Choosing Relevant Sources
Sources are relevant when they help you achieve your aims with your readers. Relevant sources may
explain terms or concepts;
provide background information;
provide evidence in support of your claims;
provide alternative viewpoints or interpretations;
lend authority to your point of view.
For more on focusing search results and selecting search terms, see Chapter 21.
A search for sources may reveal more books and articles than any researcher could ever actually consult. A search on the term home schooling in one database, for example, got 1,172 hits. Obviously, a glance at all the hits to determine which are most relevant would take far too much time. To speed up the process, resources such as library catalogs, databases, and search engines provide tools to narrow the results. For example, in one popular all-
Once you’ve reduced your search results to a manageable number, click on the remaining titles to look closely at each record. The analysis of an article’s detailed record in Figure 22.1 shows what to look for.
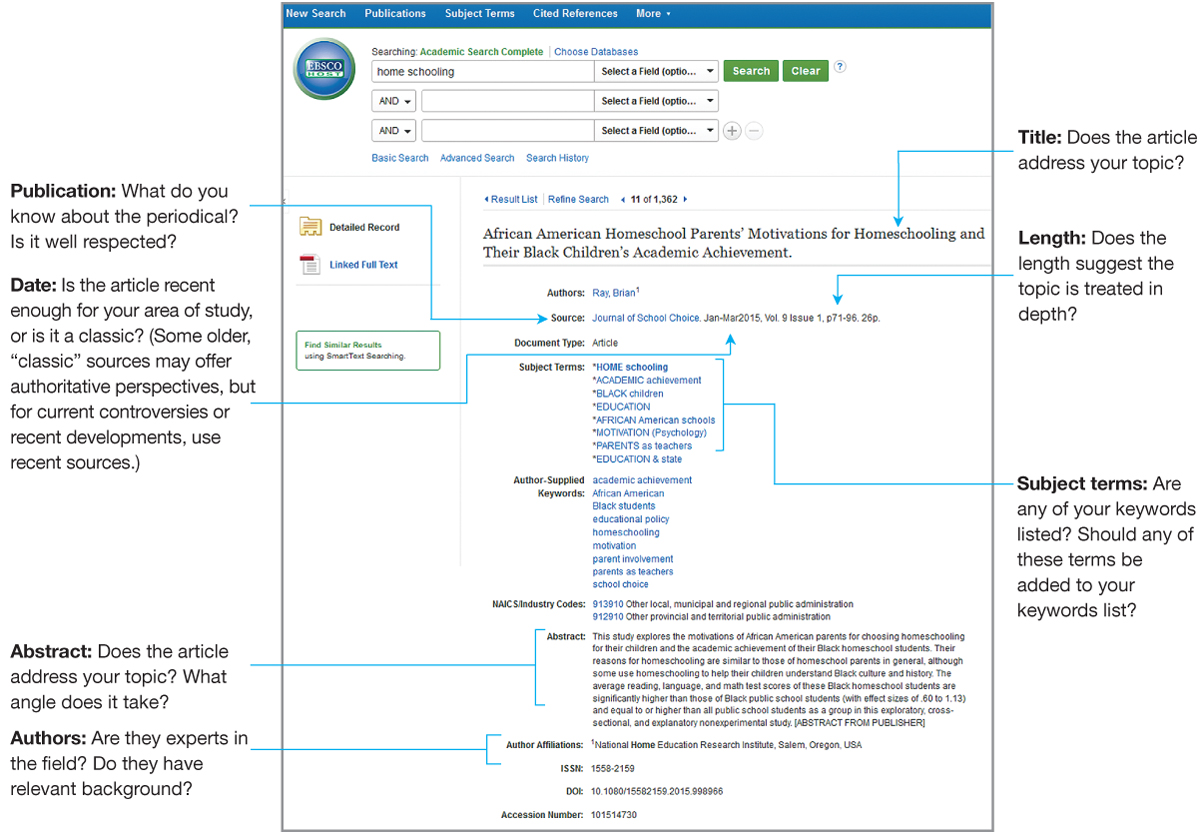
After you have identified a reasonable number of relevant sources, examine the sources themselves:
Read the preface, introduction, or conclusion of books, or the first or last few paragraphs of articles, to determine which aspect of the topic is addressed or which approach to the topic is taken. To obtain a clear picture of a topic, researchers need to consider sources that address different aspects of the topic or take different approaches.
Look at the headings or references in articles, or the table of contents and index in books, to see how much of the content relates specifically to your topic.
Page 627Consider the way the source is written: Sources written for general readers may be accessible but may not analyze the subject in depth. Extremely specialized works may be too technical. Poorly written sources may be unreliable. (See Choosing Reliable Sources for more on scholarly versus popular sources and for a discussion of why researchers should avoid sources that are poorly written or riddled with errors.)
If close scrutiny leaves you with too few sources — or too many sources from too few perspectives — conduct a search using additional or alternative keywords, or explore links to related articles, look at the references in a particularly useful article, or look for other sources by an author whose work you find useful.