Chapter 10
Carbohydrates were originally regarded as hydrates of carbon because the empirical formula of many of them is (CH2O)n.
Three amino acids can be linked by peptide bonds in only six different ways. However, three different monosaccharides can be linked in a plethora of ways. The monosaccharides can be linked in a linear or a branched manner, with α or β linkages, with bonds between C-
1 and C- 3, between C- 1 and C- 4, between C- 1 and C- 6, and so forth. There are 12,288 possible trisaccharides but only 6 different tripeptides. Complete the interactive matching exercise to see answers.
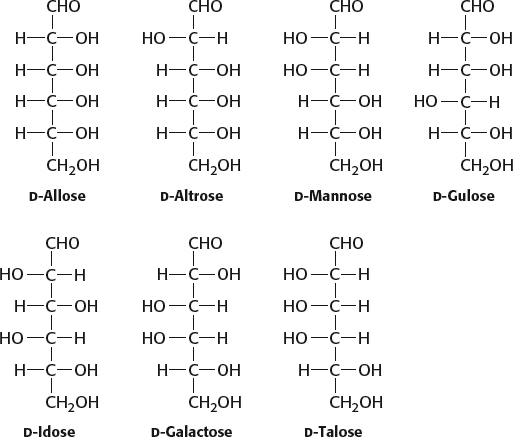
(a) Aldose–
ketose; (b) epimers; (c) aldose– ketose; (d) anomers; (e) aldose– ketose; (f) epimers Erythrose: tetrose aldose
Ribose: pentose aldose
Glyceraldehyde: triose aldose
Dihydroxyacetone: triose ketose
Erythrulose: tetrose ketose
Ribulose: pentose ketose
Fructose: hexose ketose
Glucose is reactive because of the presence of an aldehyde group in its open-
chain form. The aldehyde group slowly condenses with amino groups to form an amino ketone. No, sucrose is not a reducing sugar. The anomeric carbon atoms of glucose and fructose can act as the reducing agent, but, in sucrose, the two anomeric carbon atoms are joined by a covalent bond and thus not available to react.
From methanol
(a) β-d-Mannose; (b) β-d-galactose; (c) β-d-fructose; (d) β-d-glucosamine
Synthesize the trisaccharide, and test its effect on cell–
cell interaction. The trisaccharide itself should be a competitive inhibitor of cell adhesion if the trisaccharide unit of the glycoprotein is critical for the interaction. Not a reducing sugar; no open-
chain forms are possible. d-Galactose, d-glucose, and d-fructose. (c) d-Galactose and sucrose (glucose + fructose).
The hemiketal linkage of the α anomer is broken to form the open form. Rotation about the C-
1 and C- 2 bonds allows the formation of the β anomer, and a mixture of isomers results. 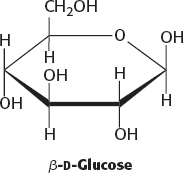
Heating converts the very sweet pyranose form into the more stable but less sweet furanose form. Consequently, the sweetness of the preparation is difficult to accurately control, which also accounts for why honey loses sweetness with time. Figure 10.6 shows the structures.
(a) Each glycogen molecule has one reducing end, whereas the number of nonreducing ends is determined by the number of branches, or α-1,6 linkages. (b) Because the number of nonreducing ends greatly exceeds the number of reducing ends in a collection of glycogen molecules, all of the degradation and synthesis of glycogen takes place at the nonreducing ends, thus maximizing the rate of degradation and synthesis.
Page C11Glycogen is a polymer of glucose linked by α-1,4-
glycosidic bonds with branches formed approximately every 10 glucose units by α-1,6- glycosidic bonds. Starch consists of two polymers of glucose. Amylose is a straight- chain polymer formed by α-1,4- glycosidic bonds. Amylopectin is similar to glycogen, but amylopectin has fewer branches, one branch per 30 or so glucose units. Cellulose is a linear polymer of glucose joined by β-1,4 linkages. Glycogen is a branched polymer with the main chain being formed by α-1,4-
glycosidic bonds. The β-1,4 linkages allow the formation of a linear polymer ideal for structural roles. The α-1,4 linkages of glycogen form a helical structure, which allows the storage of many glucose moieties in a small space. Simple glycoproteins are often secreted proteins and thus play a variety of roles. For example, the hormone EPO is a glycoprotein. Usually, the protein component constitutes the bulk of the glycoprotein by mass. In contrast, proteoglycans and mucoproteins are predominantly carbohydrates. Proteoglycans have glycosaminoglycans attached and play structural roles, as in cartilage and the extracellular matrix. Mucoproteins often serve as lubricants and have multiple carbohydrates attached through an N-acetylgalactosamine moiety.
The attachment of the carbohydrate allows EPO to stay in circulation longer and thus to function for longer periods of time than would a carbohydrate-
free EPO. A glycoprotein is a protein that is decorated with carbohydrates. A lectin is a protein that specifically recognizes carbohydrates. A lectin can also be a glycoprotein.
The glycosaminoglycan, because it is heavily charged, binds many water molecules. When cartilage is stressed, such as when your heel hits the ground, the water is released, thus cushioning the impact. When you lift your heel, the water rebinds.
It suggests that carbohydrates are on the cell surfaces of all organisms for the purpose of recognition by other organisms or by the environment.
The lectin that binds the mannose 6-
phosphate might be defective and not recognize a correctly addressed protein. 64 proteins. Each site either is or is not glycosylated, and so there are 26 = 64 possible proteins.
The wide array of possible linkages between carbohydrates in concert with the wide variety of monosaccharides and their many isomeric forms makes complex carbohydrates information-
rich molecules. As discussed in Chapter 6, many enzymes display stereochemical specificity. Clearly, the enzymes of sucrose synthesis are able to distinguish between the isomers of the substrates and link only the correct pair.
Aggrecan is heavily decorated with glycosaminoglycans. If glycosaminoglycans are released into the media, aggrecan must be undergoing degradation.
Another enzyme might be present that cleaves glycosaminoglycans from aggrecan without degrading aggrecan. Other experiments not shown established that glycosaminoglycan release is an accurate measure of aggrecan destruction.
The control provides a baseline of “background” degradation inherent in the assay.
Aggrecan degradation is greatly enhanced.
Aggrecan degradation is reduced to the background system.
It is an in vitro system in which not all the factors contributing to cartilage stabilization in vivo are present.
The proportion of the α anomer is 0.36, and that of the β anomer is 0.64.
A pyranoside reacts with two molecules of periodate; formate is one of the products. A furanoside reacts with only one molecule of periodate; formate is not formed.
Reducing ends would form 1,2,3,6-
tetramethylglucose. The branch points would yield 2,3- dimethylglucose. The remainder of the molecule would yield 2,3,6- trimethylglucose.