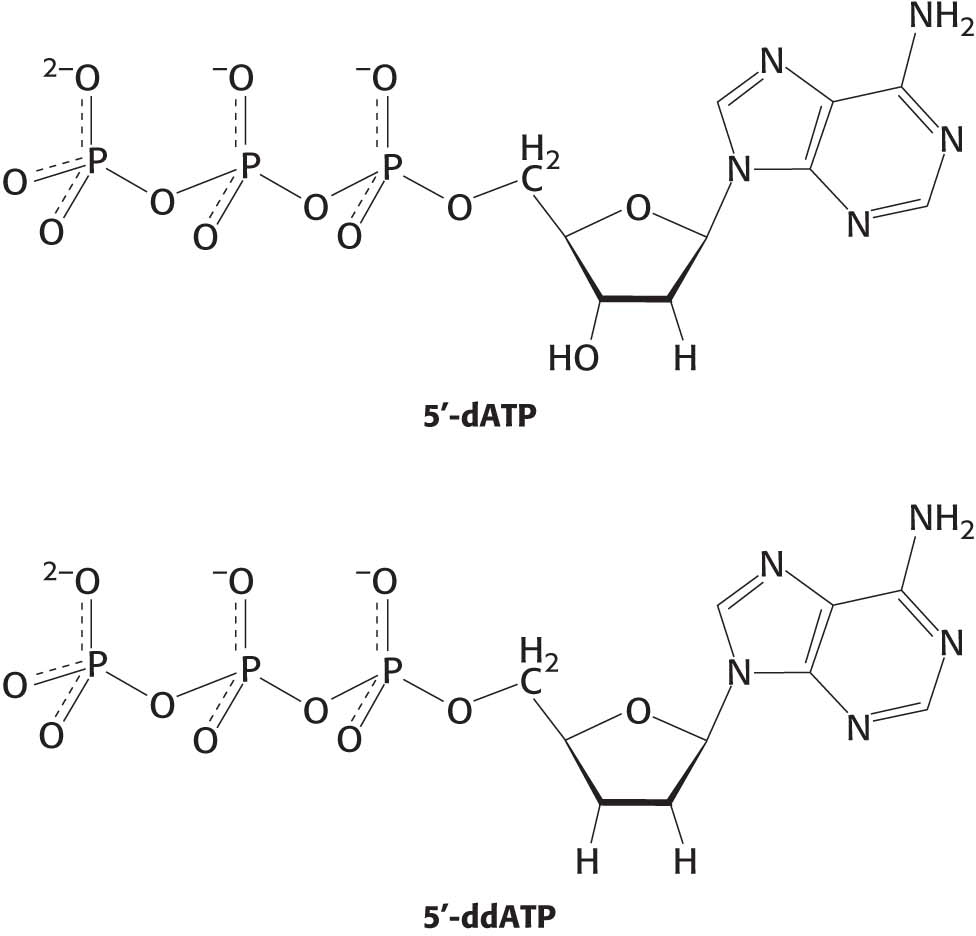
PROBLEMS
Question 34.1
1. Guide and starting point. Define template and primer as they relate to DNA synthesis. ✓ 3
Question 34.2
2. Cooperation among polymerases. Explain why DNA synthesis depends on RNA synthesis. ✓ 4
Question 34.3
3. One from many. What is an Okazaki fragment? ✓ 4
Question 34.4
4. Foremost and reluctant. Distinguish between the leading and the lagging strands in DNA synthesis. ✓ 4
Question 34.5
5. Like Homer and Marge. Match each term with its description.
DNA polymerase Template Primer Helicase Topoisomerase Exonuclease Primase Okazaki fragment DNA ligase Telomerase | Faithfully replicates the DNA Determines the sequence of a complementary nucleic acid Uses ATP to join DNA fragments Prevents the disappearance of the lagging strand Found on the lagging strand Unwinds the double helix Relaxes or introduces supercoils The initial segment of a polymer that will be extended Crucial for proofreading Synthesizes a segment of RNA |
Question 34.6
6. Which way? Explain, on the basis of nucleotide structure, why DNA synthesis proceeds in the 5′-to-
Question 34.7
7. Strength in numbers. For long double-
Question 34.8
8. Only one oar in the water. DNA replication in E. coli begins at a unique site on the circular chromosome called the origin of replication and proceeds in both directions as illustrated in part A.
What would be the effect of a mutation that yielded only one functional fork per origin of replication site (part B)? ✓ 4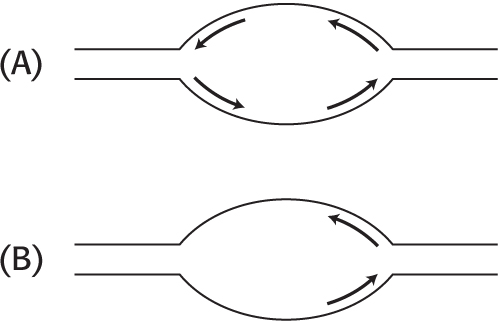
Question 34.9
9. Wound tighter than a drum. Why would replication come to a halt in the absence of topoisomerase II? ✓ 3
Question 34.10
10. And just like that, poof. He’s gone. Telomerase is not active in most human cells. Some cancer biologists have suggested that the activation of the telomerase gene would be a requirement for a cell to become cancerous. Explain. ✓ 4
Question 34.11
11. I need to unwind. With the assumption that the energy required to break an average base pair in DNA is 10 kJ mol−1
Chapter Integration Problem
Question 34.13
13. Life in a hot tub. An archaeon (Sulfolobus acidocaldarius) found in acidic hot springs contains a topoisomerase that catalyzes the ATP-
Data Interpretation and Challenge Problem
Question 34.14
14. Like a ladder. Circular DNA from SV40 virus was isolated and subjected to gel electrophoresis. The results are shown below in lane A (the control) of the electrophoretic patterns. ✓ 3
(a) Why does the DNA separate in agarose gel electrophoresis? How does the DNA in each band differ?
The DNA was then incubated with topoisomerase I for 5 minutes and again analyzed by gel electrophoresis with the results shown in lane B.
(b) What types of DNA do the various bands represent? Another sample of DNA was incubated with topoisomerase I for 30 minutes and again analyzed as shown in lane C.
(c) What is the significance of the fact that more of the DNA is in slower-
Challenge Problems
Question 34.15
15. Don’t rush it. The accuracy rate for DNA polymerase falls if the next nucleotide to be polymerized is present in high concentration. Conversely, the accuracy rate rises if the next nucleotide is present in low concentration, a phenomenon termed the “next nucleotide effect.” Suggest an explanation for this effect. ✓ 3
Question 34.16
16. Fast flying fork. (a) How fast does template DNA spin (expressed in revolutions per second) at an E. coli replication fork? (b) What is the velocity of movement (in micrometers per second) of DNA polymerase III holoenzyme relative to the template?
Question 34.17
17. Nick translation. Suppose that you wish to make a sample of DNA duplex highly radioactive to use as a DNA probe. You have a DNA endonuclease that cleaves the DNA internally to generate 3′-OH and 5′-phosphoryl groups, intact DNA polymerase I, and radioactive dNTPs. Suggest a means for making the DNA radioactive. ✓ 3
Selected Readings for this chapter can be found online at www.whfreeman.com/