
28.2 Additional Enzymes Elongate and Desaturate Fatty Acids
The major product of fatty acid synthase is palmitate, a 16-
Membrane-Bound Enzymes Generate Unsaturated Fatty Acids
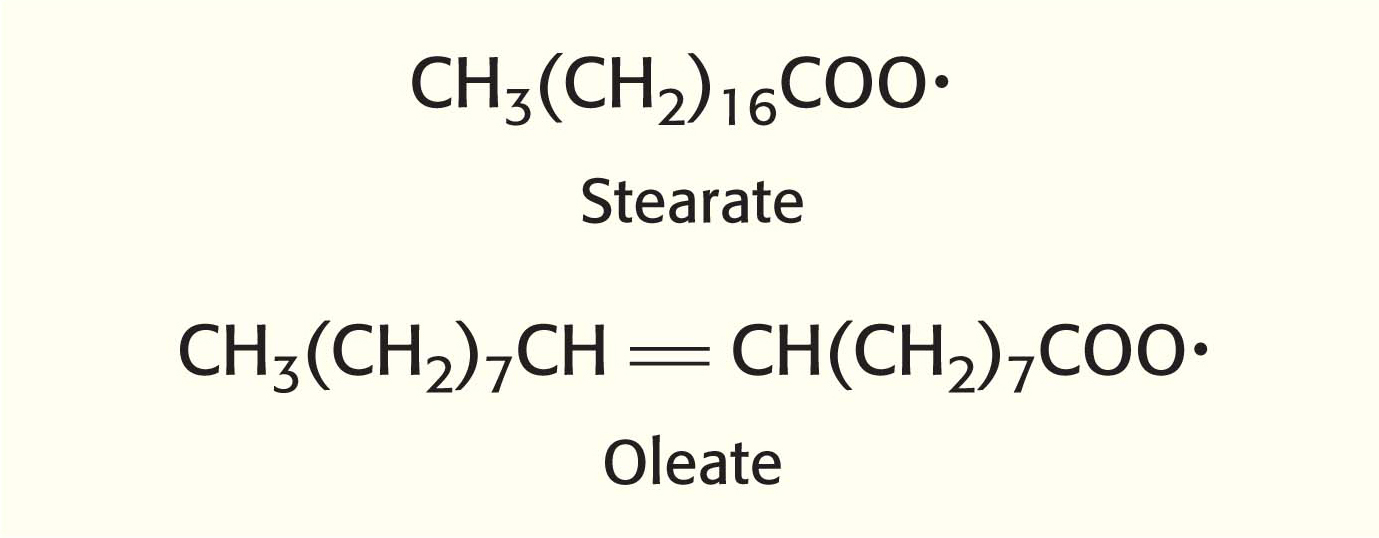
Endoplasmic reticulum systems also introduce double bonds into long-
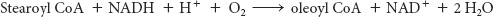
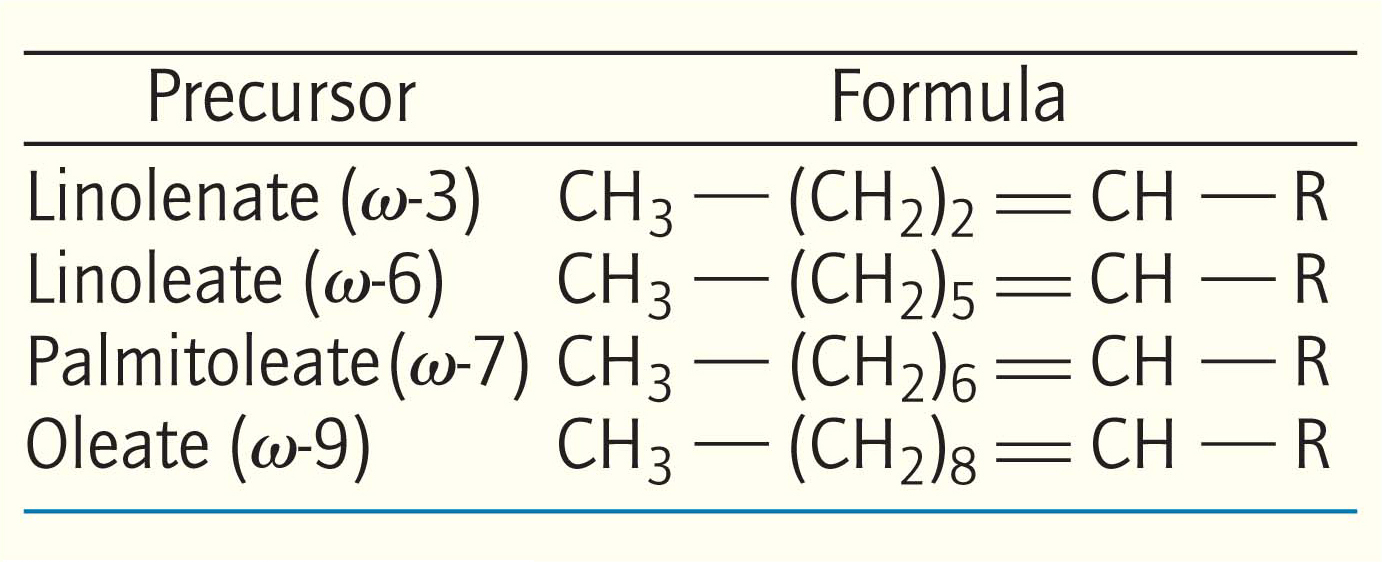
Unsaturated fatty acids in mammals are derived from either palmitoleate (16:1, 16 carbon atoms, 1 double bond), oleate (18:1), linoleate (18:2), or linolenate (18:3). Mammals lack the enzymes to introduce double bonds at carbon atoms beyond C-
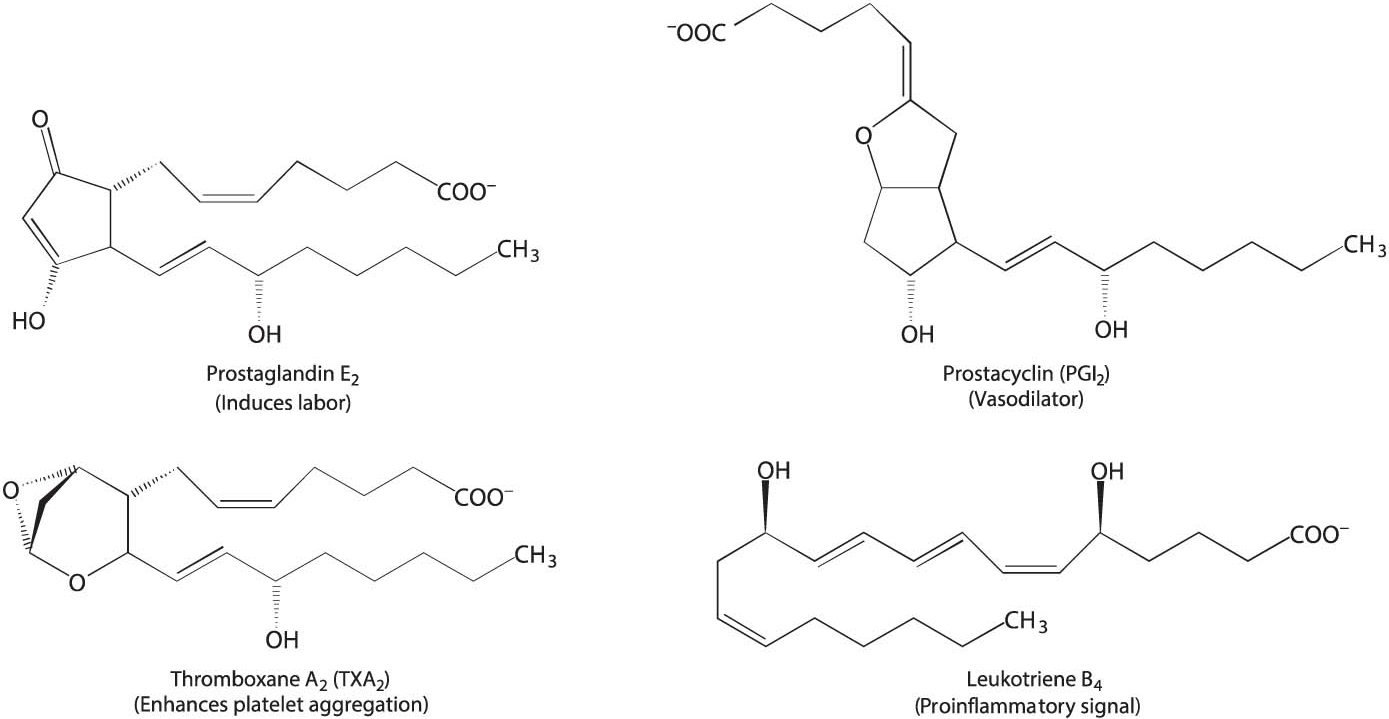
Eicosanoid Hormones Are Derived from Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids
Arachidonate, a 20:4 fatty acid derived from linoleate, is the major precursor of several classes of signal molecules: prostaglandins, prostacyclins, thromboxanes, and leukotrienes (Figure 28.6). Prostaglandins and related signal molecules are called eicosanoids (from the Greek eikosi, meaning “twenty”) because they contain 20 carbon atoms.
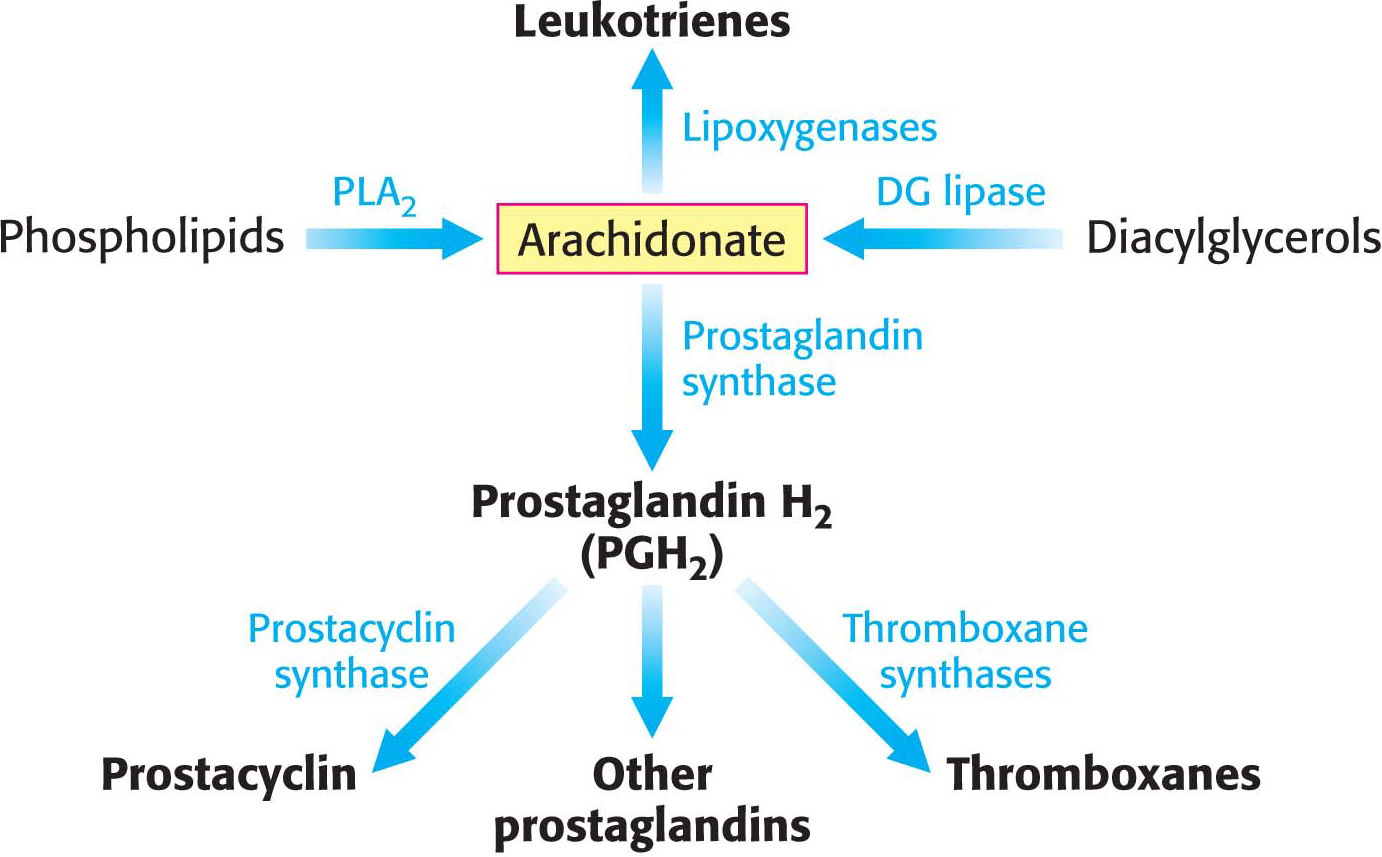
Prostaglandins and other eicosanoids are local hormones. They are short-
 CLINICAL INSIGHT
CLINICAL INSIGHTAspirin Exerts Its Effects by Covalently Modifying a Key Enzyme
Aspirin (acetylsalicylate) blocks access to the active site of the enzyme that converts arachidonate into prostaglandin H2. Because arachidonate is the precursor of other prostaglandins, prostacyclins, and thromboxanes, blocking this step affects many signaling pathways. It accounts for the wide-