12.5 Assess Your UnderstandingPrinted Page 856
Concepts and Vocabulary
True or False If a differentiable function z is defined implicitly by the equation F(x,y,z)=0, then ∂z∂x=Fx(x,y,z)Fz(x,y,z), provided Fz(x,y,z)≠0.
False
True or False If x=x(t) and y=y(t) are differentiable functions of t and if z=f(x,y) is a differentiable function of x and y, then dzdt=∂z∂x+∂z∂y.
False
Skill Building
Answers to Problems 3–40 are given in final form and in mixed form.
In Problems 3–14, find dzdt using Chain Rule I.
z=x2+y2, x=sint, y=cos(2t)
dzdt=(2x)(cost)−4ysin(2t)=2sintcost−4sin(2t)cos(2t)
z=x2−y2, x=sin(2t), y=cost
z=x2+y2, x=tet, y=te−t
dzdt=(2x)(tet+et)+(2y)(−te−t+e−t)=2t2e2t+2te2t−2t2e−2t+2te−2t
z=x2−y2, x=te−t, y=t2e−t
z=eusinv, u=√t, v=πt
dzdt=eusinv2√t+(eucosv)(π)=e√tsin(πt)2√t+πe√tcos(πt)
z=eu/v, u=√t, v=t3+1
z=eu/v, u=tet, v=et2
dzdt=eu/v(tet+et)v−ueu/v(2tet2)v2=tet+tet−t2+et+tet−t2et2−2t2et+t2+tet−t2e2t2
z=ln(uv), u=t5, v=√t+1
z=ex2+y2, x=sin(2t), y=cost
dzdt=(2xex2+y2)(2cos(2t))−(2yex2+y2)(sint)=4sin(2t)cos(2t)esin2(2t)+cos2t−2sintcostesin2(2t)+cos2t
z=ex2−y2, x=sin(2t), y=cos(2t)
z=xyx2+y2, x=sint, y=cost
dzdt=(y(−x2+y2)(x2+y2)2)(cost)+(x(x2−y2)(x2+y2)2)(−sint)=cos2t−sin2t
z=ylnx+xy+tany, x=tt+1, y=t3−t
In Problems 15–22, find dpdt using an extension of Chain Rule I.
p=x2+y2−z2, x=tet, y=te−t, z=e2t
dpdt=(2x)(tet+et)+(2y)(−te−t+e−t)−(2z)(2e2t)=2t2e2t+2te2t−2t2e−2t+2te−2t−4e4t
p=x2−y2−z2, x=te−t, y=t2e−t, z=e−t
p=exsinycosz, x=√t, y=πt, z=t2
dpdt=(exsinycosz)(12√t)+(excosycosz)(π)−(exsinysinz)(12)=e√tsin(πt)cos(t/2)2√t+πe√tcos(πt)cos(t/2)−e√tsin(πt)sin(t/2)2
p=ln(xyz), x=t5, y=√t+1, z=t2
p=wln(uv), u=tet, v=et2, w=e2t
dpdt=(wu)(tet+et)−(wv)(2tet2)+ln(uv)(2e2t)=e2t+e2tt+2e2tlnt−2t2e2t
p=weu/v, u=√t, v=t3+1, w=et
p=u2vw, u=sint, v=cost, w=et
dpdt=(2uvw)(cost)−(u2w)(sint)+(u2v)(et)=2etsintcos2t−etsin3t+etsin2tcost
p=√uvw, u=et, v=tet, w=t2e2t
In Problems 23–34, find ∂z∂u and ∂z∂v using Chain Rule II.
z=x2+y2, x=uev, y=veu
∂z∂u=(2x)(ev)+(2y)(veu)=2ue2v+2v2e2u; ∂z∂v=(2x)(uev)+(2y)(eu)=2u2e2v+2ve2u
z=x2−y2, x=ulnv, y=vlnu
z=exsiny, x=u2v, y=ln(uv)
∂z∂u=(exsiny)(2uv)+(excosy)(1u)=2uveu2vsin(ln(uv))+eu2vcos(ln(uv))u;∂z∂v=(exsiny)(u2)+(excosy)(1v)=u2eu2vsin(ln(uv))+eu2vcos(ln(uv))v
z=1ylnx, x=√uv, y=vu
z=ln(x2+y2), x=v2u, y=uv2
∂z∂u=(2xx2+y2)(−v2u2)+(2yx2+y2)(1v2)=−2v8u(u4+v8)+2u3u4+v8∂z∂v=(2xx2+y2)(2vu)+(2yx2+y2)(−2uv3)=4v7u4+v8−4u4v(u4+v8)
z=xsiny−ysinx, x=u2v, y=uv2
z=x2+y2, x=sin(u−v), y=cos(u+v)
∂z∂u=(2x)(cos(u−v))−(2y)(sin(u+v))=2sin(u−v)cos(u−v)−2sin(u+v)cos(u+v)∂z∂v=−(2x)(cos(u−v))−(2y)(sin(u+v))=−2sin(u−v)cos(u−v)−2sin(u+v)cos(u+v)
z=ex+y, x=tan−1(uv), y=ln(u+v)
z=ser, r=u2+v2, s=vu
∂z∂u=(er)(−vu2)+(ser)(2u)=−veu2+v2u2+2veu2+v2∂z∂v=(er)(1u)+(ser)(2v)=eu2+v2u+2v2eu2+v2u
z=√s2+r2, s=ln(uv), r=√uv
857
z=xy2w3, x=2u+v, y=5u−3v, w=2u+3v
∂z∂u=2y2w3+10xyw3+6xy2w2=2(5u−3v)2(2u+3v)3+10(2u+v)(5u−3v)(2u+3v)3+6(2u+v)(5u−3v)2(2u+3v)2∂z∂v=y2w3−6xyw3+9xy2w2=(5u−3v)2(2u+3v)3−6(2u+v)(5u−3v)(2u+3v)3+9(2u+v)(5u−3v)2(2u+3v)2
z=x2−y2+w, x=eu+v, y=uv, w=vu
In Problems 35–40, find each partial derivative.
Find ∂f∂u, ∂f∂v, ∂f∂w if f(x,y,z)=x2+y2+z2, x=uv, y=eu+2v+3w, z=2v+3w.
∂f∂u=(2x)(v)+(2y)(eu+2v+3w)=2uv2+2e2u+4v+6w∂f∂v=(2x)(u)+(2y)(2eu+2v+3w)+(2z)(2)=2u2v+4e2u+4v+6w+4(2v+3w)∂f∂w=(2y)(3eu+2v+3w)+(2z)(3)=6e2u+4v+6w+6(2v+3w)
Find ∂f∂u, ∂f∂v, ∂f∂w if f(x,y,z)=x−y2+z2, x=√u+v, y=(u+w)lnv, z=2−v+3w.
Find ∂f∂u, ∂f∂v, ∂f∂w if f(x,y,z)=xcosy−zcosx+x2yz, x=uvw, y=u2+v2+w2, z=w.
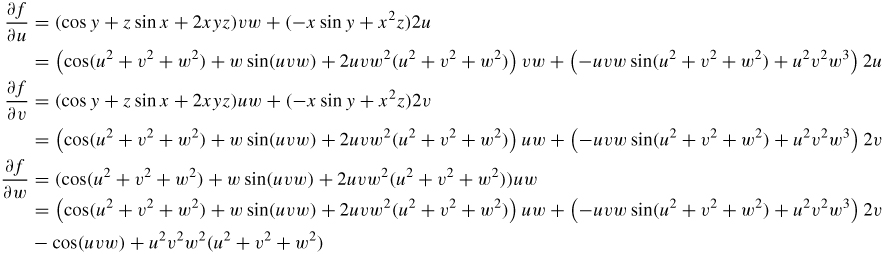
Find ∂f∂u, ∂f∂v, ∂f∂w if f(x,y,z)=x2+y2, x=sin(u−v), y=cos(u+v), z=uw2.
Find ∂f∂u, ∂f∂v, ∂f∂w, ∂f∂t if f(x,y,z)=x+2y2−z2, x=ut, y=eu+2v+3w+4t, z=u+12v+4t.
∂f∂u=t+4yeu+2v+3w+4t−2z=t+4e2u+4v+6w+8t−2(u+v/2+4t)∂f∂v=8yeu+2v+3w+4t−z=8e2u+4v+6w+8t−u−v/2−4t∂f∂w=12yeu+2v+3w+4t=12e2u+4v+6w+8t∂f∂t=u+16yeu+2v+3w+4t−8z=u+16e2u+4v+6w+8t−8(u+v/2+4t)
Find ∂f∂u, ∂f∂v, ∂f∂w, ∂f∂t if f(x,y,z)=x2+y2+z, x=sin(u+t), y=cos(v−t), z=uw2.
In Problems 41–46, y is a function of x. Find dydx.
F(x,y)=x2y−y2x+xy−5=0
dydx=−(2xy−y2+y)x2−2xy+x
F(x,y)=x3y2−xy+x2y−10=0
F(x,y)=xsiny+ysinx−2=0
dydx=−(siny+ycosx)xcosy+sinx
F(x,y)=xey+yex−xy=0
F(x,y)=x1/3+y1/3−1=0
dydx=−y2/3x2/3
F(x,y)=x2/3+y2/3−1=0
In Problems 47–52, z is a function of x and y. Find ∂z∂x and ∂z∂y.
F(x,y,z)=xz+3yz2+x2y3−5z=0
∂z∂x=−(z+2xy3)x+6yz−5; ∂z∂y=−(3z2+3x2y2)x+6yz−5
F(x,y,z)=x2z+y2z+x3y−10z=0
F(x,y,z)=sinz+ycosz+xyz−10=0
∂z∂x=−yzcosz−ysinz+xy; ∂z∂y=−(cosz+xz)cosz−ysinz+xy
F(x,y,z)=xsiny−cosz+x2z=0
F(x,y,z)=xeyz+yexz+xyz=0
∂z∂x=−(eyz+yzexz+yz)xyeyz+xyexz+xy; ∂z∂y=−(xzeyz+exz+xz)xyeyz+xyexz+xy
F(x,y,z)=eyzlnx+yexz−yz=0
In Problems 53 and 54, find ∂w∂x, ∂w∂y, and ∂w∂z.
w=(2x+3y)4z
∂w∂x=8z(2x+3y)4z−1; ∂w∂y=12z(2x+3y)4z−1; ∂w∂z=4(2x+3y)4zln(2x+3y)
w=(2x)3y+4z
Applications and Extensions
Ideal Gas Law One mole of a gas obeys the Ideal Gas Law PV=20T, where P is pressure, V is volume, and T is temperature. If the temperature T of the gas is increasing at the rate of 5 ∘C/s and if, when the temperature is 80 ∘C, the pressure P is 10N/m2 and is decreasing at the rate of 2Nm2⋅s, find the rate of change of the volume V with respect to time.
13.2 m3/ s
Melting Ice A block of ice of dimensions l, w, and h is melting. When l=3m, w=2m, h=1m, these variables are changing so that dldt=−1m/h, dwdt=−1m/h, and dhdt=−0.5m/h.
- (a) What is the rate of change in the surface area of the block of ice?
- (b) What is the rate of change in the volume of the block of ice?
Wave Equation The one-dimensional wave equation ∂2f∂x2=1v2∂2f∂t2 describes a wave traveling with speed v along the x -axis. The function f represents the displacement x from the equilibrium of the wave at time t.
- (a) Show that z=f(x,t)=sin(x+vt) satisfies the wave equation.
- (b) Show that z=f(x,t)=ex−vt satisfies the wave equation.
- (c) Show that z=f(x,t)=sinx+sin(vt) does not satisfy the wave equation.
- (d) Show that any twice-differentiable function of the form f(x+vt) is a solution of the wave equation.
- (a) See Student Solutions Manual.
- (b) See Student Solutions Manual.
- (c) See Student Solutions Manual.
- (d) See Student Solutions Manual.
Economics A toy manufacturer’s production function satisfies a Cobb–Douglas model, Q(L,M)=400L0.3M0.7, where Q is the output in thousands of units, L is the labor in thousands of hours, and M is the machine hours (in thousands). Suppose the labor hours are decreasing at a rate of 4000h/yr and the machine hours are increasing at a rate of 2000h/yr. Find the rate of change of production when
- (a) L=19 and M=21
- (b) L=21 and M=20
Related Rates Let y=f(a,b), where a=h(s,t) and b=k(s,t). Suppose when s=1 and t=3, we know that ∂h∂s=4∂k∂s=−3∂h∂t=1∂k∂t=−5
Also, suppose h(1,3)=6k(1,3)=2fa(6,2)=7fb(6,2)=2
What are ∂y∂s and ∂y∂t at the point (1,3)?
∂y∂s(1,3)=22; ∂y∂t(1,3)=−3
Related Rates Let z=f(x,y), where x=g(s,t) and y=h(s,t) . Suppose when s=2 and t=−1, we know that ∂x∂s=5∂y∂s=2∂x∂t=−3∂y∂t=−2
Also, suppose g(2,−1)=3h(2,−1)=4fx(3,4)=12fy(3,4)=7
What are ∂z∂s and ∂z∂t at the point (2,−1)?
If z=f(x,y), where x=g(u,v) and y=h(u,v), find expressions for ∂2z∂u2, ∂2z∂u ∂v, and ∂2z∂v2.
∂2z∂u2=∂z∂x∂2x∂u2+∂z∂y∂2y∂u2+∂2z∂x2(∂x∂u)2+2∂2z∂x∂y(∂x∂u)(∂y∂u)+∂2z∂y2(∂y∂u)2∂2z∂u∂v=∂z∂x∂2x∂u∂v+∂z∂y∂2y∂u∂v+∂2z∂x2∂x∂u∂x∂v+∂2z∂y2∂y∂u∂y∂v+∂2z∂x∂y(∂y∂u∂x∂v+∂y∂v∂x∂u)∂2z∂v2=∂z∂x∂2x∂v2+∂z∂y∂2y∂v2+∂2z∂x2(∂x∂v)2+2∂2z∂x∂y(∂x∂v)(∂y∂v)+∂2z∂y2(∂y∂v)2
858
If z=f(x,y) and x=rcosθ, y=rsinθ, show that (∂z∂r)2+1r2(∂z∂θ)2=(∂z∂x)2+(∂z∂y)2
If z=f(x,y), where x=ucosθ−vsinθ and y=usinθ+vcosθ, with θ a constant, show that (∂f∂u)2+(∂f∂v)2=(∂f∂x)2+(∂f∂y)2.
See Student Solutions Manual.
If z=f(u−v,v−u), show that ∂z∂u+∂z∂v=0.
(Hint: Let x=u−v and y=v−u.)
If z=vf(u2−v2), show that v∂z∂u+u∂z∂v=uzv.
See Student Solutions Manual.
If w=f(u) and u=√x2+y2+z2, show that (∂w∂x)2+(∂w∂y)2+(∂w∂z)2=(dwdu)2.
If z=f(xy), show that x∂z∂x+y∂z∂y=0.
See Student Solutions Manual.
Show that if z=f(uv,vw), then u∂z∂u+v∂z∂v+w∂z∂w=0.
Suppose we denote the expression ∂2∂x2+∂2∂y2 by Δ . If z=f(x,y), where x=rcosθ and y=rsinθ, show that Δf=∂2f∂r2+1r(∂f∂r)+1r2(∂2f∂θ2).
See Student Solutions Manual.
Prove that if F(x,y,z)=0 is differentiable, then ∂z∂x⋅∂x∂y⋅∂y∂z=−1.
Challenge Problems
- (a) Suppose that F(x,y) has continuous second-order partial derivatives and F(x,y)=0 defines y as a function of x implicitly. Show that d2ydx2=−F2yFxx−2FxFyFxy+F2xFyyF3yFy≠0
- (b) Use the result from (a) to find d2ydx2 for x3+3xy−y3=6.
- (a) See Student Solutions Manual.
- (b) d2ydx2=−6x(3x−3y2)2−6(3x2+3y)(3x−3y2)−6y(3x2+3y)2(3x−3y2)3
f(t,x)=∫x/(2√λt)0e−u2du. Show that ft=λfxx.
