PROBLEMS
Question 31.1
1. Out of thin air. Define nitrogen fixation. What organisms are responsible for nitrogen fixation? ✓ 3
Question 31.2
2. Fixing a problem. Write the equation for biological nitrogen fixation, and explain the role of ATP. ✓ 3 ✓ 4
Question 31.3
3. Like Starsky and Hutch. Match each term with its description. ✓ 3
Nitrogen fixation Nitrogenase complex Glutamate Essential amino acids Nonessential amino acids Aminotransferase Pyridoxal phosphate Tetrahydrofolate S- Homocysteine | Methylated to form methionine Coenzyme required by aminotransferases Amino acids that are dietary requirements Conversion of N2 into NH3 Transfers amino groups between keto acids Responsible for nitrogen fixation A common amino acid donor Amino acids that are readily synthesized A carrier of various one- An important methyl donor |
Question 31.4
4. Teamwork. Identify the two components of the nitrogenase complex, and describe their specific tasks. ✓ 3
Question 31.5
5. The fix is in. “The mechanistic complexity of nitrogenase is necessary because nitrogen fixation is a thermodynamically unfavorable process.” True or false? Explain. ✓ 3
Question 31.6
6. Siphoning resources. Nitrogen-
Question 31.7
7. Vital, in the truest sense. Why are certain amino acids defined as essential for human beings? ✓ 4
Question 31.8
8. From few, many. What are the seven precursors of the 20 amino acids? ✓ 4
Question 31.9
9. Common component. What cofactor is required by all aminotransferases? ✓ 4
Question 31.10
10. Common resource. If an animal is fed 15N-
Question 31.11
11. One carbon at a time. What is the role of tetrahydrofolate in biochemical systems?
Question 31.12
12. The same but different. Differentiate between S-adenosylmethionine and tetrahydrofolate.
Question 31.13
13. Telltale tag. In the reaction catalyzed by glutamine synthetase, an oxygen atom is transferred from the side chain of glutamate to orthophosphate, as shown by the results of 18O-
Question 31.14
14. Direct synthesis. Which of the 20 amino acids can be synthesized directly from a common metabolic intermediate by a transamination reaction? ✓ 4
Question 31.15
15. Lines of communication. For the following example of a branched pathway, propose a feedback-
Question 31.16
16. Cumulative feedback inhibition. Consider the branched pathway in problem 15. The first common step (A → B) is partly inhibited by both of the final products, each acting independently of the other. Suppose that a high level of Y alone decreased the rate of the A → B step from 100 to 60 s−1
Chapter Integration and Data Interpretation Problems
Question 31.17
17. One carbon, and only one carbon. We have identified three biomolecules that carry activated one-
Question 31.18
18. I’ve seen that face before. Vitamin B12 is required by methionine synthase to regenerate methionine from homocysteine. What other enzyme that we have encountered in our studies requires vitamin B12?
Question 31.19
19. Further ramifications. A person on a diet lacking in methionine would not be able to synthesize adequate amounts of proteins. However, insufficient protein synthesis would not be the only biochemical problem such a person would face. What other biosynthesis would be affected by a lack of dietary methionine?
Question 31.20
20. Light effects. The adjoining graph shows the concentration of several free amino acids in light-
(a) Of the amino acids shown, which are most affected by light–
(b) Suggest a plausible biochemical explanation for the difference observed.
(c) White asparagus, a culinary delicacy, is the result of growing asparagus plants in the dark. What chemical might you think enhances the taste of white asparagus?
Challenge Problems
Question 31.21
21. From sugar to amino acid. Write a balanced equation for the synthesis of alanine from glucose. ✓ 4
Question 31.22
22. Connections. How might increased synthesis of aspartate and glutamate affect energy production in a cell? How would the cell respond to such an effect? ✓ 4
Question 31.23
23. Comparing KM. Glutamate dehydrogenase and glutamine synthetase are present in all organisms. Most bacteria also contain another enzyme, glutamate synthase, which catalyzes the reductive amination of α-ketoglutarate with the use of glutamine as the nitrogen donor:
The side-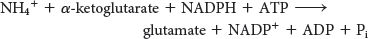
Note that this stoichiometry differs from that of the glutamate dehydrogenase reaction in that ATP is hydrolyzed. Why do bacteria sometimes use this more expensive pathway? (Hint: The KM value for NH4+ of glutamate dehydrogenase is higher than that of glutamine synthase.) ✓ 4
Selected Readings for this chapter can be found online at www.whfreeman.com/