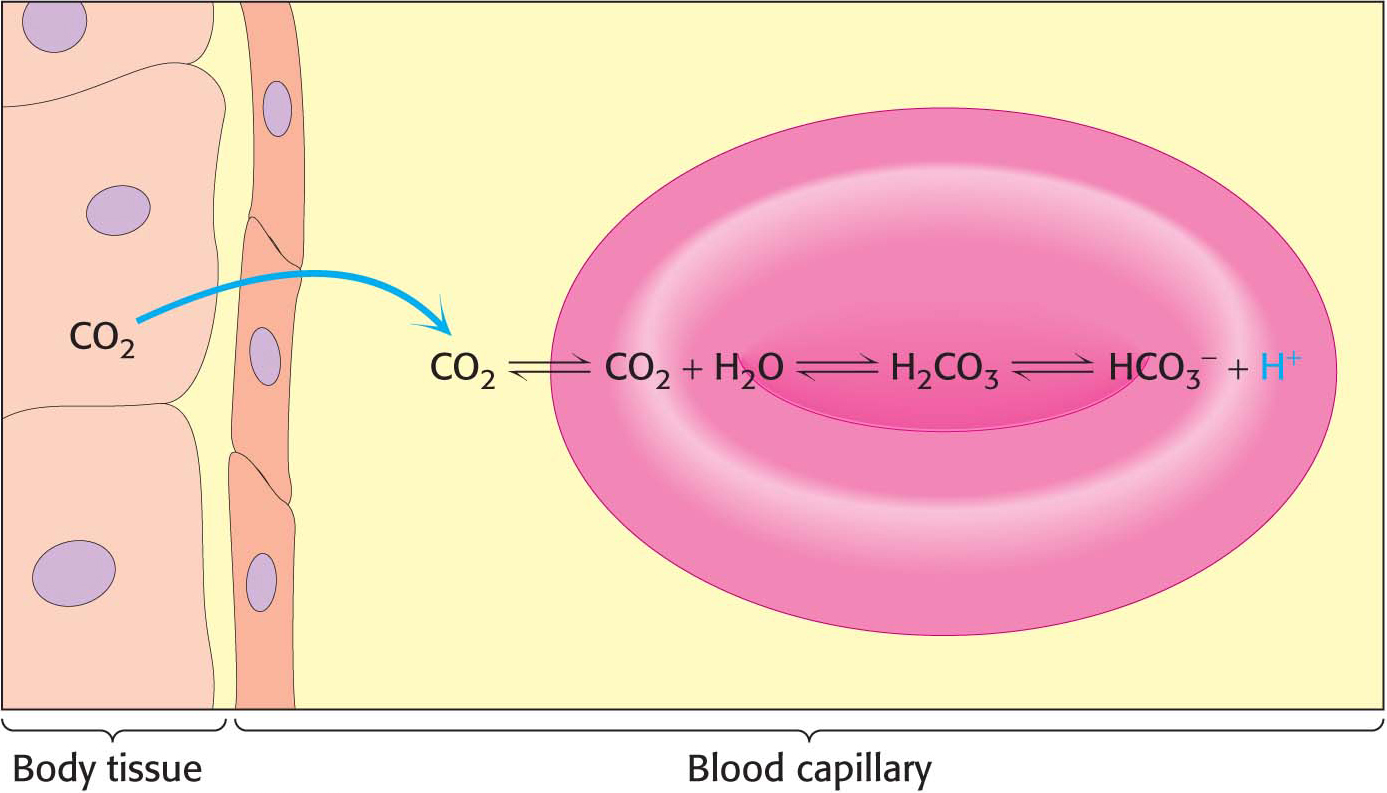
Figure 9.13 Carbon dioxide and pH. Carbon dioxide in the tissues diffuses into red blood cells. Inside a red blood cell, carbon dioxide reacts with water to form carbonic acid, in a reaction catalyzed by the enzyme carbonic anhydrase. Carbonic acid dissociates to form HCO3− and H+, resulting in a drop in pH inside the red cell.
[Leave] [Close]