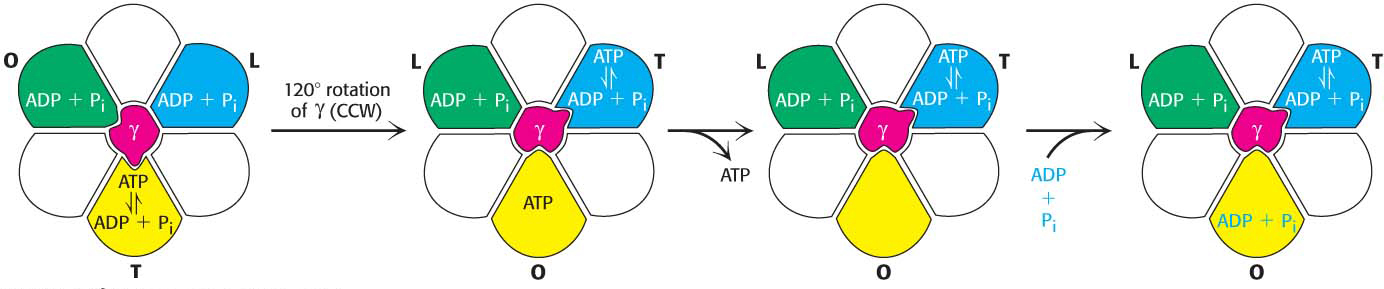
Figure 21.6 A binding-