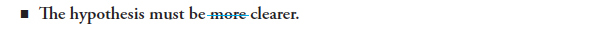9 Adjectives and Adverbs
9
Adjectives and Adverbs
Adjectives and adverbs are powerful. Used appropriately, they can add precision and force to your writing, as the following excerpt demonstrates.
Seated cross-legged on a brocade pillow, wrapped in burgundy robes, was a short, rotund man with a shiny pate. He looked very old and very tired. Chhongba bowed reverently, spoke briefly to him in the Sherpa tongue, and indicated for us to come forward.
Jon Krakauer, Into Thin Air
Adjectives modify nouns or pronouns and indicate which one, what kind, or how many. Adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, other adverbs, clauses, or entire sentences and indicate how, when, where, how often, or to what extent. (See also 1d and 1e.)
The two most common errors involving adjectives and adverbs occur when writers use (1) an adjective instead of an adverb (or vice versa) and (2) the wrong form of an adjective or adverb in a comparison. Use the following guidelines to identify and correct these and other common errors in your writing.
9a Use adverbs, not adjectives, to modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs
Although in conversation you may often use adjectives in place of adverbs, you should be careful in your writing to use adverbs to modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs.
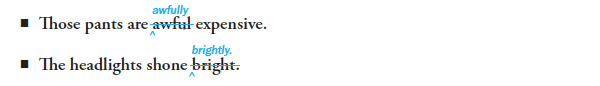
9b Use adjectives, not adverbs, after linking verbs
Linking verbs, often forms of be and other verbs such as feel, look, make, and seem, express a state of being. A linking verb takes a subject complement—a word group that completes or renames the subject of the sentence. Verbs such as feel and look can also be action verbs. When they function as action verbs in a sentence, they may be modified by an adverb.
If you are not sure whether a word should be an adjective or adverb, determine how it is used in the sentence. If the word modifies a noun, it should be an adjective.
ADJECTIVE |
|
Slow modifies the word waiter, a noun. In this sentence, looked is a linking verb. |
|
ADVERB |
|
In this sentence, looked is expressing an action and is not a linking verb; slowly modifies looked. |
9c Use good and bad as adjectives; use well and badly as adverbs

The adjective good modifies the noun student.

The adverb well modifies the verb perform.

The adverb badly modifies the verb did.
When you are describing someone’s health, well can also function as an adjective.
9d Be careful not to use adjectives such as real and sure to modify adverbs or other adjectives
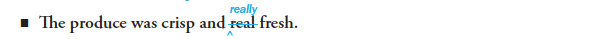
The adverb really modifies the adjective fresh.
9e Avoid double negatives
A sentence with two negative words or phrases contains a double negative, which conveys a positive meaning. Do not use two negatives in a sentence unless you want to express a positive meaning (for example, not uncommon means “common”).

POSITIVE MEANING INTENDED
Athletic sportswear is not uncommon as casual attire.
9f Use the comparative form of adjectives and adverbs to compare two things; use the superlative form to compare three or more things
Adjectives and adverbs can be used to compare two or more persons, objects, actions, or ideas. The comparative form of an adjective or adverb compares two items. The superlative form compares three or more items. Use the list below to check the comparative and superlative forms of most regular adjectives and adverbs in your sentences.
| Comparatives | Superlatives | |
| One-syllable adjectives and adverbs | Add -er: colder, faster | Add -est: coldest, fastest |
| Two-syllable adjectives | Add -er: greasier | Add -est: greasiest |
| Adjectives with three or more syllables or adverbs ending in –ly | Add more in front of the word: more beautiful, more quickly | Add most in front of the word: most beautiful, most quickly |
Irregular adjectives and adverbs form their comparative and superlative forms in unpredictable ways, as the following list illustrates.
| Comparative | Superlative | |
| Adjectives | ||
| good | better | best |
| bad | worse | worst |
| little | less | least |
| Adverbs | ||
| well | better | best |
| badly | worse | worst |
| Words That Function as Adjectives and Adverbs | ||
| many | more | most |
| some | more | most |
| much | more | most |
Do not use comparative or superlative forms with absolute concepts, such as unique and perfect. Something cannot be more or less unique, for example; it is either unique or not unique.
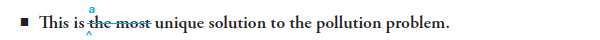
9g Check your comparisons to be sure they are complete when using comparative and superlative forms
An incomplete comparison can leave your reader confused about what is being compared.
INCOMPLETE |
The Internet works more efficiently. |
REVISED |
For sending correspondence and documents, the Internet works more efficiently than the postal service. |
INCOMPLETE |
The catcher sustained the most crippling knee injury. |
REVISED |
The catcher sustained the most crippling knee injury of his career. |
9h Do not use more or most with the -er or -est form of an adjective or adverb