
Nucleotide Metabolism


In addition to being the building blocks of proteins and peptides, amino acids serve as precursors of many kinds of small molecules that have important and diverse biological roles. Let us briefly survey some of the biomolecules that are derived from amino acids (Figure 32.1).
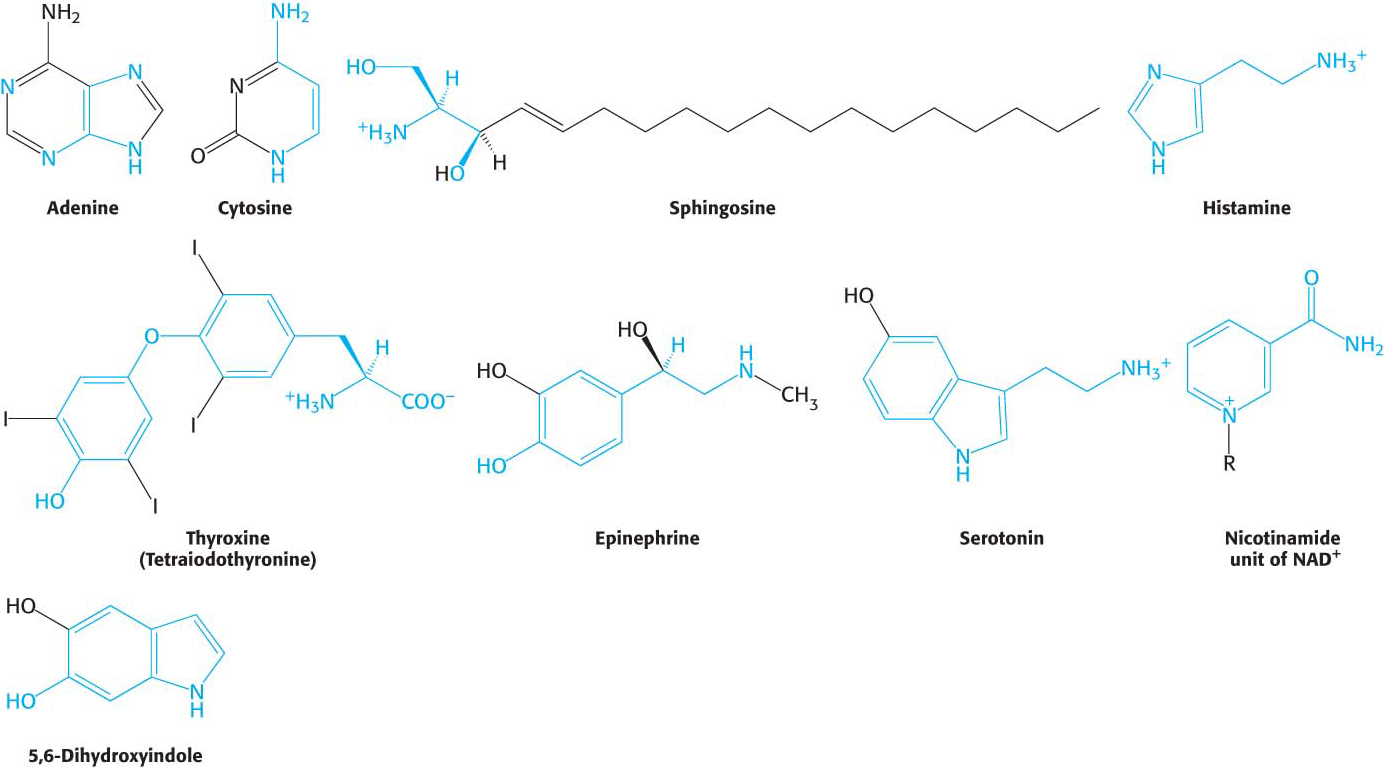
Histamine, a component of the immune system whose overproduction results in an allergic response, is derived from histidine by decarboxylation. Tyrosine is a precursor of the hormones thyroxine (tetraiodothyronine), which controls the rate of metabolic processes throughout the body, and epinephrine (adrenaline), the “fight or flight” hormone. Epinephrine is metabolized to 5,6-
We begin by examining nucleotide synthesis. The initial products of nucleotide synthesis are ribonucleotides, and we will see how ribonucleotides are converted into deoxyribonucleotides, the substrates for DNA synthesis. We then turn to the regulation of nucleotide synthesis. Finally, we consider pathological conditions that result from perturbations in nucleotide metabolism.