14.9 Assess Your UnderstandingPrinted Page 967
967
Concepts and Vocabulary
For a change of variables from x and y to u and v given by x=g1(u,v) and y=g2(u,v), the Jacobian is the determinant _____.
|∂x∂u∂x∂v∂y∂u∂y∂v|
True or False When introducing a Jacobian into an integral because of a change of variables, the absolute value of the Jacobian is used.
True
Skill Building
In Problems 3–10, find the Jacobian ∂(x,y)∂(u,v) for each change of variables from (x,y) to (u,v).
x=u+v,y=u−v
∂(x,y)∂(u,v)=−2
x=u+5,y=v−7
x=4u−v,y=3u+12v
∂(x,y)∂(u,v)=5
x=u2−v2,y=u2+v2
x=uv,y=u+v
∂(x,y)∂(u,v)=u+vv2
x=eucosv,y=eusinv
x=veu,y=ue−v
∂(x,y)∂(u,v)=−eu−v(1+uv)
x=ucosv,y=vsinu
In Problems 11–16, find the Jacobian ∂(x,y,z)∂(u,v,w) for each change of variables from (x,y,z) to (u,v,w).
x=u+v+w,y=u+v−w,z=u−v−w
∂(x,y,z)∂(u,v,w)=−4
x=2u+v+w,y=u+v−w,z=u−v
x=u+v,y=v−w,z=u−w
∂(x,y,z)∂(u,v,w)=−2
x=u+v+w,y=u+v,z=w
x=u,y=v2,z=w3
∂(x,y,z)∂(u,v,w)=6vw2
x=3(u+v),y=u−w,z=u2−w2
Area Find the area of the region R enclosed by y=4√1−x29 and y=0, using the change of variables u=x3 and v=y2.
A=6π square units
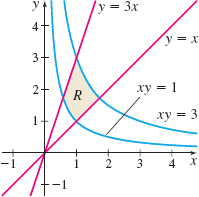
Area Find the area of the region R enclosed by xy=1, xy=3, y=x, and y=3x using the change of variables u=x and v=xy. See the figure.
In Problems 19–22:
- (a) Graph the region R in the xy-plane.
- (b) Graph the region R# in the uv-plane.
- (c) Find the Jacobian ∂(x,y)∂(u,v).
- (d) Change the variables and find the integral.
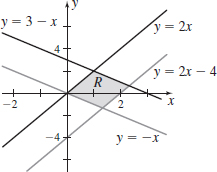
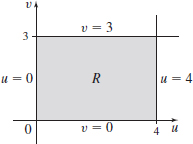
∬, where R is the region enclosed by 2x-y=0, 2x-y=4, x+y=0, and x+y=3. Use the change of variables u=2x-y and v=x+y.
- (a)
- (b)
- (c) \dfrac{\partial (x,y)}{\partial (u,v)} = \dfrac13
- (d) \dfrac{14}3
\iint\limits_{\kern-3ptR}(x^{2}+y^{2})\,{\it dA}, where R is the region enclosed by 2x-y=1, 2x-y=3, x+y=1, and x+y=2. Use the change of variables u=2x-y and v=x+y.
\iint\limits_{\kern-3ptR}xy\,{\it dA}, where R is the triangular region whose vertices are (-1,1), (1,1), and (0,0). Use the change of variables u=x+y and v=x-y.
- (a)
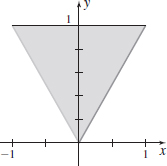
- (b)
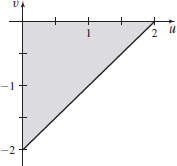
- (c) \dfrac{\partial (x,y)}{\partial (u,v)} = -\dfrac12
- (d) 0
\iint\limits_{\kern-3ptR}(x+ y) sin(x-y) {\it dA}, where R is the triangular region whose vertices are (-1,1), (1,1), and (0,0); use the change of variables u=x+y and v=x-y.
In Problems 23–26, find each integral.
\iint\limits_{\kern-3ptR}(3x-2y)\,{\it dA}, where R is the region enclosed by the ellipse 9x^{2}+16y^{2}=144. Change the variables using u=\dfrac{x}{4} and v=\dfrac{y}{3}.
0
\iint\limits_{\kern-3ptR}(x^{2}-y), {\it dA}, where R is the region enclosed by the ellipse 9x^{2}+16y^{2}=144. Change the variables using u=\dfrac{x}{4} and v=\dfrac{y}{3}.
\iiint\limits_{\kern-3ptE}(x+1)\,{\it dV}, where E is the solid enclosed by the ellipsoid \dfrac{x^{2}}{4}+\dfrac{y^{2}}{4}+ \dfrac{z^{2}}{9}=1. Change the variables using u=\dfrac{x}{2}, v=\dfrac{y }{2}, and w=\dfrac{z}{3}.
16 \pi
\iiint\limits_{\kern-3ptE}(x+2y)\,{\it dV}, where E is the region enclosed by the ellipse \dfrac{x^{2}}{9}+\dfrac{y^{2}}{4}+z^{2}=1. Change the variables using u= \dfrac{x}{3}, v=\dfrac{y}{2}, and w=z.
Applications and Extensions
In Problems 27–30, for each integral:
- (a) Graph the region R.
- (b) Choose a change of variables from (x,y) to (u,v). Graph the new region in the uv-plane.
- (c) Write each integral using the new variables.
- (d) Find each integral.
\iint\limits_{\kern-3ptR}x^{2}y\,{\it dA}, where R is the region enclosed by the lines 2x-3y=0, 2x-3y=1, x+2y=0, and x+2y=3
- (a)
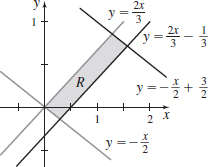
- (b)
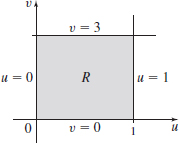
- (c) \int_0^1 \int_0^3 \left(\dfrac37 v+ \dfrac27 u\right)^2 \left(\dfrac27 v - \dfrac17 u \right)\dfrac17 \, dv \, du
- (d) \dfrac{423}{2401}
\iint\limits_{\kern-3ptR}x\,{\it dA}, where R is the region enclosed by the ellipse \dfrac{x^{2}}{9}+\dfrac{y^{2}}{16}=1
\iint\limits_{\kern-3ptR}x\cos (xy) \,{\it dA}, where R is the region enclosed by xy=1, xy=3, x=1, and x=3
- (a)
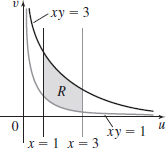
- (b)
- (c) \int_1^3 \int_1^3 \cos(v) \, dv \, du
- (d) 2 (\sin 3 - \sin 1)
\iint\limits_{\kern-3ptR}ye^{xy}\,{\it dA}, where R is the region enclosed by xy=1, xy=3, x=1, and x=3
Area Use a change of variables to find the area of the region R enclosed by the lines y=3x, y-3x=2, 2y+x=0, and y=-\dfrac{1}{2} x+5.
A = \dfrac{20}7 square units
968
Area Use a change of variables to find the area of the region R enclosed by the lines x+y=1, x+y=-3, y=2x, and y=2x+4.
Volume Use a change of variables to find the volume V of the solid E enclosed by the planes x+2y=0, x+2y=3, y-z=0, y-z=2, z=0, and z=6.
V = 36 cubic units
Volume Use a change of variables to find the volume V of the solid E enclosed by the planes x-y=0, x-y=3, z-2x=0, z-2x=4, z=1, and z=5.
Volume Find the volume of the solid E enclosed by the paraboloid z=9- x^{2}-9y^{2} and the plane z=1, given the change of variables x=3u\cos v, y=u\sin v, and z=w. See the figure.
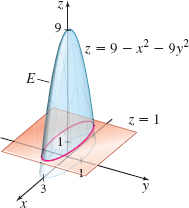
V = \dfrac{21\pi}2 cubic units
Volume Find the volume of the solid E enclosed by the ellipsoid \dfrac{x^{2}}{4}+\dfrac{y^{2}}{9}+z^{2}=1 above the xy-plane, given the change of variables u=\dfrac{x}{2}, v=\dfrac{y}{3}, and w=z.
Show that in changing from rectangular coordinates (x, y, z) to spherical coordinates (\rho, \theta, \phi), the triple integral of f over E becomes \begin{eqnarray*} &&\iiint\limits_{\kern-18ptE}f(x, y, z)\,{\it dV}\\[4pt] &&\quad=\iiint\limits_{\kern-18ptE^{\#}}f(\rho \sin \phi \cos \theta , \rho \sin \phi \sin \theta , \rho \cos \phi )\rho ^{2}\sin \phi \,d\rho \,d\theta \,d\phi \end{eqnarray*}
See the Student Solutions Manual.
Challenge Problems
A region R is enclosed by the graphs of xy=2, xy=5, y= \sqrt{x}, and y=3\sqrt{x}.
- (a) Graph the region R.
- (b) Use a change of variables that transforms R into a rectangular region R^{\#}.
- (c) Find the area of R.
