REVIEW EXERCISES
194
In Problems 1 and 2, use a definition of the derivative to find the rate of change of f at the indicated numbers.
Question
\(f(x) =\sqrt{x}\) at (a) \(c=1\), (b) \(c=4\), (c) \(c\) any positive real number
Question
\(f(x) =\dfrac{2}{x-1}\) at (a) \(c=0\), (b) \(c=2\), (c) \(c\) any real number, \(c\neq 1\)
In Problems 3–8, use a definition of the derivative to find the derivative of each function at the given number.
Question
\(F(x) =2x+5\) at 2
Question
\(f(x) =4x^{2}+1\) at -1
Question
\(f(x) =3x^{2}+5x\) at 0
Question
\(f(x) =\dfrac{3}{x}\) at 1
Question
\(f(x) =\sqrt{4x+1}\) at 0
Question
\(f(x) =\dfrac{x+1}{2x-3}\) at 1
In Problems 9–12, use a definition of the derivative to find the derivative of each function. Graph \(f\) and \(f^\prime\) on the same set of axes.
Question
\(f(x) =x-6\)
Question
\(f(x) =7-3x^{2}\)
Question
\(f(x) =\dfrac{1}{2x^{3}}\)
Question
\(f(x) =\pi\)
In Problems 13 and 14, determine whether the function f has a derivative at c. If it does, find the derivative. If it does not, explain why. Graph each function.
Question
\(f(x) =\vert x^{3}-1\vert\) at \(c=1\)
Question
\(f(x) =\left\{ \begin{array}{l@{\quad}l} 4-3x^{2} & \hbox{if }x ≤ -1 \\[3pt] -x^{3} & \hbox{if }x>-1 \end{array} \right.\) at \(c=-1\)
In Problems 15 and 16, determine if the graphs represent a function \(f\) and its derivative \(f^\prime\). If they do, indicate which is the graph of \(f\) and which is the graph of \(f^\prime\).
Question
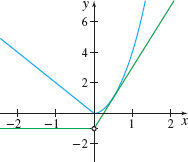
Question
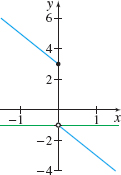
Question
Use the information in the graph of \(y=f(x)\) to sketch the graph of \(y=f^{\prime}(x)\).
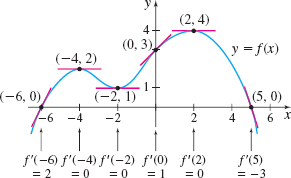
Question
Match the graph of \(y=f(x)\) with the graph of its derivative.
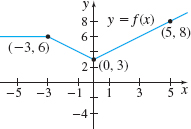
In Problems 19–60, find the derivative of each function. Where a or b appears, it is a constant.
Question
\(f(x)=x^{5}\)
Question
\(f(x)=ax^{3}\)
Question
\(f(x)=\dfrac{x^{4}}{4}\)
Question
\(f(x)=-6x^{2}\)
Question
\(f(x)=2x^{2}-3x\)
Question
\(f(x)=3x^{3}+\dfrac{2}{3}x^{2}-5x+7\)
Question
\(F(x)=7( x^{2}-4)\)
Question
\(F(x)=\dfrac{5( x+6) }{7}\)
Question
\(f(x)=5( x^{2}-3x) ( x-6)\)
Question
\(f(x)=( 2x^{3}+x) ( x^{2}-5)\)
Question
\(f(x)=\dfrac{6x^{4}-9x^{2}}{3x^{3}}\)
Question
\(f(x)=\dfrac{2x+2}{5x-3}\)
Question
\({f(x})=\dfrac{7x}{x-5}\)
Question
\({f(x)=2x}^{-12}\)
Question
\({f(x)=2x}^{2}-5x^{-2}\)
Question
\({f(x)}=2+\dfrac{3}{x}+\dfrac{4}{x^{2}}\)
Question
\(f(x)=\dfrac{a}{x}-\dfrac{b}{x^{3}}\)
Question
\(f(x)=( x^{3}-1) ^{2}\)
Question
\(f(x)=\dfrac{3}{( x^{2}-3x) ^{2}}\)
Question
\(f(x)=\dfrac{x^{2}}{x+1}\)
Question
\(s( t) =\dfrac{t^{3}}{t-2}\)
Question
\(f(x)=3x^{-2}+2x^{-1}+1\)
Question
\(F(z)=\dfrac{1}{z^{2}+1}\)
Question
\(f(v)=\dfrac{v-1}{v^{2}+1}\)
Question
\(g(z)=\dfrac{1}{1-z+z^{2}}\)
Question
\(f(x)=3e^{x}+x^{2}\)
Question
\(s(t)=1-e^{t}\)
Question
\(f(x)=ae^{x}( 2x^{2}+7x)\)
Question
\(f(x)=\dfrac{1+x}{e^{x}}\)
Question
\(f(x)=(2xe^{x}) ^{2}\)
Question
\(f(x)=x\sin x\)
Question
\(s(t)=\cos^{2}t\)
Question
\(G(u)=\tan u+\sec u\)
Question
\(g(v)=\sin v-\dfrac{1}{3}\cos v\)
Question
\(f(x)=e^{x}\sin x\)
Question
\(f(x)=e^{x}\csc x\)
Question
\(f(x)=2\sin x\cos x\)
Question
\(f(x)=(e^{x}+b) \cos x\)
Question
\(f(x)=\dfrac{\sin x}{\csc x}\)
Question
\(f(x)=\dfrac{1-\cot x}{1+\cot x}\)
Question
\(f(\theta)=\dfrac{\cos \theta}{2e^{\theta}}\)
Question
\(f(\theta )=4\theta \cot \theta \tan \theta\)
In Problems 61–66, find the first derivative and the second derivative of each function.
Question
\(f(x)=( 5x+3) ^{2}\)
Question
\(f(x)=xe^{x}\)
Question
\(g(u)=\dfrac{u}{2u+1}\)
Question
\(F(x)=e^{x}( \sin x+2\cos x)\)
Question
\(f(u)=\dfrac{\cos u}{e^{u}}\)
Question
\(F(x)=\dfrac{\sin x}{x}\)
In Problems 67–70, for each function:
- Find an equation of the tangent line to the graph of the function at the indicated point.
 Graph the function and the tangent line on the same screen.
Graph the function and the tangent line on the same screen.
Question
\(f( x) =2x^{2}-3x+7\) at \(( -1,12)\)
Question
\(y=\dfrac{x^{2}+1}{2x-1}\) at \(\left( 2,\dfrac{5}{3}\right)\)
Question
\(f( x) =x^{2}-e^{x}\) at \(( 0,-1)\)
Question
\(s( t) =1+2\sin t\) at \(( \pi ,1) \)
Question
Rectilinear Motion The distance \(s\) (in meters) that an object in rectilinear motion moves in time \(t\) (in seconds) is \[ s=f(t)= t^{2}-6t. \]
- Find the velocity at \(t=0\), at \(t=5\), and at any time \(t\).
- Find the acceleration at any time \(t\).
Question
Rectilinear Motion As an object in rectilinear motion moves, its distance \(s\) from the origin at time \(t\) is \(s( t) =t-t^{2}\), where \(s\) is in centimeters and \(t\) is in seconds.
- Find the velocity of the object at \(t=1\) second and \(t=3\) seconds.
- What is its acceleration at \(t=1\) and \(t=3\)?
Question
Business The price \(p\) in dollars per pound when \(x\) pounds of a commodity are demanded is modeled by the function \(p( x) =\dfrac{10,000}{5x+100}-5\), when between 0 and 90 pounds are demanded (purchased).
- Find the rate of change of price with respect to demand.
- What is the revenue function \(R\)? (Recall, revenue \(R\) equals price times amount purchased.)
- What is the marginal revenue \(R\prime\) at \(x=10\) and at \(x=40\) pounds?
Question
If \(f(x)=\dfrac{x-1}{x+1}\) for all \(x\neq -1\), find \(f^\prime (1)\).
Question
If \(f(x)=2+|x-3|\) for all \(x\), determine whether the derivative \(f^\prime\) exists at \(x=3\).
Question
Rectilinear Motion An object in rectilinear motion moves according to the equation \(s=2t^{3}-15t^{2}+24t+3\), where \(t\) is measured in minutes and \(s\) in meters. Determine:
- When is the object is at rest?
- Find the object’s acceleration when \(t=3\).
Question
Find the value of the limit below and specify the function \(f\) for which this is the derivative. \[ \lim\limits_{\Delta x\rightarrow 0}\frac{[4-2(x+\Delta x)]^{2}-(4-2x)^{2}}{\Delta x} \]