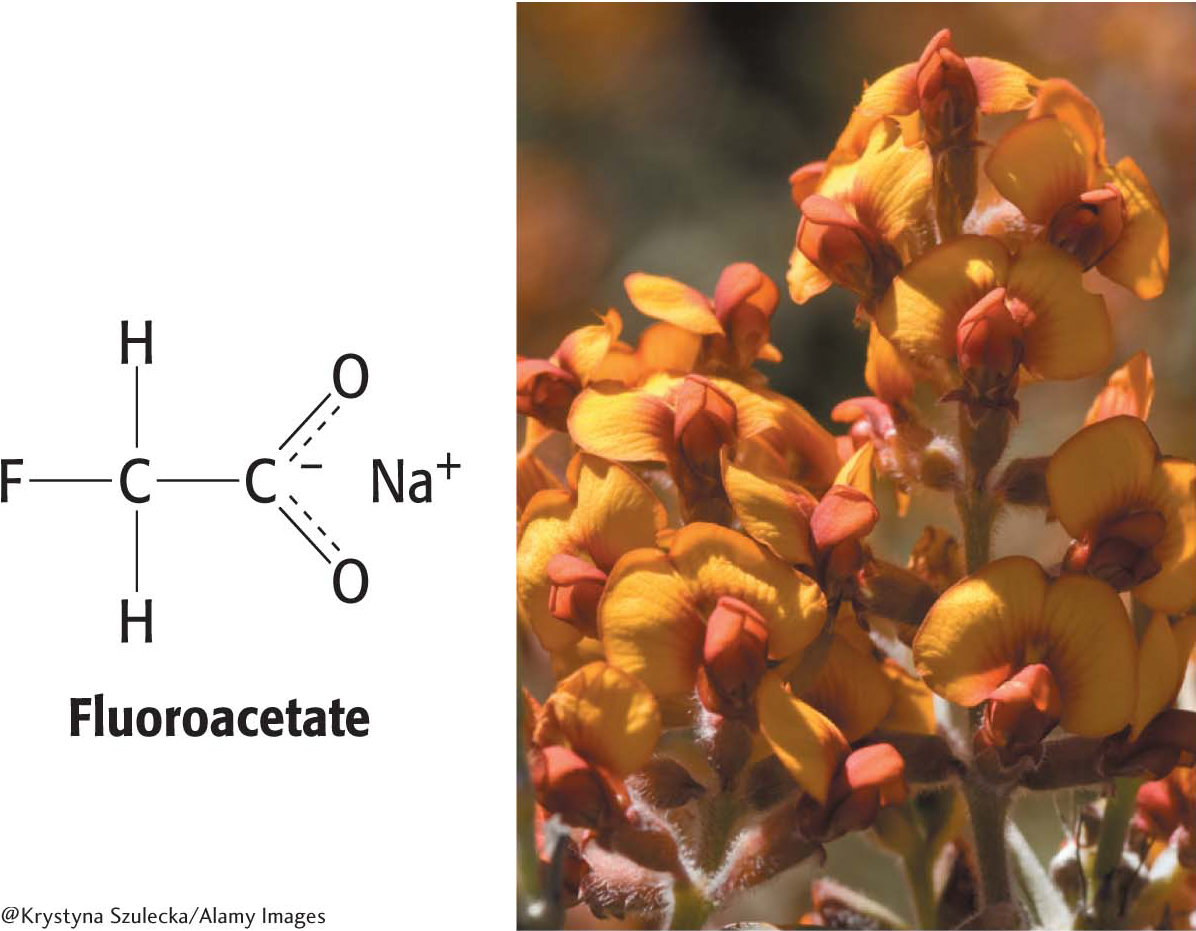
Figure 19.4 Aconitase is inhibited by a metabolite of fluoroacetate. Fluoroacetate, a toxin, is activated to fluoroacetyl CoA, which reacts with citrate to form fluorocitrate, a suicide inhibitor of aconitase. After having been irreversibly inhibited, aconitase shuts down the citric acid cycle and cellular respiration, accomplishing its role as a pesticide. Members of the genus Gastrolobium in Australia contain fluoroacetate.
[Leave] [Close]