36.1 Cellular RNA Is Synthesized by RNA Polymerases
✓ 1 Identify the key enzyme required for transcription.
The synthesis of RNA from a DNA template is called transcription and is catalyzed by a large enzyme common to all life forms called RNA polymerase (Figure 36.1). RNA polymerase requires the following components:
A Template. Double-
stranded DNA is one of the substrates for RNA synthesis. However, usually only one of the strands is transcribed. We differentiate the two strands of DNA on the basis of their relation to the RNA product. The sequence of the template strand of DNA is the complement of that of the RNA transcript (Figure 36.2). In contrast, the coding strand of DNA has the same sequence as that of the RNA transcript except for thymine (T) in place of uracil (U). The coding strand is also known as the sense (+) strand and the template strand as the antisense (−) strand. Page 660Activated Precursors. In addition to DNA, the other required substrates are the building blocks—
the ribonucleoside triphosphates ATP, GTP, UTP, and CTP— of the RNA product. A Divalent Metal Ion. RNA polymerase requires a divalent cation cofactor. Either Mg2+ or Mn2+ is effective.
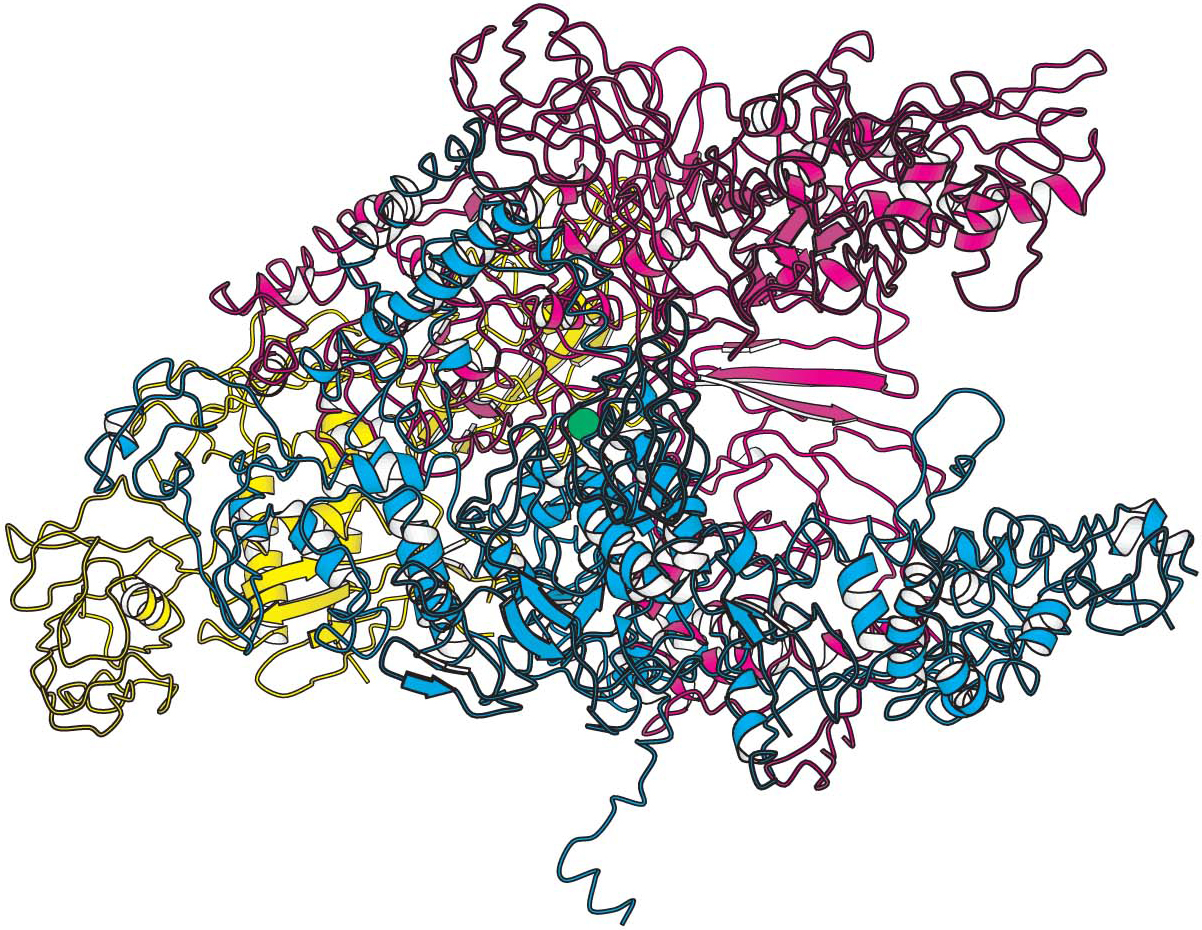
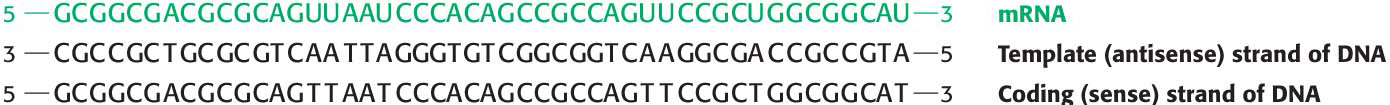
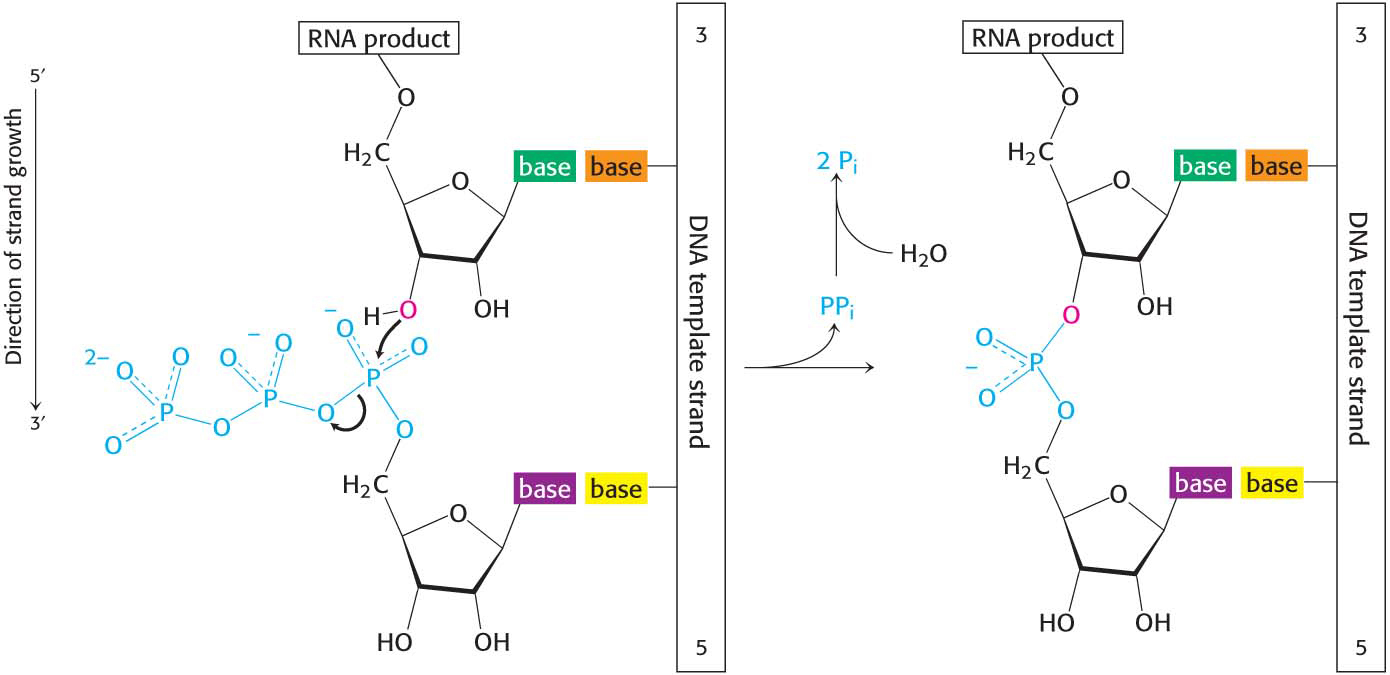
RNA polymerase catalyzes the initiation and elongation of RNA strands. The reaction catalyzed by this enzyme is
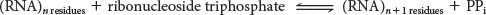
The synthesis of RNA is similar to that of DNA in several respects (Figure 36.3). First, the direction of synthesis is 5′ → 3′. Second, the mechanism of elongation is similar: the 3′-OH group at the terminus of the growing chain attacks the innermost phosphoryl group of the incoming ribonucleoside triphosphate. Third, the synthesis is driven forward by the hydrolysis of pyrophosphate. In contrast with DNA polymerase, however, RNA polymerase does not require a primer.
Genes Are the Transcriptional Units
There are many types of RNA, all of which are products of RNA polymerase. The segments of DNA that encode the various species of RNA are called genes. RNA polymerase recognizes the beginning and end of a gene by mechanisms that we will consider shortly.
Three major types of RNA are produced in all cells. Messenger RNA (mRNA) encodes the information for the synthesis of a protein, whereas transfer RNA (tRNA) and ribosomal RNA (rRNA) are crucial components in the machinery that translates the mRNA into protein. All types of cellular RNA are synthesized in E. coli by the same RNA polymerase according to instructions given by a DNA template. In mammalian cells, there is a division of labor among several different kinds of RNA polymerases (Chapter 37), although the chemistry is the same for all types.
RNA Polymerase Is Composed of Multiple Subunits
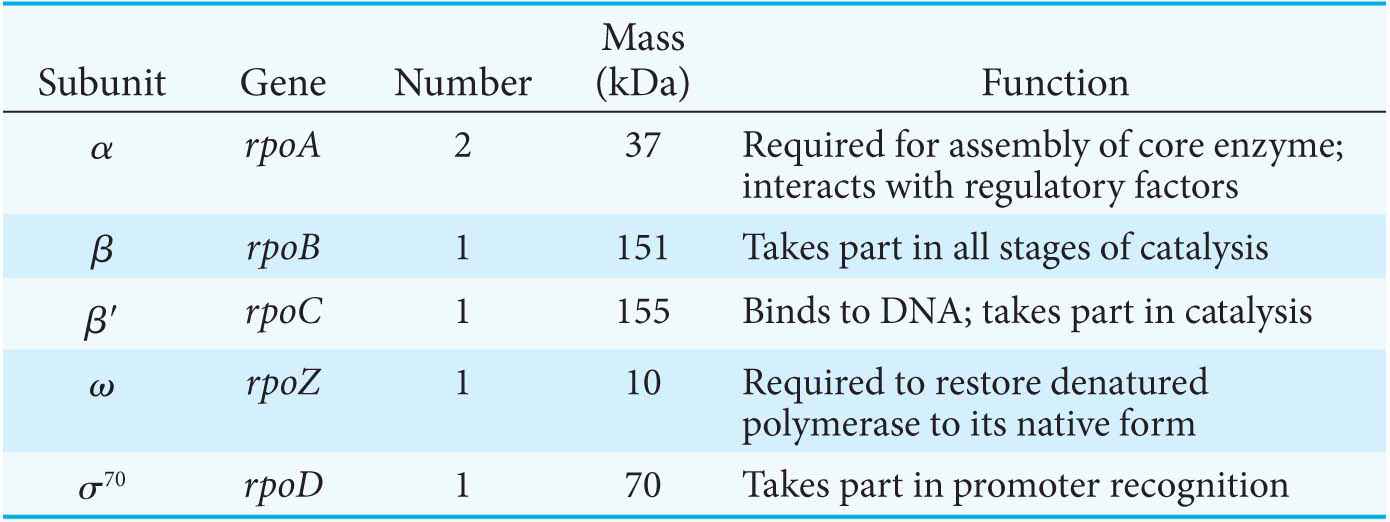
As stated earlier, the enzyme responsible for transcription in all organisms is RNA polymerase. In E. coli, RNA polymerase is a very large (∼500-