14.3 Assess Your UnderstandingPrinted Page 927
Concepts and Vocabulary
Convert the function f(x,y)=√4x2+4y2 to polar coordinates.
f(r,θ)=2r
In polar coordinates, the differential dA of area is dA = _________.
rdrdθ
True or False Geometrically, if f(x,y)≥0 and if f is continuous over a closed, bounded region R, then the double integral ∬ represents the volume of the solid under the surface z=f(x,y) and above the region R in the xy-plane.
False
True or False \iint\limits_{\kern-3ptR}r\,dr\,d\theta equals the area A of the closed, bounded region R.
True
Skill Building
In Problems 5–8, assume that z=f(x,y) is a continuous function over the region R. Express the double integral \displaystyle\iint\limits_{\displaystyle\kern-3ptR}f(x,y) \, {\it dA} over R as an iterated integral using polar coordinates.
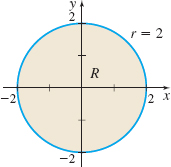
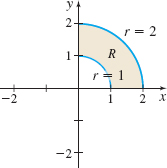
\int_0^{2\pi} \int_0^2 f(r \cos \theta, r \sin \theta) r \, dr\, d\theta
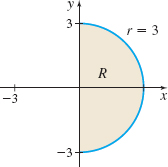
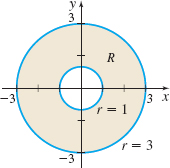
\int_0^{2\pi} \int_1^3 f(r \cos \theta, r \sin \theta) r \, dr\, d\theta
In Problems 9–14, express each double integral over the region R as an iterated integral using polar coordinates; do not integrate.
\iint\limits_{\kern-3ptR} ( x+y) \, {\it dA}, R is enclosed by x^{2}+y^{2}=9, x\geq 0, and y\geq 0.
\int_0^{\pi/2} \int_0^3 r^2 (\cos \theta + \sin \theta) \, dr \, d\theta
\iint\limits_{\kern-3ptR}(x^{2}+y^{2}) \, {\it dA}, R is enclosed by y=\sqrt{1-x^{2}} and the lines y=x and y=-x.
\iint\limits_{\kern-3ptR}x\, {\it dA}, R is enclosed by x=\sqrt{4-y^{2}}, the positive x-axis, and the line y=x.
\int_0^{\pi/4} \int_0^2 r^2 \cos \theta \, dr \, d\theta
\iint\limits_{\kern-3ptR}y\, {\it dA}, R is enclosed by y=\sqrt{16-x^{2}}, in the first quadrant.
\iint\limits_{\kern-3ptR}( x+y^{2}) \, {\it dA}, R is enclosed by x^{2}+y^{2}=1 and x^{2}+y^{2}=4.
\int_0^{2\pi} \int_1^2 (r^2 \cos \theta + r^3 \sin^2\theta) \, dr \, d\theta
\iint\limits_{\kern-3ptR}\sqrt{x^{2}+y^{2}}\, {\it dA}, R is enclosed by x^{2}+y^{2}=\dfrac{1}{4} and x^{2}+y^{2}=5.
928
In Problems 15–22, find each iterated integral.
\displaystyle\int_{0}^{\pi /4}\int_{0}^{4\sin \theta }r\cos \theta \,{\it dr}\,d\theta
\dfrac{2\sqrt{2}}3
\displaystyle\int_{0}^{5\pi /3}\int_{0}^{2\cos \theta }r\sin \theta \,{\it dr}\,d\theta
\displaystyle\int_{0}^{\pi /2}\int_{0}^{\pi /3}r\,\,d\theta\, {\it dr}
\dfrac{\pi^3}{24}
\displaystyle\int_{0}^{\pi /3}\int_{0}^{\sin \theta }r\,{\it dr}\,d\theta
\displaystyle\int_{0}^{\pi /4}\int_{0}^{\cos \theta }r\,{\it dr}\,d\theta
\dfrac{\pi+2}{16}
\displaystyle\int_{0}^{4}\int_{-\pi /4}^{\pi /4}r\cos \theta \,d\theta\, {\it dr}
\displaystyle\int_{0}^{2}\int_{-\pi /3}^{5\pi /3}r\sin \theta \,d\theta\, {\it dr}
0
\displaystyle\int_{0}^{\pi}\int_{0}^{\pi /4}r\,\,d\theta\, {\it dr}
In Problems 23–28, graph the region R, then find each double integral.
\displaystyle\iint\limits_{\kern-3ptR}3\sin \theta \,{\it dA} ,\quad0\leq r\leq 2, 0\leq \theta \leq \dfrac{\pi }{2}
6
\displaystyle\iint\limits_{\kern-3ptR}4\cos \theta \,{\it dA} ,\quad 0\leq r\leq 3, 0\leq \theta \leq \dfrac{\pi }{2}
\displaystyle\iint\limits_{\kern-3ptR}2r \sin \theta \,{\it dA} ,\quad 0\leq r\leq 1, 0\leq \theta \leq \dfrac{\pi }{2}
\dfrac23
\displaystyle\iint\limits_{\kern-3ptR}3r \cos \theta \,{\it dA} ,\quad 0\leq r\leq 2, 0\leq \theta \leq \dfrac{\pi }{4}
\displaystyle\iint\limits_{\kern-3ptR}3r^{2}\sin \theta \,{\it dA} ,\quad 0\leq r\leq 2, -\dfrac{\pi }{2}\leq \theta \leq \dfrac{\pi }{2}
0
\displaystyle\iint\limits_{\kern-3ptR}2r^{2}\cos \theta \,{\it dA} ,\quad 0\leq r\leq 4, - \dfrac{\pi }{2}\leq \theta \leq \dfrac{\pi }{2}
In Problems 29–42, find each double integral by changing to polar coordinates.
\displaystyle\int_{0}^{1}\int_{0}^{\sqrt{1-x^{2}}}\,{\it dy}\,{\it dx}
\dfrac{\pi}4
\displaystyle\int_{0}^{3}\int_{0}^{y}\sqrt{x^{2}+y^{2}}\,{\it dx}\,{\it dy}
\displaystyle\int_{-2}^{2}\int_{0}^{\sqrt{4-y^{2}}}(x^{2}+y^{2})\,{\it dx}\,{\it dy}
4\pi
\displaystyle\int_{0}^{2}\int_{0}^{\sqrt{4-x^{2}}}\sqrt{4-x^{2}-y^{2}}\, {\it dy}\,{\it dx}
\displaystyle\int_{0}^{1}\int_{0}^{\sqrt{1-x^{2}}}\cos (x^{2}+y^{2})\,{\it dy}\,{\it dx}
\dfrac{\pi}{4} \sin (1)
\displaystyle\int_{0}^{1}\int_{0}^{\sqrt{1-y^{2}}}e^{\sqrt{x^{2}+y^{2}}}\,{\it dx}\,{\it dy}
\iint\limits_{\kern-3ptR}e^{-(x^{2}+y^{2})}\,d\!A, R is the region in the first quadrant enclosed by the circles x^{2}+y^{2}=1 and x^{2}+y^{2}=4.
\dfrac{\pi(e^3-1)}{4e^4}
\displaystyle\iint\limits_{\kern-3ptR}\dfrac{y}{\sqrt{x^{2}+y^{2}}}\,d\!A, R is the region in the first quadrant inside the circle x^{2}+y^{2}=a^{2}.
\iint\limits_{\kern-3ptR}x\,d\!A, R is the region enclosed by the circle x^{2}+y^{2}=x.
\dfrac{\pi}8
\iint\limits_{\kern-3ptR}y^{2}\,d\!A, R is the region enclosed by the circle x^{2}+y^{2}=2y.
\iint\limits_{\kern-3ptR}\sqrt{x^{2}+y^{2}}\,d\!A, R is the region enclosed by r=3+\cos \theta .
21 \pi
\iint\limits_{\kern-3ptR}(x^{2}+y^{2})\,d\!A, R is the region enclosed by r=2(1+\sin \theta ).
\displaystyle\int_{-2}^{2}\int_{-\sqrt{4-y^{2}}}^{\sqrt{4-y^{2}} }(x^{2}+y^{2})^2\,{\it dx}\,{\it dy}
\dfrac{64\pi}3
\displaystyle\int_{0}^{2}\int_{\sqrt{2x-x^{2}}}^{\sqrt{4x-x^{2}}}\,{\it dy}\,{\it dx}+\int_{2}^{4}\int_{0}^{\sqrt{ 4x-x^{2}}}\,{\it dy}\,{\it dx}
Applications and Extensions
In Problems 43–52, use double integrals in polar coordinates.
Volume Find the volume of the solid enclosed by the ellipsoid x^{2}+y^{2}+4z^{2}=4.
V = \dfrac{16\pi}3 cubic units
Volume Find the volume of the solid enclosed by the paraboloid x^{2}+y^{2}=az, a > 0, the xy-plane, and the cylinder x^{2}+y^{2}=a^{2}.
Volume Find the volume of the portion of the ball (a solid sphere) of radius 4 and center at the origin that lies above the region enclosed by the circle r=4\sin \theta , as shown in the figure below.
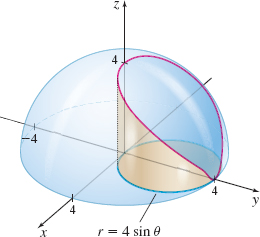
V = \dfrac{64\pi}3 - \dfrac{256}9 cubic units
Volume Find the volume of the solid cut from the ellipsoid x^{2}+y^{2}+4z^{2}=4 by the cylinder x^{2}+y^{2}=1.
Area Find the area enclosed by one loop of r^{2}=9\sin (2\theta) .
A = \dfrac92 square units
Area Find the area of the region that lies inside the circle r=4\cos \theta but outside the circle r=\cos \theta .
Area Find the area of the region in the first quadrant that lies inside the limaçon r=3+2\sin \theta but outside the circle r=4\sin \theta . See the figure.
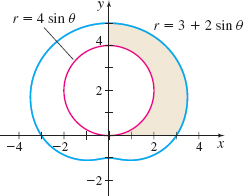
A = 6 + \dfrac{3\pi}4 square units
Area Find the area of the region that lies inside the circle r=1 but outside the cardioid r=1+\cos \theta .
Area Find the area of the region that lies inside the cardioid r=1+\cos \theta but outside the circle r=\dfrac{1}{2}.
A = \dfrac{5\pi}6 + \dfrac{7 \sqrt{3}}8 square units
929
Area Find the area of the region that lies inside the limaçon r=3-\cos \theta but outside the circle r=5\cos \theta .
In Problems 53 and 54, replace each iterated integral in polar coordinates with an iterated integral in rectangular coordinates. Do not find the integrals.
\displaystyle\int_{0}^{1/\sqrt{2}}\int_{0}^{\sin ^{-1}r}r\,d\theta \,dr
\int_0^{1/2} \int_{\sqrt{y-y^2}}^{\sqrt{1/2-y^2}} dx \, dy
\displaystyle\int_{0}^{1}\int_{\cos ^{-1}r}^{\pi /2}r^{2}\sin \theta \,d\theta \,dr
A tank in the shape of a hemisphere of radius 1 m is lying on its flat side. If the tank is filled with liquid to a depth of a meters, what is the volume of the liquid? (Hint: Position the hemisphere as shown in the figure.)
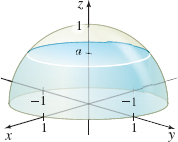
V = \pi a \!\left( 1 - \dfrac{a^2}{3} \right) cubic meters
Repeat Problem 55 if the tank is configured as in the figure, with its flat side at ground level and its rounded base under the ground.
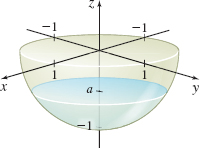
 Area
Area- (a) Use technology to graph r=\theta , 0\leq \theta \leq 2\pi .
- (b) Find the area of the region enclosed by the graph of r=\theta and the positive x-axis.
- (a)
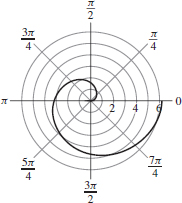
- (b) A = \dfrac{4\pi^3}{3} square units
Volume Find the volume of the solid cut from the sphere x^{2}+y^{2}+z^{2}=a^{2} by the cylinder x^{2}+y^{2}=ay, a\gt 0.
Area Find the area enclosed by one leaf of the rose r=\sin (3\theta) .
A = \dfrac{\pi}{12} square units.
Challenge Problems
- (a) Express f(x,y) =\dfrac{{1}}{x^{2} \sqrt{x^{2}+y^{2}}}\,, using polar coordinates.
- (b) Find \displaystyle\int_{1}^{2}{\int_{0}^{1}} \dfrac{1}{x^{2}\sqrt{x^{2}+y^{2}}}\, {\it dy}\,{\it dx}.
To find \int_{-\infty }^{\infty }e^{-x^{2}}\,{\it dx}, let I_{a}=\int_{0}^{a}e^{-x^{2}}\,{\it dx}.
- (a) Show that: I_{a}^{2}=\int_{0}^{a}e^{-x^{2}}\,{\it dx}\int_{0}^{a}e^{-y^{2}} {\it dy}=\int_{0}^{a} \int_{0}^{a}e^{-(x^{2}+y^{2})}\,{\it dx}\,{\it dy}
- (b) Let J_{a}=\iint\limits_{\kern-3ptR}e^{-(x^{2}+y^{2})}\,{\it dA}, where R is the quarter circle 0\leq \theta \leq \dfrac{\pi }{2}, 0\leq r\leq a . Show that \big\vert I_{a}^{2}-J_{a}\big\vert \leq \dfrac{(4-\pi )a^{2}}{4}e^{-a^{2}}
- (c) Find J_{a}.
- (d) Show that \lim_{a\rightarrow \infty }J_{a}=\dfrac{\pi }{4}\qquad \hbox{and}\qquad \lim_{a\rightarrow \infty }\,\big\vert \,I_{a}^{2}-J_{a}\big\vert =0
- (e) Show that \int_{-\infty }^{\infty }e^{-x^{2}}\,{\it dx}=\sqrt{\pi }. (This integral is of special importance in statistics.)
- (a) See the Student Solutions Manual.
- (b) See the Student Solutions Manual.
- (c) J_a = \dfrac{\pi}4 \big(1 - e^{-a^2} \big)
- (d) See the Student Solutions Manual.
- (e) See the Student Solutions Manual.