PROBLEMS
Question 12.1
1. Shared traits. Name some of the features common to all membranes. ✓ 1
Question 12.2
2. Simple diffusion. What conditions are required for a small molecule to spontaneously pass through a membrane? ✓ 2
Question 12.3
3. Bread and jam. Match each term with its description.
Integral membrane protein Peripheral membrane protein Channel Passive transport Active transport Na+–K+ ATPase Secondary transporter Antiporter Symporter Ion channel | Facilitated diffusion Interacts tightly with the membrane interior Uses the energy of one gradient to create another Allows rapid movement of molecules down a gradient across a membrane Molecules moving in the same direction Interacts with the border of a membrane Molecules moving in opposite directions Movement against a concentration gradient Inhibited by digitalis Can be voltage- |
Question 12.4
4. Solubility matters. Arrange the following substances in order of increasing permeability through a lipid bilayer: (a) glucose; (b) glycerol; (c) Cl−; (d) indole; (e) tryptophan. ✓ 2
Question 12.5
5. A helping hand. Differentiate between simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion. ✓ 2
Question 12.6
6. Gradients. Differentiate between passive transport and active transport. ✓ 3
Question 12.7
7. The golden mean. Proper membrane fluidity is vital to membrane-
Question 12.8
8. Heart beats. Outline the relation between the Na+–K+ ATPase and the strength of a heart contraction. Identify the relevant primary and secondary active-
Question 12.9
9. Hunting hippos. Somali hunters use arrows that have been dipped in high concentrations of the cardiac glycoside ouabain to kill game. Indeed, there are reports that animals the size of a hippopotamus can be killed by ouabain-
Question 12.10
10. Only so much energy. Consider Figure 12.20, which illustrates the relation between the sodium–
Question 12.11
11. Commonalities. What are two fundamental properties of all ion channels? ✓ 3
Question 12.12
12. Opening channels. Differentiate between ligand-
Question 12.13
13. Behind the scenes. Is the following statement true or false? Explain. ✓ 3
The sodium–
Question 12.14
14. Powering movement. List two forms of energy that can power active transport. ✓ 3
Question 12.15
15. Greasy patch. A stretch of 20 amino acids is sufficient to form an α helix long enough to span the lipid bilayer of a membrane. How could this piece of information be used to search for membrane proteins in a data bank of primary sequences of proteins?
Question 12.16
16. Water-
Question 12.17
17. Embedded or not. Differentiate between peripheral proteins and integral proteins.
Question 12.18
18. Water-
Question 12.19
19. Pumping sodium. Design an experiment to show that the action of the sodium-
Question 12.20
20. Different directions. The K+ channel and the Na+ channel have similar structures and are arranged in the same orientation in the cell membrane. Yet the Na+ channel allows sodium ions to flow into the cell and the K+ channel allows potassium ions to flow out of the cell. Explain. ✓ 3
Chapter Integration Problems
Question 12.21
21. Energy considerations. Explain why an a helix is especially suitable for a transmembrane-
Question 12.22
22. Speed and efficiency matter. The neurotransmitter acetylcholine, which activates a ligand-
Question 12.23
23. Relief for sore joints. Both aspirin and ibuprofen inhibit prostaglandin H2 synthase-
Data Interpretation and Challenge Problems
Question 12.24
24. Cholesterol effects. The red curve on the following graph shows the fluidity of the fatty acids of a phospholipid bilayer as a function of temperature. The blue curve shows the fluidity in the presence of cholesterol. ✓ 2
(a) What is the effect of cholesterol?
(b) Why might this effect be biologically important?
Question 12.25
25. Transport differences. The rate of transport of two molecules, indole and glucose, across a cell membrane is shown in the following illustration. What are the differences between the transport mechanisms of the two m olecules? Suppose that ouabain, a specific inhibitor of the Na+–K+ ATPase, inhibited the transport of glucose. What would this inhibition suggest about the mechanism of transport? ✓ 3
Question 12.26
26. Desert fish. Certain fish living in desert streams alter their membrane-
Question 12.27
27. A handy protective device. The multidrug-
Question 12.28
28. Looking-
Question 12.29
29. Tarantula toxin. Acid sensing is associated with pain, tasting, and other biological activities. Acid sensing is carried out by a ligand-
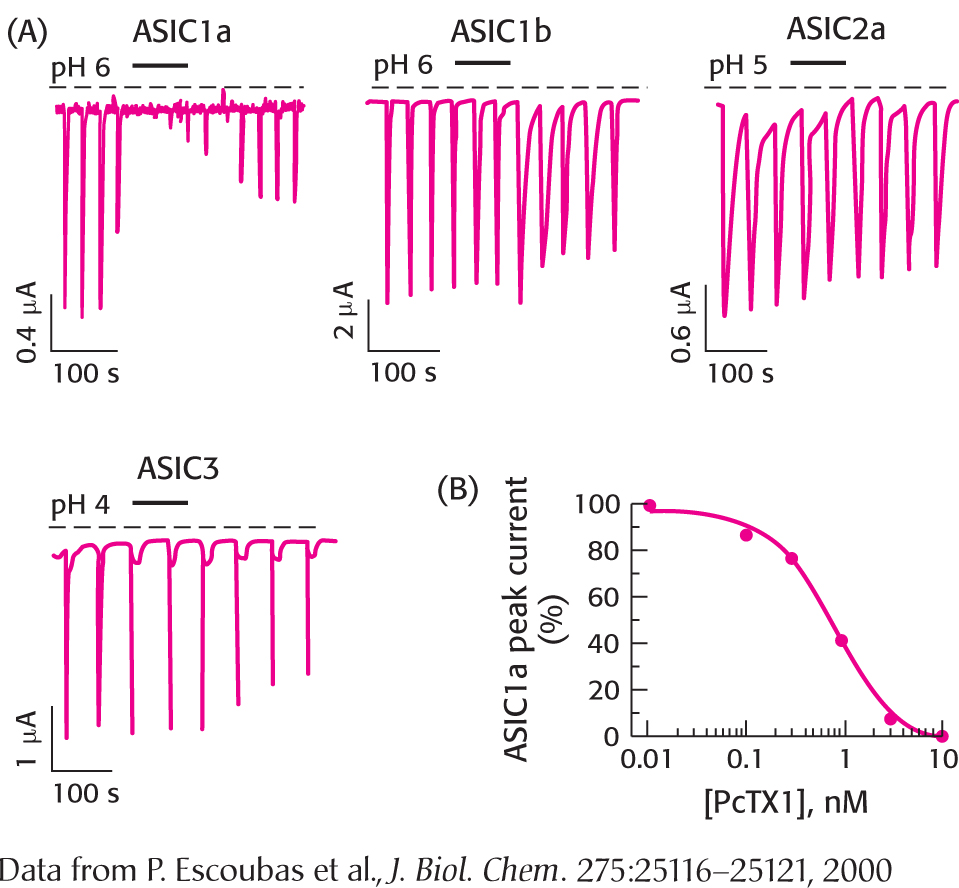
(a) Which of the ASIC family members—
(b) Is the effect of the toxin reversible? Explain.
(c) What concentration of PcTX1 yields 50% inhibition of the sensitive channel?
Question 12.30
30. Channel problems 1. A number of pathological conditions result from mutations in the acetylcholine receptor channel, an ion channel that is activated by the binding of acetylcholine. One such mutation causes muscle weakness and rapid fatigue. An investigation of the acetylcholine-
Question 12.31
31. Channel problems 2. The acetylcholine receptor channel can undergo mutation leading to fast-
Challenge Problems
Question 12.32
32. A dangerous snail. Cone snails are carnivores that inject a powerful set of toxins into their prey, leading to rapid paralysis. Many of these toxins are found to bind to specific ion-
Question 12.33
33. A perfect fit. Provide an energetic explanation for how the potassium channel allows passage of the potassium ion but not the smaller sodium ion. ✓ 3
Selected Readings for this chapter can be found online at www.whfreeman.com/