32.1 An Overview of Nucleotide Biosynthesis and Nomenclature
✓ 5 Describe how nucleotides are synthesized.
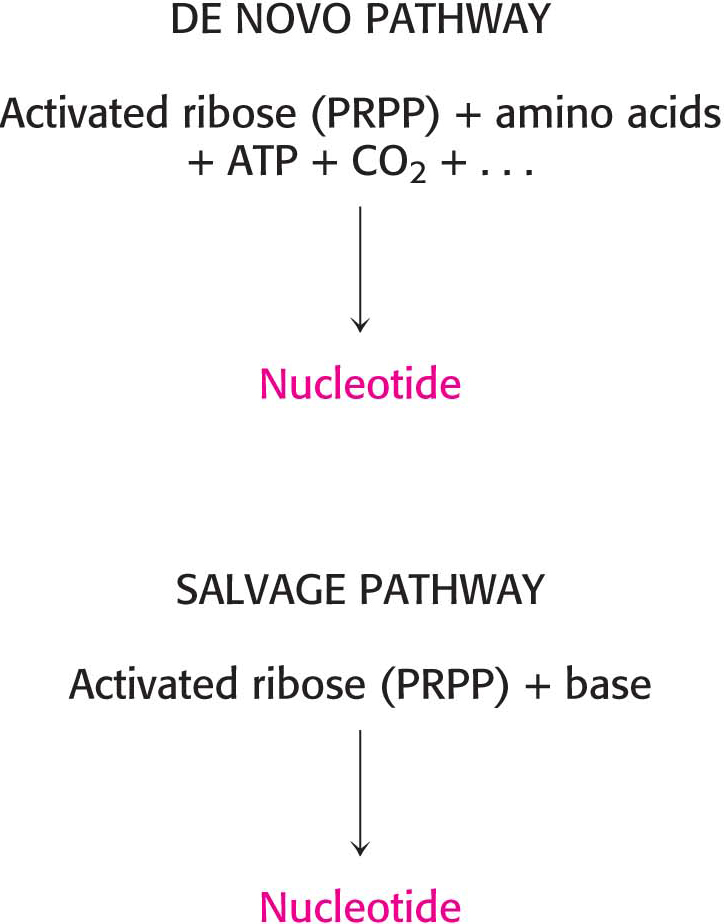
The pathways for the biosynthesis of nucleotides fall into two classes: de novo pathways and salvage pathways (Figure 32.2). In de novo pathways, the nucleotide bases are assembled from simpler compounds. The framework for a pyrimidine base is assembled first and then attached to ribose. In contrast, the framework for a purine base is synthesized piece by piece directly onto a ribose-
De novo synthesis and most salvage pathways lead to the synthesis of ribonucleotides. However, DNA is built from deoxyribonucleotides. All deoxyribonucleotides are synthesized from the corresponding ribonucleotides. The deoxyribose sugar is generated by the reduction of ribose within a fully formed nucleotide. Furthermore, the methyl group that distinguishes the thymine of DNA from the uracil of RNA is added at the last step in the pathway.
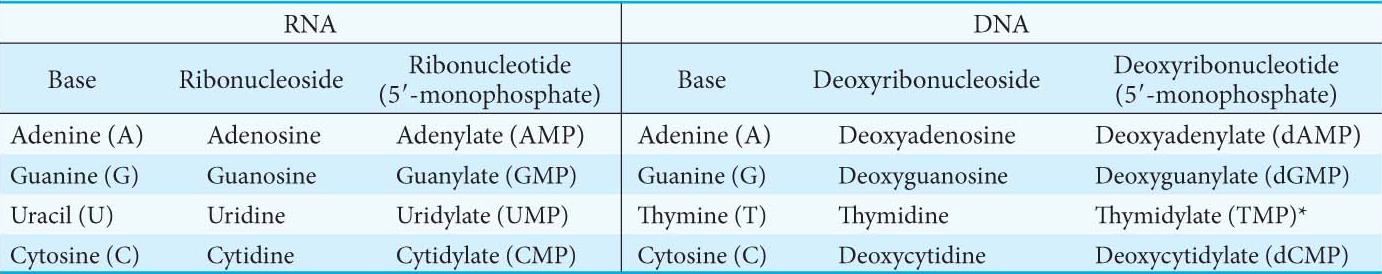
A nucleoside consists of a purine or pyrimidine base linked to a sugar, and a nucleotide is a phosphate ester of a nucleoside. For instance, adenosine is a nucleoside composed of the base adenine and the sugar ribose. ATP is a nucleotide, the phosphate ester (in this case, a triphosphate) of adenosine. The names of the major bases of RNA and DNA, as well as those of their nucleoside and nucleotide derivatives, are given in Table 32.1.