7.2 Assess Your UnderstandingPrinted Page 486
Concepts and Vocabulary
True or False To find ∫cos5xdx, factor out cosx and use the identity cos2x=1−sin2x.
True
True or False To find ∫sin(2x)cos(3x)dx, use a product-to-sum identity.
True
Skill Building
In Problems 3–10, find each integral.
∫cos5xdx
sin5x5−2sin3x3+sinx+C
∫sin3xdx
∫sin6xdx
516x−14sin(2x)+364sin(4x)+148sin3(2x)+C
∫cos4xdx
∫sin2(πx)dx
x2−sin(2πx)4π+C
∫cos4(2x)dx
∫π0cos5x dx
0
∫π/3−π/3sin3xdx
In Problems 11–18, find each integral.
∫sin3xcos2xdx
cos5x5−cos3x3+C
∫sin4xcos3xdx
∫sin2xcos2xdx
x8−sin(4x)32+C
∫sin4xcos2xdx
∫sinxcos1/3xdx
−34cos4/3x+C
∫cos3xsin1/2xdx
∫sin2(x2)cos3(x2)dx
23sin3x2−25sin5x2+C
∫sin3(4x)cos3(4x)dx
In Problems 19–26, find each integral.
∫tan3xsec2xdx
14tan4x+C
∫tanxsec5xdx
∫tan2xsec2xdx
tan3x3+C
∫tan5xsec2xdx
∫tan2xsec3xdx
14sec3xtanx−18secxtanx−18ln|secx+tanx|+C
∫tan4xsecxdx
∫cot3xcscxdx
cscx−csc3x3+C
∫cot3xcsc2xdx
In Problems 27–34, find each integral.
∫sin(3x)cosxdx
−18cos(4x)−14cos(2x)+C
∫sinxcos(3x)dx
∫cosxcos(3x)dx
18sin(4x)+14sin(2x)+C
∫cos(2x)cosxdx
∫sin(2x)sin(4x)dx
14sin(2x)−112sin(6x)+C
∫sin(3x)sinxdx
∫π/20sin(2x)sinxdx
23
∫π0cosxcos(4x)dx
In Problems 35–56, find each integral.
∫sin2xcosxdx
sin3x3+C
∫sin3xcosxdx
∫sinxdxcos2x
secx+C
∫cosxdxsin4x
∫cos3(3x)dx
13sin(3x)−19sin3(3x)+C
∫sin5(3x)dx
∫π0sin3xcos5xdx
0
∫π/20sin3xcos3xdx
∫tan3xdx
ln|cosx|+12sec2x+C
∫cot5xdx
∫sec6xtan3xdx
−12cot2x+2ln|tanx|+12tan2x+C
∫tan1/2xsec2xdx
∫csc2xcot5xdx
−16cot6x+C
∫cotxcsc2xdx
487
∫cot(2x)csc4(2x) dx
−18csc4(2x)+C
∫cot2(2x)csc3(2x)dx
∫π/40tan4xsec3xdx
7√248+ln(1+√2)16
∫π/40tan2xsecxdx
∫sin(x2)cos(3x2)dx
−14cos(2x)+12cosx+C
∫cos(−x)sin(4x)dx
∫sin(x2)sin(3x2)dx
12sinx−14sin(2x)+C
∫cos(πx)cos(3πx)dx
Applications and Extensions
Volume of a Solid of Revolution Find the volume of the solid of revolution generated by revolving the region bounded by the graph of y=sinx and the x-axis from x=0 to x=π about the x-axis. See the figure below.
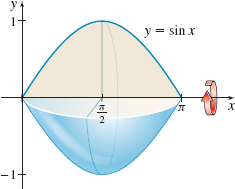
π22
Volume of a Solid of Revolution Find the volume of the solid of revolution generated by revolving the region bounded by the graphs of y=cosx, y=sinx, and x=0 from x=0 to x=π4 about the x-axis.
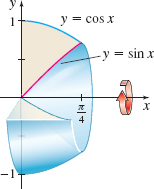
Average Value
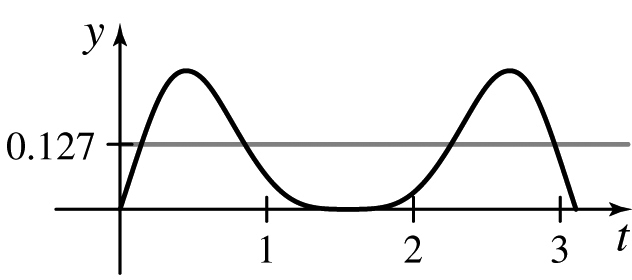
- (a) Find the average value of f(x)=sinxcos4x over the interval [0,π].
- (b) Give a geometric interpretation to the average value.
- (c)
 Use graphing technology to graph f and the average value on the same screen.
Use graphing technology to graph f and the average value on the same screen.
- (a) 25π
- (b) Answers will vary.
- (c)
Rectilinear Motion The acceleration a of an object at time t is given by a(t)=cos2tsint m/s2. At t=0, the object is at the origin and its speed is 5m/s. Find its distance from the origin at any time t.
Area and Volume Let A be the area of the region in the first quadrant bounded by the graphs of y=secx, y=2sinx, and the y-axis.
- (a) Find A.
- (b) Find the volume of the solid of revolution generated by revolving the region about the x-axis.
- (a) ln(√2+1)+√2−2
- (b) 4π−π22

- (a) Use technology to graph the function f(x)=sinnx, 0≤x≤π, for n=5, n=10, n=20, and n=50.
- (b) Find ∫π0sinnxdx correct to three decimal places for n=5, n=10, n=20, and n=50.
- (c) What does (a) suggest about the shape of the graph of f(x)=sinnx, 0≤x≤π, as n→∞.
- (d)
 Find lim.
Find lim.
Find \int \sin ^{4}x\,dx.
- (a) Using the methods of this section.
- (b) Using the reduction formula given in Problem 61 in Section 7.1.
- (c) Verify that both results are equivalent.
- (d)
 Use a CAS to find \int \sin ^{4}x~dx.
Use a CAS to find \int \sin ^{4}x~dx.
- (a) \dfrac{3x}{8}-\dfrac{1}{4}\sin (2x) + \dfrac{1}{32}\sin (4x) +C
- (b) -\dfrac{1}{4}\sin^3x\,\cos x-\dfrac{3}{8}\sin x \,\cos x + \dfrac{3}{8}x + C
- (c) See the Student Solutions
- (d) same as (a)
- (a) Use the substitution u=\sin x to find a function f for which \int \sin x\cos x\,dx=f(x)+C_{1}.
- (b) Use the substitution u=\cos x to find a function g for which \int \sin x\cos x\,dx=g(x)+C_{2}.
- (c) Use the trigonometric identity \sin (2x)=2\sin x\cos x to find a function h for which \int \sin x\cos x\,dx=h(x)+C_{3}.
- (d) Compare the functions f and g. Find a relationship between C_{1} and C_{2}.
- (e) Compare the functions f and h. Find a relationship between C_{1} and C_{3}.
Derive a formula for \int \sin (mx) \sin (nx) \,dx,\quad m ≠ n.
\dfrac{1}{2(m-n)}\sin [(m-n)x] - \dfrac{1}{2(m+n)} \sin [(m+n)x] +C
Derive a formula for \int \sin (mx) \cos (nx) \,dx,\quad m ≠ n.
Derive a formula for \int \cos (mx) \cos (nx) \,dx,\quad m ≠ n.
\dfrac{1}{2(m-n)}\sin [(m-n)x] + \dfrac{1}{2(m+n)} \sin [(m+n)x] +C
Challenge Problems
Use the substitution \sqrt{x}\,=\,\sin y to find \int_{0}^{1/2}\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{1-x}}\,dx. \bigg(Hint: sin^{2}y\,{=}\,\dfrac{1\,{-}\,\cos (2y)}{2}.\bigg)
Use an appropriate substitution to show that \int_{0}^{\pi /2}\sin ^{n}\theta \,d\theta =\,\int_{0}^{\pi /2}\cos ^{n}\theta \,d\theta .
See the Student Solutions Manual.
- (a) What is wrong with the following?
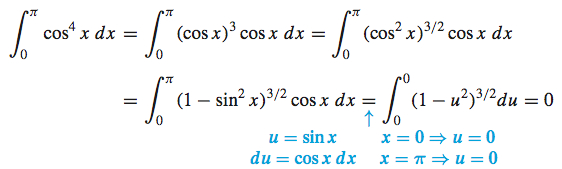
- (b) Find \int_{0}^{\pi }\cos ^{4}x~dx.
- (a) What is wrong with the following?
