PROBLEMS
Question 33.1
1. A “t” instead of an “s”? Differentiate between a nucleoside and a nucleotide. ✓ 1
Question 33.2
2. A lovely pair. What is a Watson–
Question 33.3
3. Almost like base pairs. Match each term with its description.
Base stacking B- A- Z- Topoisomers Supercoiling Histone Chromatin Nucleosome Nucleosome core particle | Stabilization of the double helix due to van der Waals forces Form of DNA found under dehydrating conditions DNA and associated proteins DNA in a left- Results from extensive digestion of chromatin by DNAse DNA molecules with the same sequence but differ in coiling Composed of 200 base pairs of DNA and 8 histones Constitute half the mass of a chromosome Twisting of the axis of a DNA helix into a superhelix Most common form of DNA |
Question 33.4
4. Chargaff rules! Biochemist Erwin Chargaff was the first to note that, in DNA, [A] = [T] and [G] = [C], equalities now called Chargaff’s rule. With the use of this rule, determine the percentages of all the bases in DNA that is 20% thymine. ✓ 1
Question 33.5
5. But not always. A single strand of RNA is 20% U. What can you predict about the percentages of the remaining bases?
Question 33.6
6. Size matters. Why are GC and AT the only base pairs permissible in the double helix? ✓ 1
Question 33.7
7. Complements. Write the complementary sequence (in the standard 5′ → 3′ notation) for (a) GATCAA, (b) TCGAAC, (c) ACGCGT, and (d) TACCAT.
Question 33.8
8. Compositional constraint. The composition (in mole-
Question 33.9
9. Inside out. Single-
Question 33.10
10. Axial ratio. What is the axial ratio (length:diameter) of a DNA molecule 20 μm long?
Question 33.11
11. Strong, but not strong enough. Why does heat denature, or melt, DNA in solution?
Question 33.12
12. Coming and going. What does it mean to say that the DNA strands in a double helix have opposite directionality?
Question 33.13
13. Lost DNA. The DNA of a deletion mutant of λ bacteriophage has a length of 15 μm instead of 17 μm. How many base pairs are missing from this mutant?
Question 33.14
14. An unseen pattern. What result would Meselson and Stahl have obtained if the replication of DNA were conservative (i.e., the parental double helix stayed together)? Give the expected distribution of DNA molecules after 1.0 and 2.0 generations for conservative replication.
Question 33.15
15. Overcharged. DNA in the form of a double helix must be associated with cations, usually Mg2+. Why is this requirement the case? ✓ 2
Question 33.16
16. Packing it in. Does packing DNA into nucleosomes account for the compaction found in a metaphase chromosome (the most condensed form of a chromosome)? ✓ 2
Question 33.17
17. Resistance is futile. Chromatin viewed with the electron microscope has the appearance of beads on a string. Partial digestion of chromatin with DNAse yields the isolated beads, containing fragments of DNA approximately 200 bp in length bound to the eight histones. More extensive digestion yields a reduced DNA fragment of 145 bp bound to the histone octamer. Why is more extensive digestion required to yield the 145-
Question 33.18
18. Charge neutralization. Given the histone amino acid sequences illustrated here, estimate the charge of a histone octamer at pH 7. Assume that histidine residues are uncharged at this pH value. How does this charge compare with the charge on 150 base pairs of DNA? ✓ 2
Histone H2A
msgrgkqggkarakaktrssraglqfpvgrvhrllrkgnyservgagapvylaavleyltaeilelagna
ardnkktriiprhlqlairndeelnkllgrvtiaqggvlpniqavllpkkteshhkakgk
Histone H2B
mpepaksapapkkgskkavtkaqkkdgkkrkrsrkesysvyvykvlkqvhpdtgisskamgimnsfvndi
feriageasrlahynkrstitsreiqtavrlllpgelakhavsegtkavtkytssk
Histone H3
martkqtarkstggkaprkqlatkaarksapstggvkkphryrpgtvalreirryqkstellirklpfqr
lvreiaqdfktdlrfqsaaigalqeaseaylvglfedtnlcaihakrvtimpkdiqlarrirgera
Histone H4
msgrgkggkglgkggakrhrkvlrdniqgitkpairrlarrggvkrisgliyeetrgvlkvflenvirda
vtytehakrktvtamdvvyalkrqgrtlygfgg
Question 33.19
19. Around we go. Assuming that 145 base pairs of DNA wrap around the histone octamer 1¾ times, estimate the radius of the histone octamer. Assume 3.4 Å per base pair, and simplify the calculation by assuming that the wrapping is in two rather than three dimensions and neglecting the thickness of the DNA. ✓ 2
Data Interpretation Problems
Question 33.20
20. 3 is greater than 2. The illustration below graphs the relation between the percentage of GC base pairs in DNA and the melting temperature. Suggest a possible explanation for these results.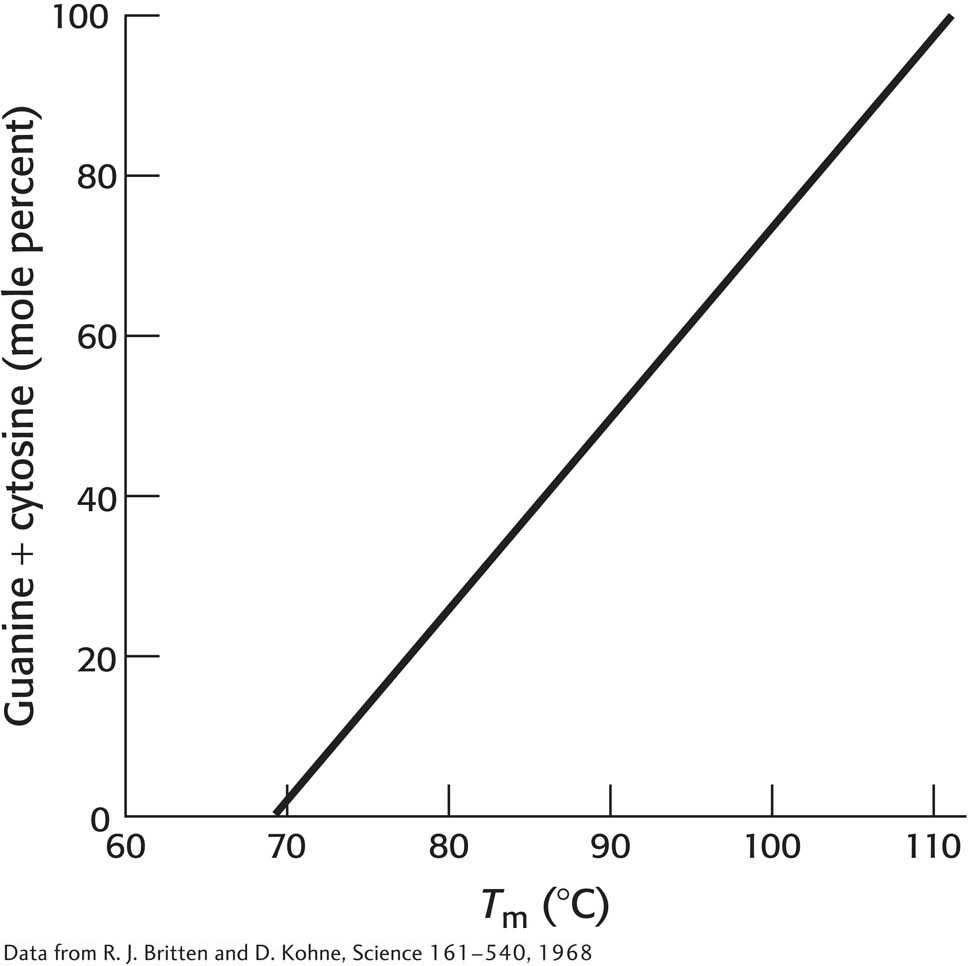
Question 33.21
21. Blast from the past. The illustration below is a graph called a C0t curve (pronounced “cot”). The y axis shows the percentage of DNA that is double stranded. The x axis is the product of the concentration of DNA and the time required for the double-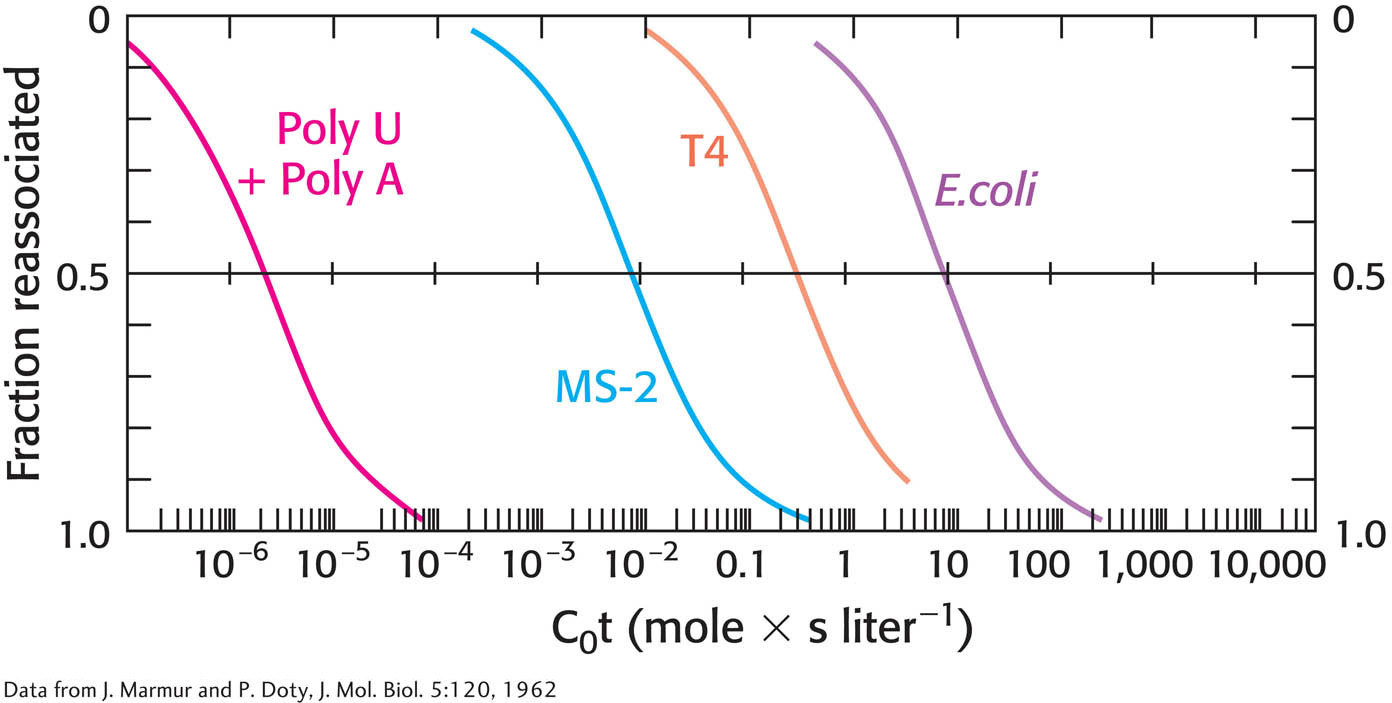
Challenge Problems
Question 33.23
23. Uniqueness. The human genome contains 3 billion base pairs arranged in a vast array of sequences. What is the minimum length of a DNA sequence that will, in all probability, appear only once in the human genome? You need consider only one strand and may assume that all four nucleotides have the same probability of appearance.
Question 33.24
24. Information content. (a) How many different 8-
Question 33.25
25. A tougher strand. RNA is readily hydrolyzed by alkali, whereas DNA is not. Why?
Question 33.26
26. A picture is worth a thousand words. Write a reaction sequence showing why RNA is more susceptible to nucleophilic attack than DNA.
Selected Readings for this chapter can be found online at www.whfreeman.com/
