4.5 Assess Your UnderstandingPrinted Page 305
Concepts and Vocabulary
True or False f(x)g(x) is an indeterminate form at c of the type 00 if lim does not exist.
False
True or False If \dfrac{f(x) }{g(x) } is an indeterminate form at c of the type \dfrac{0}{0}, then L’Hôpital’s Rule states that \lim\limits_{x\rightarrow c}\dfrac{f(x) }{g(x) }= \lim\limits_{x\rightarrow c}\left[ \dfrac{d}{dx}\left( \dfrac{f(x) }{g(x) }\right) \right].
False
True or False \dfrac{1}{x} is an indeterminate form at 0.
False
True or False x\ln x is not an indeterminate form at 0^{+} because \lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 0^{+}}x=0 and \lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 0^{+}}\ln x=-\infty, and 0\cdot -\infty =0.
False
In your own words, explain why \infty -\infty is an indeterminate form, but \infty +\infty is not an indeterminate form.
Answers will vary.
In your own words, explain why 0\cdot \infty \neq 0.
Answers will vary.
Skill Building
In Problems 7–26:
- (a) Determine whether each expression is an indeterminate form at c.
- (b) If it is, identify the type. If it is not an indeterminate form, say why.
\dfrac{1-e^{x}}{x}, c=0
(a) Yes (b)\dfrac{0}{0}
\dfrac{1-e^{x}}{x-1}, c=0
\dfrac{e^{x}}{x}, c=0
(a) No (b) Answers will vary.
\dfrac{e^{x}}{x}, c=\infty
\dfrac{\ln x}{x^{2}}, c=\infty
(a) Yes (b) \dfrac{\infty}{\infty}
\dfrac{\ln ( x+1) }{e^{x}-1}, c=0
\dfrac{\sec x}{x},c=0
(a) No (b) Answers will vary.
\dfrac{x}{\sec x-1}, c=0
\dfrac{\sin x( 1-\cos x) }{x^{2}}, c=0
(a) Yes (b) \dfrac{0}{0}
\dfrac{\sin x-1}{\cos x}, c=\dfrac{\pi }{2}
\dfrac{\tan x-1}{\sin ( 4x-\pi ) }, c=\dfrac{\pi }{4}
(a) Yes (b) \dfrac{0}{0}
\dfrac{e^{x}-e^{-x}}{1-\cos x},c=0
306
x^{2}e^{-x}, c=\infty
(a) Yes (b) 0\,{\cdot}\,\infty
x\;\cot\;x, c=0
\csc \dfrac{x}{2}-\cot \dfrac{x}{2}, c=0
(a) Yes (b) \infty-\infty
\dfrac{x}{x-1}+\dfrac{1}{\ln x}, c=1
\left( \dfrac{1}{x^{2}}\right) ^{\sin x}, c=0
(a) Yes (b) \infty^0
(e^{x}+x)^{1/x}, c=0
( x^{2}-1) ^{x}, c=0
(a) No (b) Answers will vary.
( \sin x) ^{x}, c=0
In Problems 27–42, identify each quotient as an indeterminate form of the type \dfrac{0}{0} or \dfrac{\infty }{\infty }. Then find the limit.
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 2}\dfrac{x^{2}+x-6}{x^{2}-3x+2}
\dfrac{0}{0}, 5
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 1}\dfrac{2x^{3}+5x^{2}-4x-3}{x^{3}+x^{2}-10x+8}
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 1}\dfrac{\ln x}{x^{2}-1}
\dfrac{0}{0}, \dfrac{1}{2}
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac{\ln (1-x)}{e^{x}-1}
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac{e^{x}-e^{-x}}{\sin x}
\dfrac{0}{0}, 2
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac{\tan (2x) }{\ln (1+x)}
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 1}\dfrac{\sin ( \pi x) }{x-1}
\dfrac{0}{0}, -\pi
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \pi }\dfrac{1+\cos x}{\sin (2x) }
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty }\dfrac{x^{2}}{e^{x}}
\dfrac{\infty}{\infty}, 0
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty } \dfrac{e^{x}}{x^{4}}
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty }\dfrac{\ln x}{e^{x}}
\dfrac{\infty}{\infty}, 0
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty }\dfrac{x+\ln x}{x\ln x}
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac{e^{x}-1-\!\sin x}{1-\cos x}
\dfrac{0}{0}, 1
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac{e^{x}-e^{-x}-2\;\sin\;x}{3x^{3}}
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac{\sin x-x}{x^{3}}
\dfrac{0}{0}, -\dfrac{1}{6}
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac{x^{3}}{\cos x-1}
In Problems 43–58, identify each expression as an indeterminate form of the type 0\cdot \infty , \infty -\infty , 0^{0}, 1^{\infty}, or \infty ^{0}. Then find the limit.
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 0^{+}}(x^{2}\;\ln\;x)
0 \cdot \infty, 0
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty }(xe^{-x})
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty} [x(e^{1/x}-1)]
0 \cdot \infty, 1
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \pi /2} [ (1-\!\sin x)\tan x]
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \pi /2}(\sec x-\tan x)
\infty - \infty, 0
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 0}\left( \cot x-\dfrac{1}{x}\right)
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 1}\left( \dfrac{1}{\ln x}-\dfrac{x}{\ln x}\right)
\infty - \infty, -1
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 0}\left( \dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{1}{e^{x}-1}\right)
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 0^{+}}(2x)^{3x}
0^0, 1
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 0^{+}}x^{x^{2}}
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty }( x+1)^{e^{-x}}
\infty^0, 1
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty }(1+x^{2})^{1/x}
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 0^{+}}(\csc x)^{\sin x}
\infty^0, 1
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty }x^{1/x}
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \pi /2^{-}}(\sin x)^{\tan x}
1^\infty, 1
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 0}(\cos x)^{1/x}
In Problems 59–90, find each limit.
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 0^{+}}\dfrac{\cot x}{\cot (2x) }
2
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \,\infty }\dfrac{\ln (\ln x)}{\ln x}
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 1/2^{-}}\dfrac{\ln (1-2x)}{\tan ( \pi x) }
0
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 1^{-}}\dfrac{\ln (1-x)}{\cot ( \pi x) }
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty }\dfrac{x^{4}+x^{3}}{e^{x}+1}
0
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty }\dfrac{x^{2}+x-1}{e^{x}+ e^{-x}}
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac{xe^{4x}-x}{1-\cos (2x) }
2
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac{x\tan x}{1-\cos x}
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac{\tan ^{-1}x}{x}
1
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac{\tan ^{-1}x}{\sin ^{-1}x}
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac{\cos x-1}{\cos (2x) -1}
\dfrac{1}{4}
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac{\tan x-\!\sin x}{x^{3}}
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 0^{+}}(x^{1/2} \ \ln x)
0
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty } [ (x-1)e^{-x^{2}}]
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \pi /2} [ \tan x \ \ln (\sin x) ]
0
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 0^{+}}[ \sin x \ \ln (\sin x)]
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 0}\ [ \csc x \ \ln (x+1)]
1
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \pi /4}[(1-\tan x) \ \sec (2x) ]
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow a}\left[ (a^{2}-x^{2}) \ \tan \left( \dfrac{\pi x}{2a}\right) \right]
\dfrac{4a^2}{\pi}
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 1^{+}}\,\left[ (1-x)\tan \!\left(\!\dfrac{1}{2}\pi x\!\right)\! \right]
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 1}\left( \dfrac{1}{\ln x}-\dfrac{1}{x-1}\right)
\dfrac{1}{2}
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 1}\left(\! \dfrac{x}{x-1}-\dfrac{1}{\ln x}\! \right)
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \pi /2}\left( x\;\tan\;x-\dfrac{\pi }{2}\sec x\right)
-1
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \pi }(\cot\;x-x\;\csc\;x)
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 1^{-}}(1-x)^{\tan\;( \pi x) }
1
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 0^{+}}x^{\sqrt{\scriptstyle x}}
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 0}\left( \dfrac{\sin\;x}{x}\right) ^{\!\!1/x}
1
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty }\left(\! 1+\dfrac{5}{x}+\dfrac{3}{x^{2}}\!\right) ^{\!\!x}
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow ( \pi /2) ^{-}}( \tan x) ^{\cos x}
1
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 0^{+}}( x^{2}+x) ^{-\ln x}
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 0}( \cosh x) ^{e^{x}}
1
\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 0^{+}}(\sinh x) ^{x}
Applications and Extensions
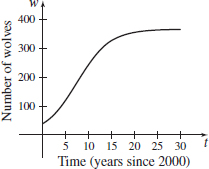
Wolf Population In 2002 there were 65 wolves in Wyoming outside of Yellowstone National Park, and in 2010 there were 247 wolves. Suppose the population w of wolves in the region at time t follows the logistic growth curve w=w(t)=\dfrac{Ke^{rt}}{\dfrac{K}{40}+e^{rt}-1}
where K=366, r=0.283, and t=0 represents the population in the year 2000.
- (a) Find \lim\limits_{t\rightarrow \infty }w(t).
- (b) Interpret the answer found in (a).
- (c)
 Use graphing technology to graph w=w(t).
Use graphing technology to graph w=w(t).
- (a) 366
- (b) Answers will vary. \(
- (c)
Skydiving The downward velocity v of a skydiver with nonlinear air resistance can be modeled by v=v(t) =-A+RA\frac{e^{Bt+C}-1}{e^{Bt+C}+1}
where t is the time in seconds, and A,B,C, and R are positive constants with R>1.
- (a) Find \lim\limits_{t\rightarrow \infty }v(t) .
- (b) Interpret the limit found in (a).
- (c)
 If the velocity v is measured in feet per second, reasonable values of the constants are A=108.6, B=0.554, C=0.804, and R=2.62. Graph the velocity of the skydiver with respect to time.
If the velocity v is measured in feet per second, reasonable values of the constants are A=108.6, B=0.554, C=0.804, and R=2.62. Graph the velocity of the skydiver with respect to time.
307
Electricity The equation governing the amount of current I (in amperes) in a simple RL circuit consisting of a resistance R (in ohms), an inductance L (in henrys), and an electromotive force E (in volts) is \ I=\dfrac{E}{R}( 1-e^{-Rt/L}) .
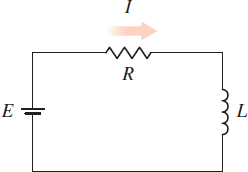
- (a) Find \lim\limits_{t\rightarrow \infty }I(t) and \lim\limits_{R\rightarrow 0^{+}}I(t).
- (b) Interpret these limits.
- (a) \dfrac{E}{R}, \dfrac{Et}{L}
- (b) Answers will vary.
Find \lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac{a^{x}-b^{x}}{x}, where a\neq 1 and b\neq 1 are positive real numbers.
Show that \lim\limits_{x\,\rightarrow \,\infty } \frac{\ln x}{x^{n}}=0, for n \ge 1 an integer.
See Student Solutions Manual.
Show that \lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \,\infty } \frac{x^{n}}{e^{x}}=0 for n \ge 1 an integer.
Show that \lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 0^{+}}(\cos\;x+2\;\sin x)^{\cot\;x}=e^{2}.
See Student Solutions Manual.
Find \lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \,\infty } \dfrac{P(x)}{e^{x}}, where P is a polynomial function.
Find \lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty }\left[ \ln (x+1)-\ln (x-1)\right] .
0
Show that \lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 0^{+}}\dfrac{e^{-1/x^{2}}}{x}=0. Hint: Write \dfrac{e^{-1/x^{2}}}{x}=\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{x}}{e^{1/x^{2}}}.
If n is an integer, show that \lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 0^{+}}\dfrac{e^{-1/x^{2}}}{x^{n}}=0.
See Student Solutions Manual.
Show that \lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty }\sqrt[x]{x}=1.
Show that \lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty }\left( 1+\dfrac{a}{x}\right) ^{\!\!x}=e^{a}, a any real number.
See Student Solutions Manual.
Show that \lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty }\left( \dfrac{x+a}{x-a}\right) ^{\!\!x}= e^{2a}, a\ne 0.
- (a) Show that the function below has a derivative at 0. What is f^{\prime }(0)? f(x)= \left\{ \begin{array}{l{\qquad}l{\quad}rcl} e^{-1/x^{2}} & \hbox{if} & x&\neq& 0 \\ 0 & \hbox{if} & x&=&0 \end{array} \right.
- (b)
 Graph f using a graphing utility.
Graph f using a graphing utility.
- (a) See Student Solutions Manual. f^{\prime}(0) = 0
- (b)
If a,b\neq 0 and c>0 are real numbers, show that \lim\limits_{x\rightarrow c}\dfrac{x^{a}-c^{a}}{x^{b}-c^{b}}=\dfrac{a}{b} c^{a-b}.
Prove L’Hôpital’s rule when \dfrac{f(x)}{g(x) } is an indeterminate form at -\infty of the type \dfrac{0}{0}.
See Student Solutions Manual.
Challenge Problems
Explain why L’Hôpital’s Rule does not apply to \lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac{x^{2}\sin \dfrac{1}{x}}{\sin x}.
Find each limit:
- (a) \lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty }\left( 1+\dfrac{1}{x }\right) ^{\!\!\!-x^{2}}
- (b) \lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty }\left( 1+\dfrac{\ln a}{x}\right) ^{\!\!x}, a>1
- (c) \lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty }\left( 1+\dfrac{1}{x}\right) ^{\!\!x^{2}}
- (d) \lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty }\left( 1+\dfrac{\sin x}{x}\right) ^{\!\!x}
- (e) \lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty }( e^{x}) ^{-1/\ln x}
- (f) \lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty } \left[ \left( \dfrac{1}{a}\right) ^{\!\!x}\right] ^{-1/x}, 0<a<1
- (g) \lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty }x^{1/x}
- (h) \lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty }( a^{x}) ^{1/x}, a>1
- (i) \lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty } [ (2+\sin x) ^{x}] ^{1/x}
- (j) \lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0^{+}}x^{-1/\ln x}
- (a) 0
- (b) a
- (c) \infty
- (d) Does not exist.
- (e) 0
- (f) a
- (g) 1
- (h) a
- (i) Does not exist.
- (j) e^{-1}
Find constants A, B, C, and D so that \lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac{\sin ( Ax) +Bx+Cx^{2}+Dx^{3}}{x^{5}}=\dfrac{4}{15}.
A function f has derivatives of all orders.
- (a) Find \lim\limits_{h\rightarrow 0}\dfrac{f(x+2h)-2\,f(x+h)+f(x)}{h^{2}}.
- (b) Find \lim\limits_{h\rightarrow 0}\dfrac{f(x+3h)-3\,f(x+2h)+3\,f(x+h)-f(x)}{h^{3}}.
- (c) Generalize parts (a) and (b).
- (a) f''(x)
- (b) f'''(x)
- (c) \lim_{h \to 0} \dfrac{\sum_{k=0}^n (-1)^k \dfrac{n!}{k! (n-k)!} f(x + (n-k)h)}{h^n} = f^{(n)}(x)
The formulas in Problem 111 can be used to approximate derivatives. Approximate f^\prime (2), \ f^{\prime \prime} (2), and f’’’ (2) from the table. The data are for f(x)=\ln x. Compare the exact values with your approximations.
x 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 {f(x)} 0.6931 0.7419 0.7885 0.8329 0.8755
Consider the function f( t,x) =\dfrac{x^{t+1}-1}{t+1}, where x>0 and t\neq -1.
- (a) For x fixed at x_{0}, show that \lim\limits_{t\rightarrow -1}f( t,x_0) =\ln\;x_{0}.
- (b) For x fixed, define a function F( t,x) , where x>0, that is continuous so F( t,x) =f( t,x) for all t\neq -1.
- (c) For t fixed, show that \dfrac{d}{dx}F( t,x) =x^{t}, for x>0 and all t.
Source: Michael W. Ecker (2012, September), Unifying Results via L’Hôpital’s Rule. Journal of the American Mathematical Association of Two Year Colleges, 4(1) pp. 9–10.
See Student Solutions Manual.
