PROBLEMS
Question 26.1
1. Biochemical taxonomy.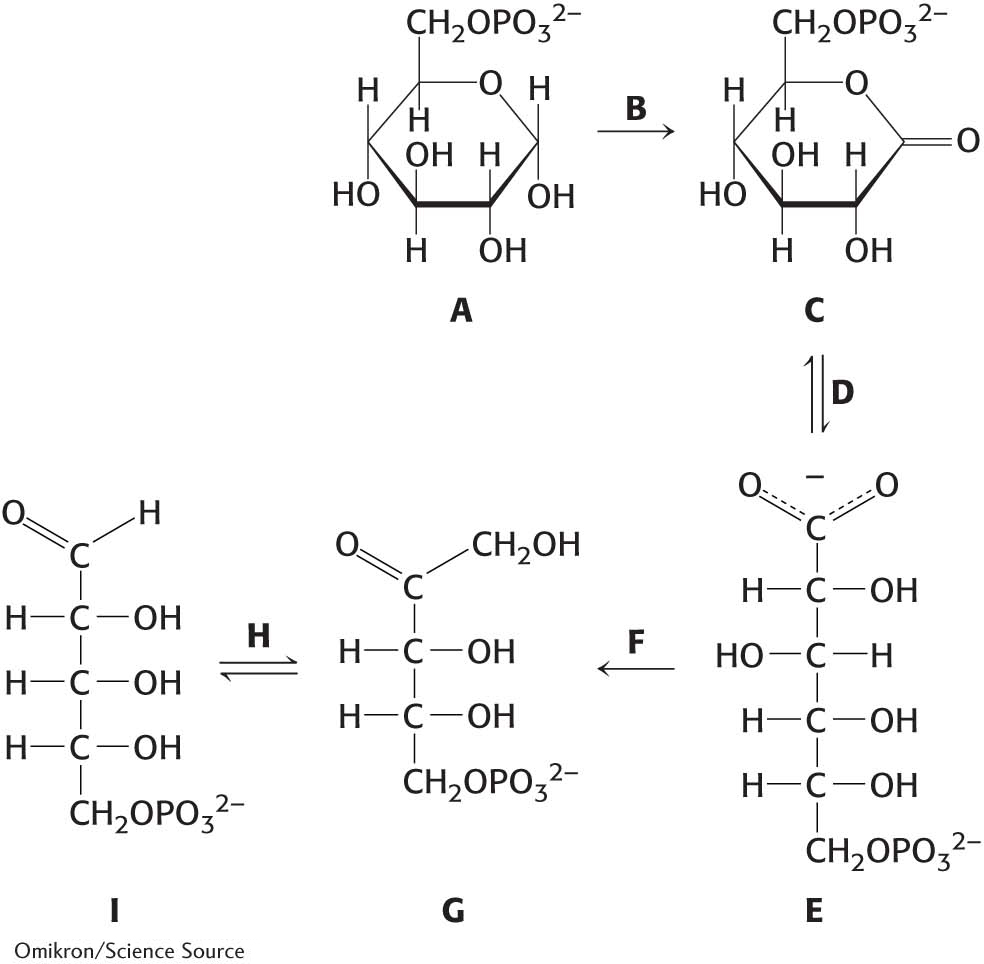
(a) Identify 6-
(b) Which reactions produce NADPH? _______
(c) Identify ribulose 5-
(d) What reaction generates CO2? _______
(e) Identify 6-
(f) Which reaction is catalyzed by phosphopentose isomerase? _______
(g) Identify ribose 5-
(h) Which reaction is catalyzed by lactonase? _______
(i) Identify glucose 6-
(j) Which reaction is catalyzed by 6-
(k) Which reaction is catalyzed by glucose 6-
Question 26.2
2. Phase shift. The pentose phosphate pathway is composed of two distinct phases. What are the two phases, and what are their roles? ✓ 6
Question 26.3
3. Designed to control or govern. What is the key regulatory enzyme in the pentose phosphate pathway, and what is its most prominent regulatory signal? ✓ 7
Question 26.4
4. No respiration. Glucose is normally completely oxidized to CO2 in the mitochondria. Under what circumstance can glucose be completely oxidized to CO2 in the cytoplasm? ✓ 6
Question 26.5
5. Watch your diet, Doctor. Noted psychiatrist Hannibal Lecter once remarked to FBI Agent Starling that he enjoyed liver with some fava beans and a nice Chianti. Why might this diet be dangerous for some people? ✓ 7
Question 26.6
6. Offal or awful? Liver and other organ meats contain large quantities of nucleic acids. In the course of digestion, RNA is hydrolyzed to ribose, among other chemicals. Explain how ribose can be used as a fuel. ✓ 6
Question 26.7
7. A required ATP. The metabolism of glucose 6-
Which reaction requires the ATP?
Question 26.8
8. Tracing glucose. Glucose labeled with 14C at C-
Question 26.9
9. No redundancy. Why do deficiencies in glucose 6-
Chapter Integration Problems
Question 26.10
10. Through the looking glass. Explain why the Calvin cycle and the pentose phosphate are almost mirror images of each other.
Question 26.11
11. Recurring decarboxylations. Which reaction in the citric acid cycle is most analogous to the oxidative decarboxylation of 6-
Challenge Problems
Question 26.12
12. You do what you can do. Red blood cells lack mitochondria. These cells process glucose to lactate, but they also generate CO2. What is the purpose of producing lactate? How can red blood cells generate CO2 if they lack mitochondria? ✓ 6
Question 26.13
13. Carbon shuffling. Ribose 5-
Question 26.14
14. Synthetic stoichiometries. What is the stoichiometry of the synthesis of (a) ribose 5-
Question 26.15
15. Reductive power. What ratio of NADPH to NADP+ is required to sustain [GSH] = 10 mM and [GSSG] = 1 mM? Use the redox potentials given in Table 20.1.
Question 26.16
16. Catching carbons. Radioactive-
Selected Readings for this chapter can be found online at www.whfreeman.com/