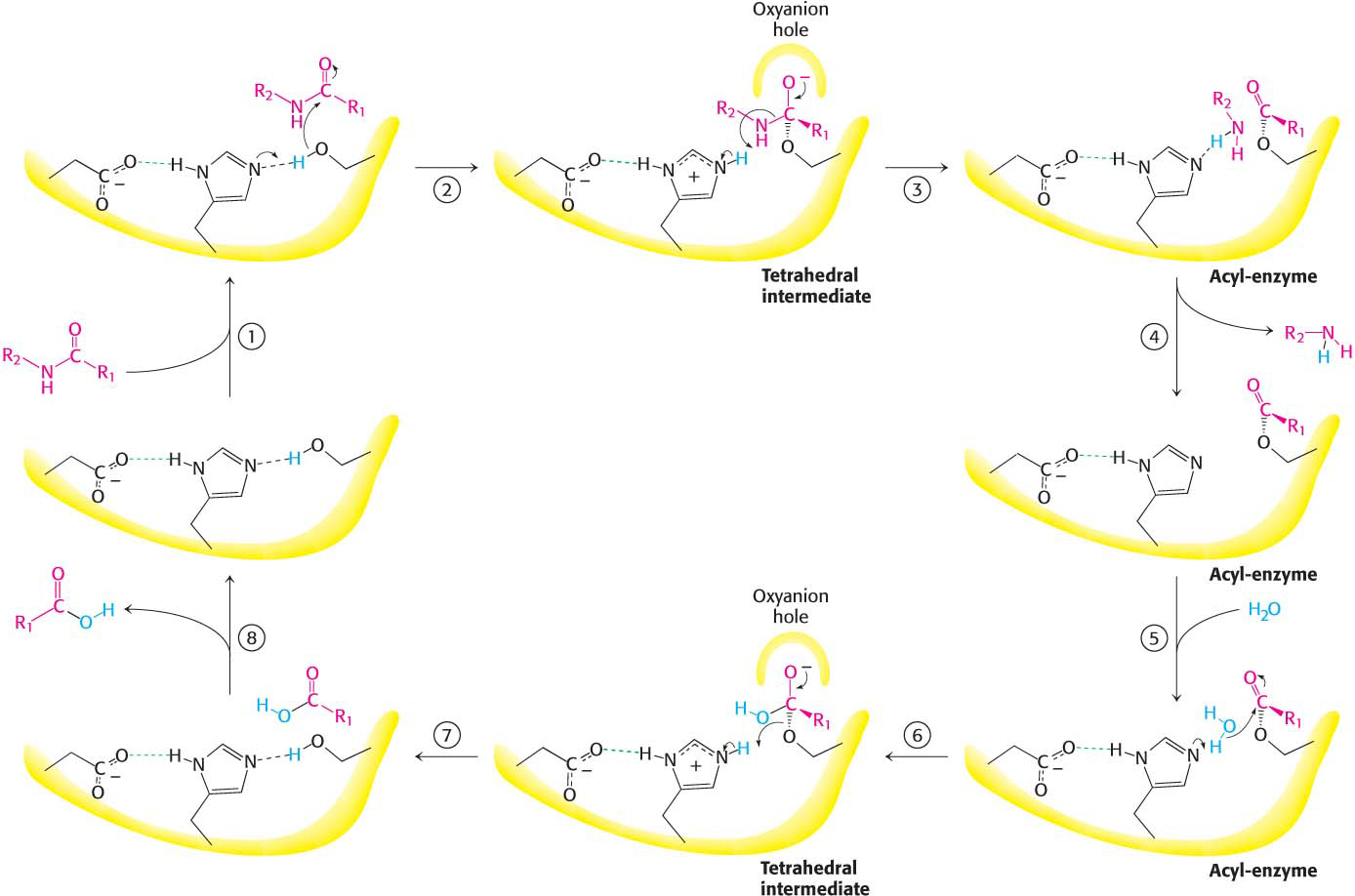
Figure 8.25 Peptide hydrolysis by chymotrypsin. The mechanism of peptide hydrolysis illustrates the principles of covalent and acid–base catalysis. The reaction proceeds in eight steps: (1) substrate binding, (2) serine’s nucleophilic attack on the peptide carbonyl group, (3) collapse of the tetrahedral intermediate, (4) release of the amine component, (5) water binding, (6) water’s nucleophilic attack on the acyl-enzyme intermediate, (7) collapse of the tetrahedral intermediate, and (8) release of the carboxylic acid component. The dashed green lines represent hydrogen bonds.
[Leave] [Close]