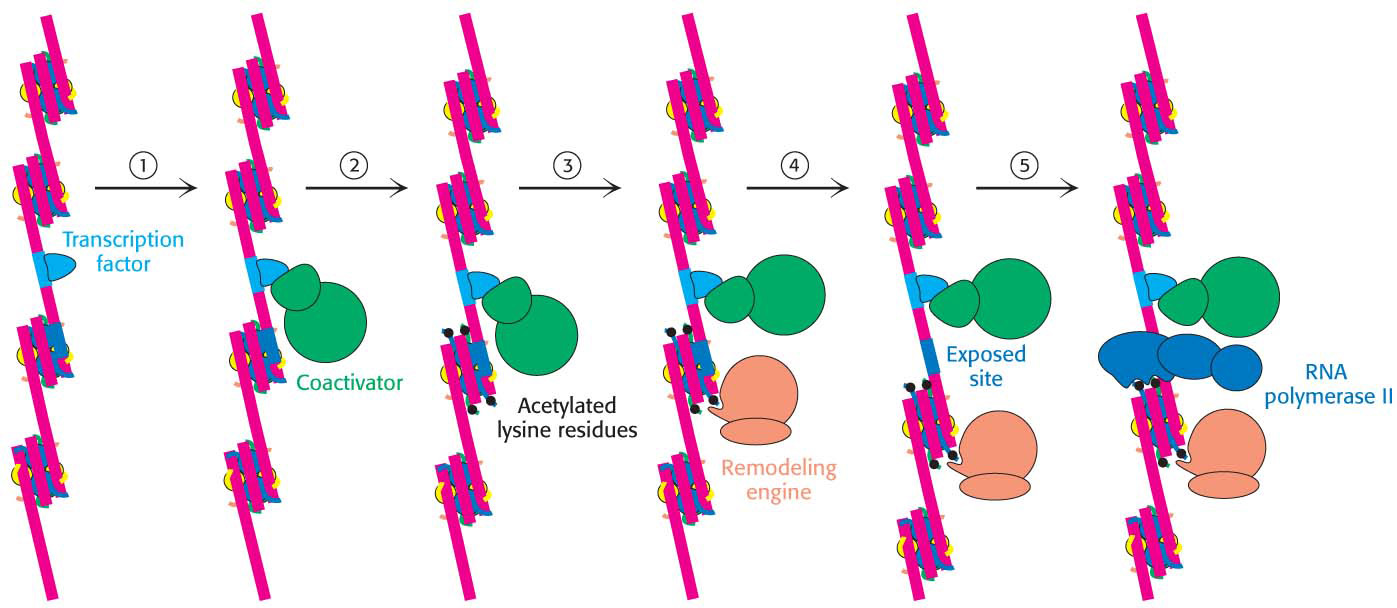
Figure 37.13 Chromatin remodeling. Eukaryotic gene regulation begins with an activated transcription factor bound to a specific site on DNA. One scheme for the initiation of transcription by RNA polymerase II requires five steps: (1) recruitment of a coactivator, (2) acetylation of lysine residues in the histone tails, (3) binding of a remodeling-engine complex to the acetylated lysine residues, (4) ATP-dependent remodeling of the chromatin structure to expose a binding site for RNA polymerase or for other factors, and (5) recruitment of RNA polymerase II. Only two subunits are shown for each complex, although the actual complexes are much larger.
[Leave] [Close]