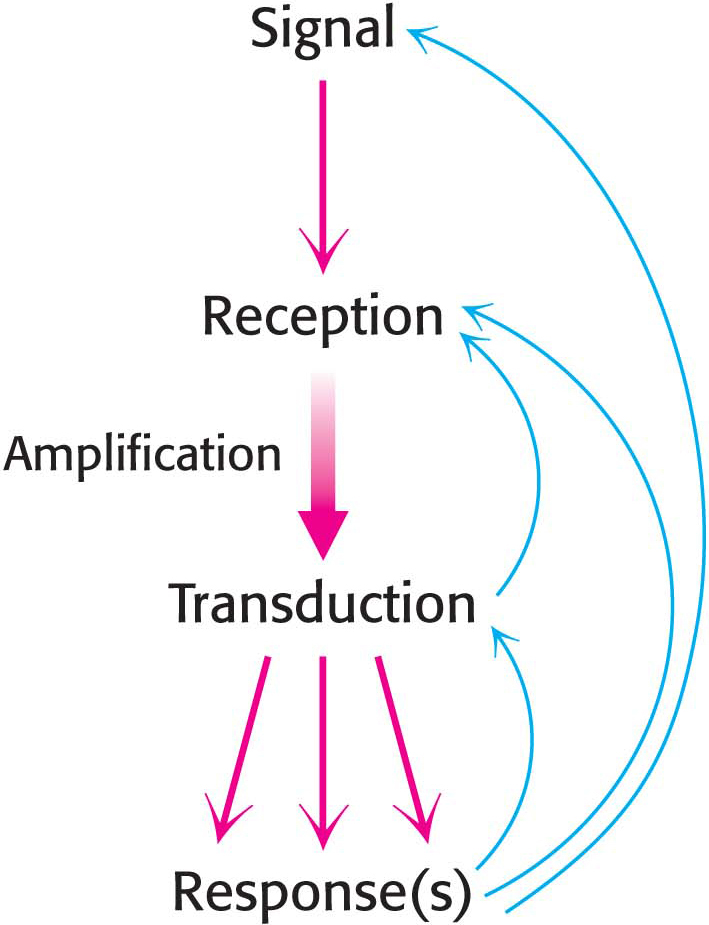
Figure 13.1 Principles of signal transduction. An environmental signal is first received by interaction with a cellular component, most often a cell-surface receptor. The information that the signal has arrived is then converted into other chemical forms, or transduced. The transduction process often comprises many steps. The signal is often amplified before evoking a response. Feedback pathways (blue arrows) regulate the entire signaling process.
[Leave] [Close]