Chapter 3
ELVISISLIVINGINLASVEGAS
TWITCHYLITTLEFERRETARENTYOUMALFOY (Twitchy little ferret, aren’t you Malfoy?)
A: Proline, Pro, P; B: tyrosine, Tyr, Y; C: leucine, Leu, L; D: lysine, Lys, K
(a) C, A; (b) D; (c) B, D; (d) B, D; (e) B
Complete the interactive matching exercise to see answers.
(a) Ala; (b) Tyr; (c) Ser; (d) His
pH 7: no net charge. pH 12: −1.
Calculate the pI by taking the average of the two pKa values. Thus, pI = (pKaacid + pKaamino)/2 = (2.72 + 9.60)/2 = 6.16.
Arginine, lysine, and histidine
Nonessential amino acids can be synthesized from other molecules in the body. Essential amino acids cannot and thus must be consumed in the diet.
Phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan
The side chains of aspartate, glutamate, histidine, cysteine, tyrosine, lysine, and arginine
Tyrosine
Ser, Glu, Tyr, and Thr
Using the Henderson–
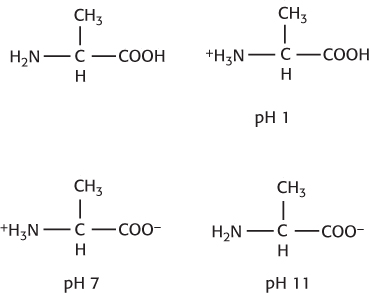
Hasselbalch equation, we find the ratio of alanine- COOH to alanine- COO− at pH 7 to be 10−4. The ratio of alanine- NH2 to alanine- NH3+, determined in the same fashion, is 10−1. Thus, the ratio of neutral alanine to the zwitterionic species is 10−4 × 10−1 = 10−5. Recall that the pKa is the pH at which the concentration of the unionized form of a molecule is equal to the ionized form. The carboxylic acid group in Figure 3.2 has a pKa of slightly more than 2, whereas the amino groups have a pKa of 9.
To answer this, we need only apply the Henderson–
Hasselbalch equation to the ionization of NH3+. NH3+ is the acid and NH2 the conjugate base. For pH 9.8,
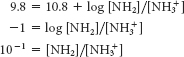 Page C3
Page C3Thus, the fraction of protonated molecules = 10/(10 + 1) = 91%.
For pH 11.8,
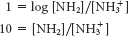
Thus, the fraction of protonated molecules 1/(10 + 1) = 9%.
We need to apply the Henderson–
Hasselbalch equation to the ionization of the carboxylic acid. For pH 2.1,
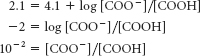
Thus, the fraction of protonated molecules = 100/(100 + 1) = 99%.
For pH 7.1,
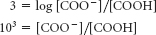
Thus, the fraction of protonated molecules = 1/(1000 + 1) = 10−3.