PROBLEMS
Question 32.1
1. From the beginning or extract and save and reuse. Differentiate between the de novo synthesis of nucleotides and salvage-
Question 32.2
2. Activated ribose phosphate. Write a balanced equation for the synthesis of PRPP from glucose through the oxidative branch of the pentose phosphate pathway.
Question 32.3
3. Making a pyrimidine. Write a balanced equation for the synthesis of orotate from glutamine, CO2, and aspartate. ✓ 5
Question 32.4
4. Identifying the donor. What is the activated reactant in the biosynthesis of each of the following compounds? ✓ 5
(a) Phosphoribosylamine
(b) Carbamoylaspartate
(c) Orotidylate (from orotate)
Question 32.5
5. An “s” instead of a “t”? Differentiate between a nucleoside and a nucleotide.
Question 32.6
6. Associate ‘em. Match the term on the right with the description on the left. ✓ 5
Excessive urate Lack of adenosine deaminase Lack of HGPRT Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase Inosinate Ribonucleotide reductase Lack of folic acid Glutamine phosphoribosyl transferase Single ring Bicyclic ring Precursor to CTP | Immunodeficiency Committed step in purine synthesis Deoxynucleotide synthesis Precursor to both ATP and GTP Gout UTP First step in pyrimidine synthesis Lesch– Pyrimidine Purine Spina bifida |
Question 32.7
7. The price of methylation. Write a balanced equation for the synthesis of TMP from dUMP that is coupled to the conversion of serine into glycine.
Question 32.8
8. Sulfa action. Bacterial growth is inhibited by sulfanilamide and related sulfa drugs, and there is a concomitant accumulation of 5-
Propose a mechanism for the inhibitory effect of sulfanilamide.
Question 32.9
9. A generous donor. What major biosynthetic reactions utilize PRPP?
Question 32.10
10. Bringing equilibrium. What is the reciprocal substrate relation in the synthesis of ATP and GTP? ✓ 6
Question 32.11
11. Calculate the ATP footprint. How many molecules of ATP are required to synthesize one molecule of CTP from scratch?
Question 32.12
12. Find the label. Suppose that cells are grown on amino acids that have all been labeled at the α carbons with 13C. Identify the atoms in cytosine and guanine that will be labeled with 13C. ✓ 5
Question 32.13
13. On the trail of carbons. Tissue-
Question 32.14
14. Blockages. What intermediate in purine synthesis will accumulate if a strain of bacteria is lacking each of the following biochemicals? ✓ 5
(a) Aspartate
(b) Tetrahydrofolate
(c) Glycine
(d) Glutamine
Question 32.15
15. Mechanism of action. What is the biochemical basis of allopurinol treatment for gout? ✓ 6
Question 32.16
16. Adjunct therapy. Allopurinol is sometimes given to patients with acute leukemia who are being treated with anticancer drugs. Why is allopurinol used? ✓ 6
Question 32.17
17. Folate deficiency. Suppose that someone was suffering from a folate deficiency. What cells would you think might be most affected? Symptoms may include diarrhea and anemia.
Question 32.18
18. Correcting deficiencies. Suppose that a person is found who is deficient in an enzyme required for IMP synthesis. How might this person be treated?
Question 32.19
19. Labeled nitrogen. Purine biosynthesis is allowed to take place in the presence of [15N]aspartate, and the newly synthesized GTP and ATP are isolated. What positions are labeled in the two nucleotides? ✓ 5
Question 32.20
20. Needed supplies. Why are cancer cells especially sensitive to inhibitors of TMP synthesis? ✓ 6
Chapter Integration Problems
Question 32.21
21. They’re everywhere! Nucleotides play a variety of roles in the cell. Give an example of a nucleotide that acts in each of the following roles or processes.
(a) Second messenger
(b) Phosphoryl-
(c) Activation of carbohydrates
(d) Activation of acetyl groups
(e) Transfer of electrons
(f) Chemotherapy
(g) Allosteric effector
Question 32.22
22. Exercising muscle. Some interesting reactions take place in muscle tissue to facilitate the generation of ATP for contraction. ✓ 6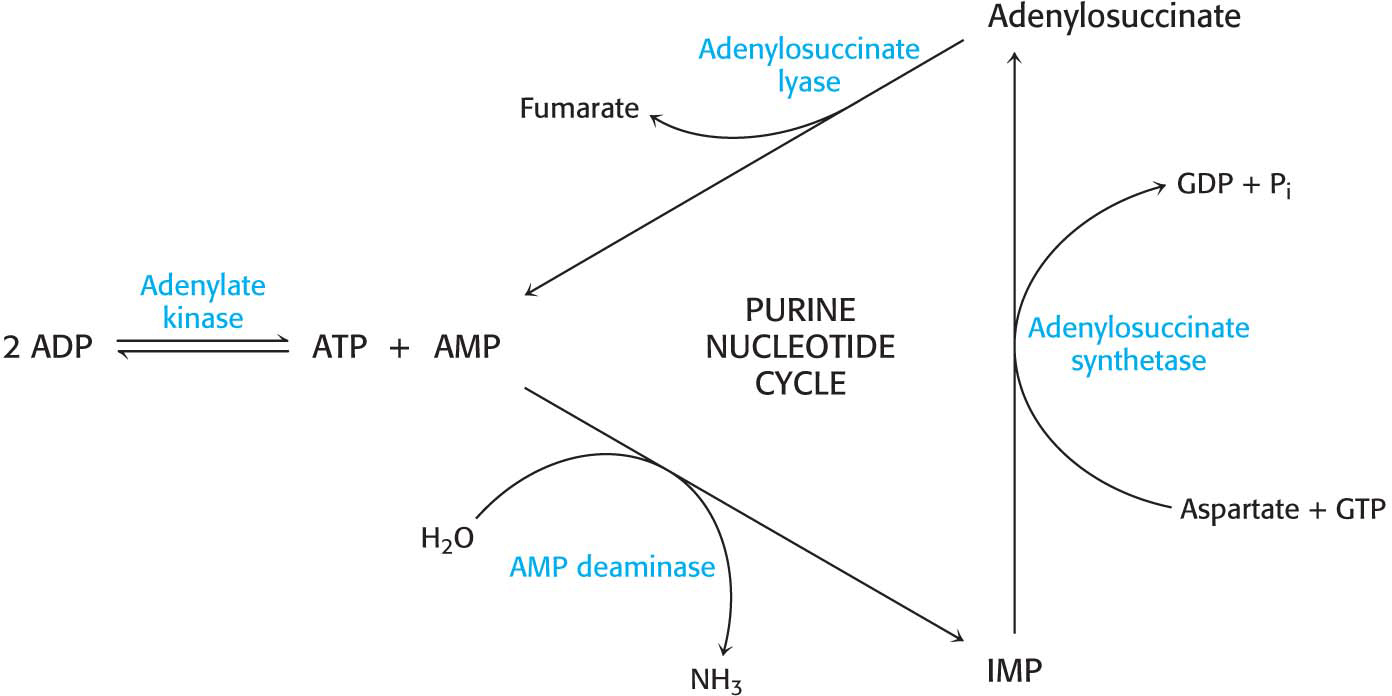
In muscle contraction, ATP is converted into ADP. Adenylate kinase converts two molecules of ADP into a molecule of ATP and AMP.
(a) Why is this reaction beneficial to contracting muscle?
(b) Why is the equilibrium for the adenylate kinase approximately equal to 1?
Muscle can metabolize AMP by using the purine nucleotide cycle. The initial step in this cycle, catalyzed by AMP deaminase, is the conversion of AMP into IMP.
(c) Why might the deamination of AMP facilitate ATP formation in muscle?
(d) How does the purine nucleotide cycle assist the aerobic generation of ATP?
Question 32.23
23. Different strokes. Human beings contain two different carbamoyl phosphate synthetase enzymes. One uses glutamine as a substrate, whereas the other uses ammonia. What are the functions of these two enzymes?
Question 32.24
24. Your pet duck. You suspect that your pet duck has gout. Why should you think twice before administering a dose of allopurinol-
Challenge Problems
Question 32.25
25. Inhibiting purine biosynthesis. Amidotransferases are inhibited by the antibiotic and antitumor agent azaserine (O-diazoacetyl-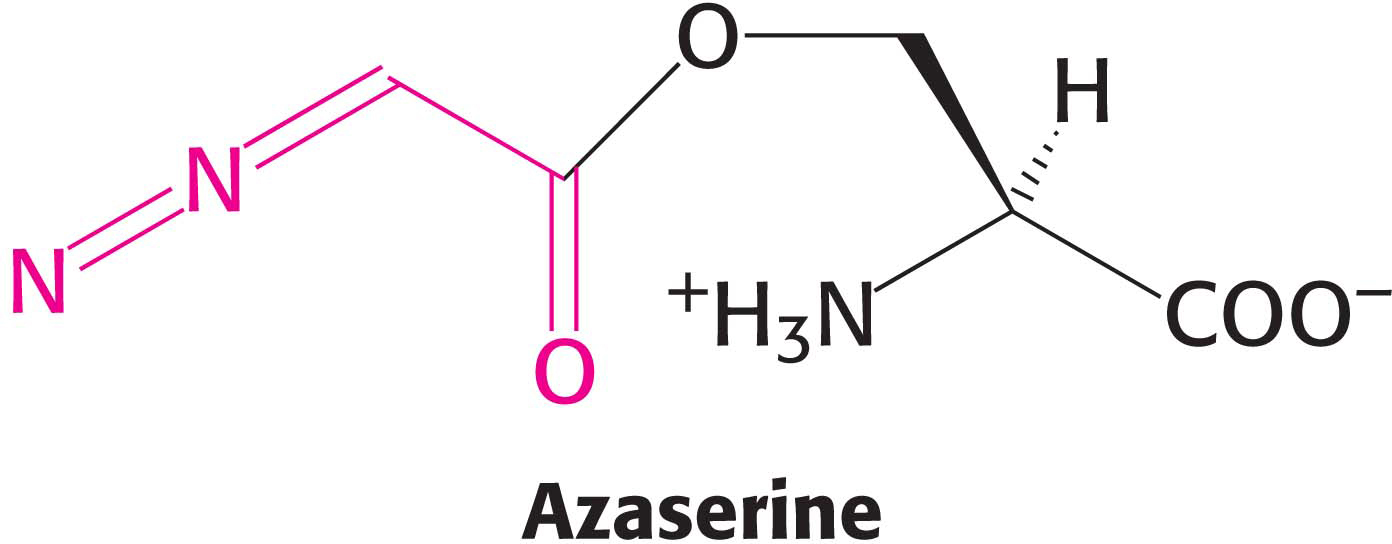
Which intermediates in purine biosynthesis would accumulate in cells treated with azaserine?
Question 32.26
26. HAT medium. Mutant cells unable to synthesize nucleotides by salvage pathways are very useful tools in molecular and cell biology. Suppose that cell A lacks thymidine kinase, the enzyme catalyzing the phosphorylation of thymidine to thymidylate, and that cell B lacks hypoxanthine-
(a) Cell A and cell B do not proliferate in a HAT medium containing hypoxanthine, aminopterin or amethopterin (methotrexate), and thymine. However, cell C formed by the fusion of cells A and B grows in this medium. Why?
(b) Suppose that you wanted to introduce foreign genes into cell A. Devise a simple means of distinguishing between cells that have taken up foreign DNA and those that have not. ✓ 5
Question 32.27
27. Hyperuricemia. Many patients with glucose 6-
Question 32.28
28. Labeled carbon. Succinate uniformly labeled with 14C is added to cells actively engaged in pyrimidine biosynthesis. Propose a pathway by which carbon atoms from succinate can be incorporated into a pyrimidine. At what positions is the pyrimidine labeled? ✓ 5
Selected Readings for this chapter can be found online at www.whfreeman.com/